| Identification | More | [Name]
Lapatinib | [CAS]
231277-92-2 | [Synonyms]
lapatinib
n-[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-6-[5-[(2-methylsulfonylethylamino)methyl]-2-furyl]quinazolin-4-amine
4-Quinazolinamine, N-[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-6-[5-[[[2-(methylsulfonyl)ethyl]amino]methyl]-2-furanyl]-
Lapatinib(TINIBS)
N-[3-Chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-6-[5-[(2-methylsulfonylethylamino)methyl]-2-furyl]quinazolin-4-amine | [EINECS(EC#)]
1806241-263-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C29H26ClFN4O4S | [MDL Number]
MFCD09264194 | [Molecular Weight]
581.058 | [MOL File]
231277-92-2.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
144-146oC | [Boiling point ]
750.7±60.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.381±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C | [solubility ]
Soluble in DMSO (up to 200 mg/ml) | [form ]
solid | [pka]
6.34±0.19(Predicted) | [color ]
Yellow | [Stability:]
Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. | [InChIKey]
BCFGMOOMADDAQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
N1=C2C(C=C(C3=CC=C(CNCCS(C)(=O)=O)O3)C=C2)=C(NC2=CC=C(OCC3=CC=CC(F)=C3)C(Cl)=C2)N=C1 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
231277-92-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Indications and Usage]
Lapatinib is a drug targeting breast cancer developed by British GlaxoSmithKline Co.
Human ErbB receptors belong to the type I tyrosine kinase (TK) receptor family, including ErbB1 (EGFR), ErbB2 (HER2), ErbB3 (HER3), and ErbB4 (HER4). The ErbB-1 (EGFR) and ErbB-2 (HER-2) receptors are often overexpressed or otherwise altered in cancer patients. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (ErbB-2, HER-2) is known to be a human oncogene closely related with breast cancer. Its high expression in breast cancer often predicts lymph node metastasis and poor tumor differentiation, with poor prognosis. HER-2 is one of the target molecules for breast cancer-specific therapy. Lapatinib can act simultaneously on both Her-1 Her-2. The biological effects of this method inhibiting the proliferation and growth of tumor cells are much larger than only acting on one target. The combination of Lapatinib with Capecitabine is used to treat patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer with overexpression of human epidermal receptor2, already treated with anthracyclines, paclitaxel, and trastuzumab. Clinical trials have shown that Lapatinib also effectively treats HER2-type cancer patients with Herceptin resistance.
| [Mechanisms of Action]
Lapatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor which can effectively inhibit the tyrosine kinase activity of human epidermal growth factor receptors 1 and 2 (ErbB1, ErbB2). It can uniquely act in a variety of ways, ensuring that breast cancer cells cannot receive growth signals. It inhibits intracellular EGFR (ErbB-1) and HER2 (ErbB-2) ATP sites, preventing tumor cell phosphorylation and activation, blocking down-regulation signals through the homogeneity and heterogeneity of EGFR (ErbB-1) and HER2 (ErbB-1) dimerization. | [Binding Mode]
Lapatinib is a type I1/2 inhibitor that binds to a DFG-in, αC helix-out inactive conformation of EGFR. The quinazoline N1 forms a hydrogen bond with the amide NH group of Met793 of the hinge. Although the aniline nitrogen is not involved in any direct hydrogen-bonding interactions with the protein, it serves to increase the basicity of quinazoline N1. The proximal methylsulfonylethylamino group, which functions to increase aqueous solubility of the drug, extends toward the solvent exposed region.
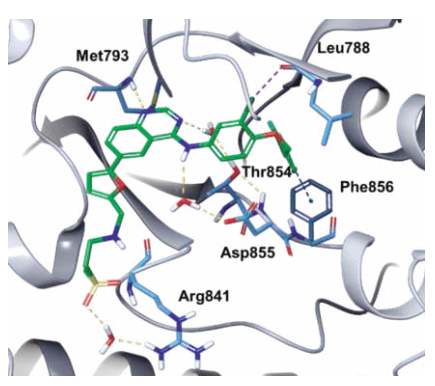 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Lapatinib (231277-92-2), a new member of the 4-anilinoquinazoline class of RTK inhibitors
(RTKIs), was launched as an oral treatment for breast cancer.
