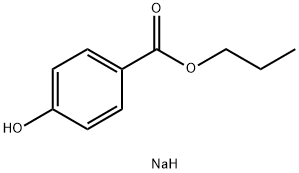
Sodium propylparaben synthesis
- Product Name:Sodium propylparaben
- CAS Number:35285-69-9
- Molecular formula:C10H13NaO3
- Molecular Weight:204.2

94-13-3
784 suppliers
$16.00/25g

35285-69-9
385 suppliers
$27.00/25g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with sodium hydride in diethylene glycol dimethyl etherProduct distribution / selectivity;
Steps:
2; 3
EXAMPLE 2Synthesis of Poly{[2-(2-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy](4-carboxylatophenoxy)phosphazene} (CP1)A suspension of sodium hydride (0.086 g; 0.003 moles) in 1,4-dioxane (0.002 L) was slowly added to a solution of 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)pyrrolidone (2.08 g; 0.016 moles) in 0.010 L of 1,4-dioxane under nitrogen to form sodium 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)pyrrolidone. Sodium propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate was prepared by adding a suspension of sodium hydride (0.61 g; 0.025 moles) in diglyme (0.004 L) to a solution of propyl ester of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (5.19 g; 0.029 moles) in 0.010 L diglyme under dry nitrogen. 0.0005 L of the sodium propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate solution was added to the sodium 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)pyrrolidone solution at ambient temperature.0.002 L of polydichlorophosphazene (0.116 g; 0.001 moles) was then added slowly at room temperature over a period of five minutes. Following the addition, the temperature was raised to 50° C., and stirred for fifteen hours. 0.001 L of 12.7 N aqueous potassium hydroxide solution was slowly added, and the reaction mixture was stirred for one hour at 50° C.The precipitate was collected by decantation, dried and dissolved in water. The polymer then was purified chromatographically as described above. The yield of polymer (CP1) was 0.228 g (75% of theoretical). Polymer characterization data is presented in Tables 1 and 2.The composition of mixed substituent polymer was determined using two methods. (1) It was calculated based on the ratio between the peak areas of ethylene protons of the ethylpyrrolidone side group and the aromatic protons of the carboxylatophenoxy side group in 1H NMR. (2) The composition was established using HPLC based on the differences in the UV absorbance of PCPP and PYRP at 254 nm in PBS (pH 7.4). Calibration curves were obtained for the mixtures of PCPP and PYRP by plotting HPLC peak areas at 254 nm versus mixture composition. The total polymer concentration was maintained at 1 mg/mL and the results were processed using Millenium (Waters, Milford, Mass.) software. A copolymer was then analyzed by HPLC using the same conditions and its molar composition was determined using calibration curves obtained for the mixtures of homopolymers. Polymer composition data is presented in Table 2.; EXAMPLE 3Synthesis of Poly{[2-(2-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy](4-carboxylatophenoxy)phosphazene} (CP2)A suspension of sodium hydride (0.247 g; 0.0098 moles) in 1,4-dioxane (0.105 L) was slowly added to 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-pyrrolidone (5.989 g; 0.0464 moles) in 1,4-dioxane (0.025 L) under a dry nitrogen to form a sodium 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-pyrrolidone solution. Sodium propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate was prepared by adding a suspension of sodium hydride (0.707 g; 0.0279 moles) in diglyme (0.003 L) to 4-hydroxybenzoate propyl ester (6.055 g; 0.3360 moles) in diglyme (0.010 L) under a dry nitrogen atmosphere. 0.003 L polydichlorophosphazene (0.232 g; 0.002 moles) was diluted with 0.013 L diglyme at room temperature under nitrogen and then heated to 50° C. 0.0024 L of the sodium propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate was added while stirring. The temperature was increased to 100° C., the reaction mixture was stirred for three hours and then cooled to 50° C. To this 0.015 L of the sodium 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-pyrrolidone solution was slowly added and the reaction continued for twenty hours. 0.010 L of 12.7 N potassium hydroxide solution was slowly added, and stirred for one hour at 50° C. The precipitated polymer was collected, dissolved in distilled water, and precipitated by adding 1 N hydrochloric acid until pH 3. The precipitate was re-dissolved in 0.05 M of ammonium bicarbonate and purified by preparative HPLC as described above. The yield of polymer (CP2) was 0.29 g (38.6% of theoretical). Polymer composition was determined as described in Example 2. Characterization data is presented in Tables 1 and 2.
References:
Andrianov, Alexander K.;Marin, Alexander US2008/166390, 2008, A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 4; 5