Calciumchlorid Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
GERUCHLOSE, STARK HYGROSKOPISCHE FARBLOSE KRISTALLE.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Erhitzen auf hohe Temperaturen und beim Verbrennen unter Bildung giftiger und ?tzender Rauche. Schwache Base in w?ssriger L?sung. Greift Zink in Gegenwart von Wasser unter Bildung leichtentzündlichen Wasserstoffgases an. L?st sich sehr heftig in Wasser unter starker Hitzeentwicklung.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2005).
MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation des Aerosols.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfung bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine gesundheitssch?dliche Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch beim Dispergieren schnell erreicht werden.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz reizt die Haut und die Atemwege.
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
Wiederholter oder andauernder Hautkontakt kann Dermatitis hervorrufen. M?glich sind Auswirkungen auf die Nasenschleimhaut mit nachfolgenden Geschwüren.
LECKAGE
Verschüttetes Material in Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste mit viel Wasser wegspülen. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P2-Filter für sch?dliche Partikel.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R36:Reizt die Augen.
R36/38:Reizt die Augen und die Haut.
R41:Gefahr ernster Augensch?den.
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S39:Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S24:Berührung mit der Haut vermeiden.
S22:Staub nicht einatmen.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Calcium chloride, CaC12, is colorless deliquescent solid that is soluble in water and ethanol. It is formed from the reaction of calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid or calcium hydroxide and ammonium chloride. It is used in medicine, as an antifreeze, and as a coagulant.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
White crystal, powder or flake; highly hygroscopic; the compound and its solutions absorb moisture from the air at various rates depending on calcium chloride concentrations, relative humidity and vapor pressure of water in the air, temperature, surface area of exposed material, and the rate of air circulation; at 40% and 95% relative humidity and 25°C, one gram anhydrous calcium chloride may absorb about 1.4 g and 17 g water, respectively. (Shearer, W. L. 1978 . In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 3rd ed., vol. 4, pp. 432-6. New York: Wiley Interscience); density 2.15, 2.24, 1.85, 1.83 and 1.71 g/cm3 for the anhydrous salt and its mono-, di-, tetra- and hexahydrates, respectively; anhydrous salts melts at 772°C, while the mono-, di-, tetra- and hexahydrates decompose at 260°, 175°, 45.5° and 30°C, respectively; the anhydrous salt vaporizes at 1,935°C; highly soluble in water, moderate to high solubility in alcohol.
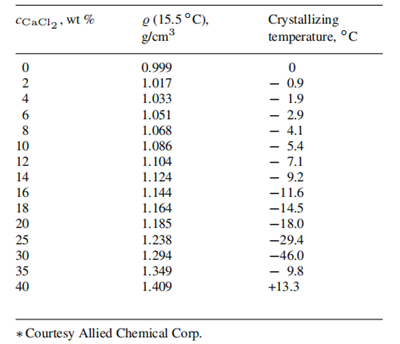
Densities and crystallizing temperatures of commercial calcium chloride solutions (Courtesy Allied Corp.):
Occurrence
Calcium chloride may be found in nature as the mineral tachhydrite, CaCl
2?2MgCl
2?12H
2O. It also is found in other minerals. Its concentration in sea water is about 0.15%.
Calcium chloride has several industrial applications. The major applications of this compound are in deicing of roads, dust control, imparting stability to roads and buildings, and to improve traction in tractor tires. It is mixed with ice to make freezing mixtures. Hexahydrate mixed with crushed ice can lower the temperature of the cooling bath to below -50°C. It also is used as a desiccant for dehydrating gases and liquids. It is added to cement in various proportions to manufacture different types of concrete. Other uses are in adhesives, to lower gel temperatures, and as a calcium source in liquid feed supplements for dairy cattle. Also, the compound is used to control particle size development and reduce coalescence in plastics.
Verwenden
Calcium chloride is highly hygroscopic and is often used as a desiccant.
synthetische
Calcium chloride is obtained as a by-product in the manufacture of sodium carbonate (soda ash) by ammonia-soda (Solvay) process. The process involves the reaction of sodium chloride with calcium carbonate and ammonia. Calcium chloride is currently produced in bulk amounts by evaporation of natural underground brines. In the laboratory, calcium chloride can be prepared by treating limestone with hydrochloric acid followed by evaporation of solution to obtain crystals. The crystals are dehydrated to obtain anhydrous salt. Calcium oxide or hydroxide may be used instead of carbonate.
Definition
calcium chloride: A white deliquescentcompound, CaCl
2, which issoluble in water; r.d. 2.15; m.p.782°C; b.p. >1600°C. There are anumber of hydrated forms, includingthe monohydrate, CaCl
2.H
2O, the dihydrate,CaCl
2.2H
2O (r.d. 0.84), andthe hexahydrate, CaCl
2.6H
2O (trigonal;r.d. 1.71; the hexahydrate loses4H
2O at 30°C and the remaining2H
2O at 200°C). Large quantities of itare formed as a byproduct of theSolvay process and it can be preparedby dissolving calcium carbonateor calcium oxide in hydrochloricacid. Crystals of the anhydrous saltcan only be obtained if the hydratedsalt is heated in a stream of hydrogenchloride. Solid calcium chloride isused in mines and on roads to reducedust problems, whilst the molten saltis the electrolyte in the extraction ofcalcium. An aqueous solution of calciumchloride is used in refrigerationplants.
Vorbereitung Methode
Calcium chloride is a principal byproduct from the Solvay process.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Calcium Chloride (CaCl
2) is a water soluble ionic crystal with a high enthalpy change of solution. It is majorly derived from limestone and is a by-product of the Solvay process. It is an anhydrous salt that has a hygroscopic nature and can be used as a desiccant.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Deliquescent. Water soluble. Adding Calcium chloride to hot water caused violent boiling, [MCA Case History No. 69].
