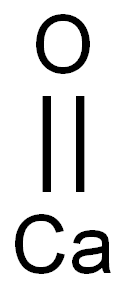????(???)
|
|
????(???) ??
- ???
- 2570 °C
- ?? ?
- 2850 °C (lit.)
- ??
- 3.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- ?? ??
- 800-1200kg/m3
- ???
- 1.83
- ???
- 2850°C
- ?? ??
- no restrictions.
- ???
- 1.65g/l ??? ??? ??? ????.
- ??? ??
- ??
- ??
- ??~???~?? ?? ????
- Specific Gravity
- 3.3
- ??????(pH)
- 12.6 (H2O, 20℃)(saturated solution)
- ??
- ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ??
- ???
- ?? ??
- ??
- Air & Moisture Sensitive
- Crystal Structure
- Cubic
- crystal system
- Cube
- Merck
- 14,1686
- Space group
- Fm3m
- Lattice constant
a/nm b/nm c/nm α/o β/o γ/o V/nm3 0.4776 0.4776 0.4776 90 90 90 0.1089
- Dielectric constant
- 2.2(Ambient)
- ?? ??
- ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3
OSHA: TWA 5 mg/m3
NIOSH: IDLH 25 mg/m3; TWA 2 mg/m3
- ???
- ?????? ?? ? ?????? ?????. ?, ??, ??, ??? ???? ????.
- InChIKey
- ODINCKMPIJJUCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- CAS ??????
- 1305-78-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | C,Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 34-41-37/38 | ||
| ????? | 26-36/37/39-45-25-39 | ||
| ????(UN No.) | 1910 | ||
| OEB | B | ||
| OEL | TWA: 2 mg/m3 | ||
| WGK ?? | 1 | ||
| RTECS ?? | EW3100000 | ||
| F ?????? | 10-21-34 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| ?? ?? | 8 | ||
| ???? | III | ||
| HS ?? | 28259019 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 1305-78-8(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| IDLA | 25 mg/m3 | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-04588 |
????(???) C??? ??, ??, ??
????
? (1) ???? : ? ?? 5g? ? 100mL ? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ?? ??. ? ?? ??? ?? ?? ???? ?? ??? ?? ??? ??? ??? ?? ??? ???? ????. ???? ?? ?? ?????? ???? ?? ??? ???? 105℃?? 1?? ??? ?, ? ?? 1.0% ????? ??.
??(2) ??? ?? ???? : ? ?? 0.5g? ? 30mL ? ???? 15mL? ??? 1?? ?? ?? ?? ???? 40mL? ??? ??? ???. ?????? 2??? ??? ??? ??? ????? ??? ???????? ?? ?????. ? ?? ????? 1?? ?? ???? ?? ?? ?? ??? 100mL? ?? ????. ?? 50mL? ?? 0.5mL? ??? ????? ?? ?????? 800±25℃?? ??? ? ??? ??? ?, ? ?? 3.6% ????? ??.
??(3) ???? : ? ?? 1g? ??? ?? 「?????」? ???? (8)? ?? ????(50ppm ??).
??(4) ?? : ? ??? ?????? ?? ??? ?, ? ?? 4.0ppm ????? ??.
??(5) ?? : ? ?? 1.5g? ?? ? 10mL? ???? ???? 15mL? ?? ?? ?? 30mL? ?? ??? ?? ?????? ??. ??, ?????? 0.3mL? ??? ?? ??? 20mL? ? ?? ????? ??. ???? 20mL ? ???? ????? 2g, ???? 1mL? ? ??????? 0.5mL? ??? 15?? ??? ?, ????? ???? ??? ???? ?? ????? ??(0.03% ??).
??(6) ? : 「???????」? ???? (2)? ?? ????(2.0ppm ??).
????
? ? ?? 1g? ? 20mL? ??? ?? ??? ??? ?? ?? ????? ? ???? ??? ????.
???
? ?? 1g? ??? ? ??? ??? ?? ??? ?? ???? 20mL? ??? ?? ?? ?? ??? 500mL? ??. ? ? 50mL? ??? ? 50mL? ?? ???? ???????? 15mL ? ?????????(C20H12O11S3Na2) 0.3g? ?? ?? 0.05M ?.?.?.??.???? ????. ???? ??? ??? ???? ??? ? ??? ??.