Lapatinib has dual affinity for EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinases. It is indicated
in combination with capecitabine for treating patients with advanced or
metastatic breast cancer whose tumors overexpress HER2 and who have
received prior therapy including an anthracycline, a taxane, and trastuzumab.
Previously marketed drugs from the 4-anilinoquinazoline class include
erlotinib (Tarceva) and gefitinib (IressaTM), both of which are indicated for
treating non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). As with erlotinib and gefitinib, To Market, To Market 2007 475 lapatinib is an ATP-competitive kinase inhibitor. It inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity EGFR and HER-2 with apparent Ki values of 3 and 13 nM, respectively, and has slow off-rate kinetics (t1/2X300 min).
In addition, dividing the daily dose of lapatinib results in approximately 2-fold higher exposure at steady state compared to the same total dose administered once daily.
The chemical synthesis of lapatinib entails the condensation of 4-chloro-6-iodoquinazoline and 3-chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)aniline to produce a diaryl amine intermediate followed by Stille coupling of the iodo group with 5-dioxolanyl-2-(tributylstannyl)furan and subsequent acid hydrolysis of the cyclic ketal to the corresponding aldehyde. Finally, reductive amination of the aldehyde intermediate with 2-(methanesulfonyl) ethylamine in the presence of sodium triacetoxyborohydride produces lapatinib.
.
| [Originator]
GSK (US) | [Uses]
An antineoplastic agent used in breast cancer research | [Uses]
antineoplastic, tyrosine kinase inhibitor | [Uses]
Lapatinib Ditosylate (GW572016, GW2016, Tykerb, Tyverb) is a potent EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitor with IC50 of 10.8 and 9.2 nM, respectively. | [Uses]
Lapatinib, used in the form of Lapatinib Ditosylate, is a potent EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitor with IC50 of 10.8 and 9.2 nM, respectively. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Lapatinib is an organofluorine compound, an organochlorine compound, a member of quinazolines and a member of furans. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It is functionally related to a monofluorobenzene. | [Brand name]
Tykerb | [General Description]
Class: receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: HER2-positive breast cancer
Elimination half-life = 24 h
Protein binding = 99% | [Clinical Use]
#N/A | [target]
EGFR | [Drug interactions]
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: avoid with rifabutin, rifampicin and
telithromycin.
Antidepressants: avoid with St John’s wort.
Antidiabetics: avoid with repaglinide.
Antiepileptics: concentration reduced by
carbamazepine - avoid; possibly reduced
fosphenytoin and phenytoin concentration - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole
- avoid; avoid with itraconazole, posaconazole and
voriconazole.
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine (increased risk
of agranulocytosis); avoid with pimozide.
Antivirals: avoid with boceprevir, ritonavir and
saquinavir.
Cytotoxics: concentration of pazopanib increased;
possible increased risk of neutropenia with docetaxel
and paclitaxel; concentration of active metabolite of
irinotecan increased, consider reducing irinotecan
dose.
Grapefruit juice: avoid concomitant us | [Metabolism]
Extensive hepatic metabolism, mainly by cytochrome
P450 isoenzymes CYP3A4 and CYP3A5; CYP2C19
and CYP2C8 account for some minor metabolism.
About 27% and 14% of an oral dose is recovered in the
faeces, as parent lapatinib and metabolites, respectively;
renal excretion is negligible. | [storage]
Store at -20°C | [References]
1) Wood?et al. (2004),?A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells;? Cancer Res.,?64?6652
2) Burris?et al. (2004),?Dual kinase inhibition in the treatment of breast cancer: initial experience with the EGFR/ErbB-2 inhibitor lapatinib;? Oncologist,?9?10
3) Chu?et al. (2005),?The dual ErbB1/ErbB2 inhibitor, lapatinib (GW572016) cooperates with tamoxifen to inhibit both cell proliferation- and estrogen-dependent gene expression in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer;? Cancer Res.,?65?18 |
|
|