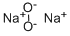?????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
Sodium peroxide has a molecular formula of Na2O2 and is an inorganic peroxide salt. It is a yellowish-white powder that turns yellow when heated. Sodium peroxide absorbs water and carbon dioxide from the air and is soluble in cold water. It is a strong oxidizing agent, is corrosive and can cause burns to the eyes and skin, and is also toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Sodium peroxide is water reactive and a dangerous fire and explosion risk in contact with water, alcohol, or acids. Sodium peroxide forms self-igniting mixtures with powdered metals and organic materials. It is incompatible with ethyl or methyl alcohol, glacial acetic acid, carbon disulfide, glycerin, ethylene glycol, and ethyl acetate. The four-digit UN identification number is 1504. The NFPA 704 designation is health 3, flammability 0, and reactivity 1. The 704 diamond has the prefix “oxy” in the white space at the bottom. It is used as bleach and as an oxygen-generating material for diving bells and submarines.
??? ??
Sodium peroxide, Na202, is a fire-hazardous white powder that yellows when heated and causes ignition when in contact with water. Sodium peroxide is decomposed by heating, although this is not easily accomplished. It is stable in dry air; however, in moist air,or when acted on by water, it decomposes readily. It can be a powerful oxidizer and a powerful reducing agent, depending on conditions. Sodium peroxide is also used as a bleach, in medicine soap, and in the decomposition of minerals.
??
Sodium peroxide historically was used to bleach wood pulp
for the production of paper and textiles. It is mainly used for
specialized laboratory operations, for example, the extraction
of minerals from various ores. Sodium peroxide is used
as an oxidizing agent and is used as an oxygen source by
reacting with carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and sodium
carbonate; it is thus particularly useful in scuba gear, submarines,
and so on.
??
Exists as impurity
(about 10%) in sodium peroxide, obtained by heat-
ing sodium peroxide in oxygen, reacts with water
to yield hydrogen peroxide, oxygen, and sodium
hydroxide.
?? ??
A yellow-white to yellow granular solid. Mixtures with combustible material are readily ignited by friction, heat, or contact with moisture. May vigorously decompose under prolonged exposure to heat, causing the rupture of the containers.
??? ?? ??
Reacts vigorously with water, large amounts react explosively [Haz. Chem. Data 1969. p. 201].
?? ???
Sodium peroxide reacts violently with reducing agents, combustible materials and light metals. Reacts exothermically and rapidly or even explosively with water to form a strong base (NaOH) and oxygen (O2) [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980 p. 854]. A mixture with ammonium persulfate can explode if subjected to friction (crushing in a mortar), if heated, or if a stream of gaseous carbon dioxide is passed over Sodium peroxide [Mellor 10:464 1946-47]. Reacts very vigorously with gaseous hydrogen sulfide; even in the absence of air, the reaction may be accompanied by flame [Mellor 10:132 1946-47]. An explosion results when gaseous carbon dioxide is passed over a mixture of Sodium peroxide with powdered magnesium [Mellor 2:490 1946-47] . Mixtures with acetic acid or acetic anhydride can explode if not kept cold [Von Schwartz 1918 p. 321]. Spontaneously flammable in contact with aniline, benzene, diethyl ether, or organic materials such as paper and wood. Mixtures with charcoal, glycerine, certain oils, and phosphorus burn or explode [Mellor 2:490 1946-47]. A mixture with calcium carbide (powdered) burst into flame when exposed to damp air and exploded when heated [Mellor 2:490 1946-47]. Decomposes, often violently in the presence of catalytic quantities of manganese dioxide [Mellor 2 Supp. 2:635 1961]. Mixing with sulfur monochloride leads to a violent reaction [Mellor 2 Supp. 2:634 1961]. Can react with and cause the ignition of fuels.
???
Dangerous fire and explosion risk in contact
with water, alcohols, acids, powdered metals, and
organic materials. Strong oxidizing agent. Keep dry.
Irritant.
????
TOXIC; inhalation or contact with vapor, substance, or decomposition products may cause severe injury or death. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
????
May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). React vigorously and/or explosively with water. Produce toxic and/or corrosive substances on contact with water. Flammable/toxic gases may accumulate in tanks and hopper cars. Some may produce flammable hydrogen gas upon contact with metals. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Safety Profile
A severe irritant to shin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Dangerous fire hazard by chemical reaction; a powerfuloxidizing agent. Reacts explosively or violently under the appropriate conditions with water, acids, powdered metals, acetic acid, acetic anhydride, Al, (Al + CO2), aluminum + aluminum chloride, almond oil, (NH4)2S208, aniline, Sb, As, benzene, boron nitride, calcium aceqlide, charcoal, Cu, cotton wool, (KNO3 + dextrose), diethyl ether, fibrous materials + water, glucose + potassium nitrate, hexamethylene-tetramine, hydrogen sulfide, hydroxy compounds (e.g., ethanol, ethylene glycol, glycerol, sugar), magnesium, (Mg + CO2), MnO2, metals, metals + carbon dioxide + water, nonmetals (e.g., carbon, phosphorus, antimony, arsenic, boron, sulfur, selenium), nonmetal halides (e.g., diselenium dichloride, disulfur dichloride, phosphorus trichloride), organic matter, paraffin, K, silver chloride + charcoal, soap, Na, sodium dioxide, SCl, Sn, Zn, wood, peroxyformic acid, reducing materials. Will react with water or steam to produce heat and toxic fumes. To fight fire, use carbon dioxide or dry chemical. Combustible materials ignited by contact with sodium peroxide should be smothered with soda ash, salt or dolomite mixtures. Chemical fire extinguishers should not be used. If the fire cannot be smothered, it should be flooded with large quantities of water from a hose. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O. See also SODIUM HYDROXIDE and PEROXIDES, INORGANIC.
?????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??