| Hazard Information | Back Directory |
[General Description]
Pale yellow liquid with iridescent sheen. |
[Reactivity Profile]
An ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. |
[Air & Water Reactions]
Insoluble in water. |
[Fire Hazard]
This chemical is probably combustible. |
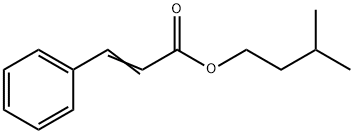
[Description]
Isoamyl cinnamate has a balsamic odor reminiscent of cocoa. May
be prepared by esterification of cinnamic acid with commercial
isoamyl alcohols, which vary in isomer distribution according to
source. |
[Chemical Properties]
Isoamyl cinnamate has a balsamic odor reminiscent of cocoa. |
[Chemical Properties]
pale yellow liquid with an iridescent sheen |
[Occurrence]
Reported found in cinnamon and port wine |
[Uses]
Isoamyl cinnamate is Used in perfumes for Oriental notes, Chypre, Ambre, and as a fixative-blender in spicy
fragrance types (Carnation etc.). Quite stable
in soap and a fair fixative. However, it tends
to polymerize in storage. An increasing cloudiness, accompanied by increased viscosity and
decreased odor level are signs of beginning
polymerization. It is used in flavors for imitation Butter, Caramel, Fruit, Honey, Peach, Pineapple, Strawberry, etc. and in traces in Vanilla compositions to introduce warm-balsamic notes
resembling Cocoa or Chocolate. Concentrations in finished foods: up to
12 ppm in candy or baked goods. |
[Definition]
ChEBI: Isoamyl cinnamate is a cinnamate ester. |
[Preparation]
By esterification of cinnamic acid with commercial isoamyl alcohols, which vary in isomer distribution according to
source. |
[Taste threshold values]
Taste characteristics at 35 ppm: sweet, floral, powdery, berry, and spice nuances |