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
Bromine trifluoride rapidly attacks the following salts: barium chloride, cadmium chloride, Calcium chloride, cesium chloride, lithium chloride, silver chloride, rubidium chloride, potassium bromide, potassium chloride, potassium iodide, rhodium tetrabromide, sodium bromide, sodium chloride, and sodium iodide [Mellor 2 Supp. 1:164, 165 1956]. Long term exposure of Calcium chloride solution upon a zinc coated galvanized iron vessel caused slow evolution of hydrogen which ignited and exploded [Bretherick, 5th Ed., 1995].
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes irritation of nose and throat. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Contact with eyes (particularly by dust) causes irritation and possible transient corneal injury. Contact of solid with dry skin causes mild irritation; strong solutions can cause marked irritation, even a superficial burn.
Pharmazeutische Anwendungen
The main applications of calcium chloride as an excipient relate to
its dehydrating properties and, therefore, it has been used as an
antimicrobial preservative, as a desiccant, and as an astringent in
eye lotions.
Therapeutically, calcium chloride injection 10% (as the dihydrate
form) is used to treat hypocalcemia.
Sicherheitsprofil
Moderately toxic by
ingestion. Poison by intravenous,
intramuscular, intraperitoneal, and
subcutaneous routes. Human systemic
effects: dermatitis, changes in calcium.
Questionable carcinogen with experimental
tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported.
Reacts violently with (B203 + CaO), BrF3.
Reaction with zinc releases explosive
hydrogen gas. Catalyzes exothermic
polymerization of methyl vinyl ether.
Exothermic reaction with water. When
heated to decomposition it emits toxic
fumes of Cl-. See also CALCIUM
COMPOUNDS and CHLORIDES.
Sicherheit(Safety)
Calcium chloride is used in topical, ophthalmic, and injection
preparations. The pure form of calcium chloride is toxic by
intravenous, intramuscular, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous
routes, and moderately toxic by ingestion, causing stomach and
heart disturbances. It is a severe eye irritant and can cause
dermatitis.
LD
50 (mouse, IP): 0.21 g/kg
LD
50 (mouse, IV): 0.042 g/kg
LD
50 (mouse, oral): 1.94 g/kg
LD
50 (mouse, SC): 0.82 g/kg
LD
50 (rat, IM): 0.025 g/kg
LD
50 (rat, IP): 0.26 g/kg
LD
50 (rat, oral): 1.0 g/kg
LD
50 (rat, SC): 2.63 g/kg
m?gliche Exposition
Calcium chloride is used as road salt
for melting snow, a drying agent in desiccators, for dehydrating organic liquids and gases, in refrigeration brines
and antifreeze, as a dust-proofing agent, food additives,
concrete hardening accelerator, and others. May react with
strong oxidizers.
Lager
Calcium chloride is chemically stable; however, it should be
protected from moisture. Store in airtight containers in a cool, dry
place.
Versand/Shipping
There are no label or maximum shipping quantity requirements set by DOT.
l?uterung methode
It is available as fused granules or cubic crystals. It is very hygroscopic, very soluble in H2O (exothermic), and EtOH. Store it in a tightly closed container. [Ehrlich in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 931 1963.]
Inkompatibilit?ten
Calcium chloride is incompatible with soluble carbonates, phosphates,
sulfates, and tartrates. It reacts violently with bromine
trifluoride, and a reaction with zinc releases explosive hydrogen gas.
It has an exothermic reaction with water, and when heated to
decomposition it emits toxic fumes of chlorine.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database
(injections, ophthalmic preparations, suspensions, creams).
Included in medicines licensed in the UK (eye drops; intraocular
irrigation; vaccines; injection powders for reconstitution; nebulizer
solution; oral suspension).
Calciumchlorid Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
1-METHYL-3-PHENYL-1H-PYRAZOLE-5-CARBALDEHYDE
3-Methylbutylbutyrat
5-Methyl-4-nitroisoxazole
polymer bactericidal flocculent
materials of oral delivery system for peptide drugs and their controlled release
HEPARIN CALCIUM
Pentoxyverin
Ethyl-1-naphthylether
1-[4-(BROMOMETHYL)PHENYL]-1H-PYRAZOLE
(R)-1-Boc-3-(hyroxymethyl)piperidine
1-(2-ETHOXYETHYL)PIPERAZINE
Dye-fixing agent G
1-Bromooctadecane
N-Allylthioharnstoff
3-(2-THIENYL)PROPIONIC ACID
Butan-1-thiol
(8α,9R)-1-Benzyl-9-hydroxycinchonaniumchlorid
1,3-Dimethoxybenzol
Calcium-4-[(5-chlor-4-methyl-2-sulfonatophenyl)azo]-3-hydroxy-2-naphthoat
3-AMIDINOPYRIDINIUM CHLORIDE
2-Fluoro-p-Xylene
Ethylhexanoat
4-CHLORO-2-METHYLBENZALDEHYDE
1-Chlor-4-ethoxybenzol
3,5-DIMETHYL-4-NITROISOXAZOLE
Calcium-3-hydroxy-4-[(4-methyl-2-sulfonatophenyl)azo]-2-naphthoat
Phenylisothiocyanat
2,3-Dimethylbuta-1,3-dien
Calcium
Isopentylacetat
Ethyloleat
N,N,N',N'-Tetramethyl-p-phenylendiamindihydrochlorid
3-Methylbutylisovalerat
1,2-Dibrompropan
Butylbutyrat
Hexans?ure-2-propenylester
(S)-3-(Boc-amino)pyrrolidine
(3-Chlorprop-1-enyl)benzol
(1,1-DIMETHYL-PROP-2-YNYL)-HYDRAZINE
2-Bromethylethylether