0.05M ?.?.?.??.?? 1mL = 2.804mg CaO
??? ??
Calcium oxide, CaO, occurs as white or grayish-white lumps or granular powder. The presence of iron gives it a yellowish or brownish tint.??? ??
Calcium oxide is a white caustic crystalline alkali substance that goes by the common name lime. The term lime is used both generically for several calcium compounds and with adjectives to qualify different forms of lime. This entry equates lime, also called quicklime or burnt lime, with the compound calcium oxide. Hydrated lime, made by combining lime with water, is calcium hydroxide and is often referred to as slaked lime (Ca(OH)2). Dolomite limes contain magnesium as well as calcium. Limestone is the compound calcium carbonate. The term lime comes from the Old English word l?m for a sticky substance and denotes lime’s traditional use to produce mortar. Calx was the Latin word for lime and was used to name the element calcium.??
Calcium oxide dates from prehistoric times. It is produced by heating limestone to drive off carbon dioxide in a process called calcination: CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g). At temperatures of several hundred degrees Celsius, the reaction is reversible and calcium oxide will react with atmospheric carbon dioxide to produce calcium carbonate. Efficient calcium oxide production is favored at temperatures in excess of 1,000°C. In prehistoric times limestone was heated in open fires to produce lime. Over time, lined pits and kilns were used to produce lime. Brick lime kilns were extensively built starting in the 17th century and the technology to produce lime has remained relatively constant since then.??
Calcium Oxide is a general food additive consisting of white granules or powder of poor water solubility. it is obtained by heating limestone (calcium carbonate) in a furnace. it is also termed lime or quicklime. it is used as an anticaking agent, firming agent, and nutritive supple- ment in applications such as grain products and soft candy.?? ??
Calcium oxide is commercially obtained from limestone. The carbonate is roasted in a shaft or rotary kiln at temperatures below 1,200°C until all CO2 is driven off. The compound is obtained as either technical, refractory or agri cultural grade product. The commercial product usually contains 90 to 95% free CaO. The impurities are mostly calcium carbonate, magnesium carbon ate, magnesium oxide, iron oxide and aluminum oxide.??
ChEBI: Calcium oxide is a member of the class of calcium oxides of calcium and oxygen in a 1:1 ratio. It has a role as a fertilizer.?? ??
Calcium oxide appears as an odorless, white or gray-white solid in the form of hard lumps. A strong irritant to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Used in insecticides and fertilizers.??? ?? ??
Crumbles on exposure to moist air. Reacts with water to form corrosive calcium hydroxide, with evolution of much heat. Temperatures as high as 800° C have been reached with addition of water (moisture in air or soil). The heat of this reaction has caused ignition of neighboring quantities of sulfur, gunpowder, wood, and straw [Mellor 3: 673 1946-47].?? ???
A base and an oxidizing agent. Neutralizes acids with generation of heat. Nonflammable, but will support combustion by liberation of oxygen, especially in the presence of organic materials. Reacts very violently with liquid hydrofluoric acid [Mellor 2, Supp. 1:129 1956]. Reacts extremely violently with phosphorus pentaoxide when reaction is initiated by local heating [Mellor 8 Supp.3:406 1971].???
Evolves heat on exposure to water. Danger- ous near organic materials. Upper respiratory tract irritant.????
Causes burns on mucous membrane and skin. Inhalation of dust causes sneezing.????
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Vapors may accumulate in confined areas (basement, tanks, hopper/tank cars etc.). Substance will react with water (some violently), releasing corrosive and/or toxic gases and runoff. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water.???
Calcium oxide (CaO) is a white powder with a neutralizing value or calcium carbonate equivalent (CCE) of 179%, compared to 100% for calcium carbonate (CaCO3). For quick results, either calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] is used. Calcium oxide is also known as lime, unslaked lime, burned lime or quicklime. Roasting CaCO3 in a furnace makes calcium oxide. A complete mixing of calcium oxide with soil is difficult because it cakes due to absorption of water.?? ??
Lime is the most widely used reagent in the mineral industry for flotation of sulfides and, in some cases, non-sulfide minerals. The word “lime” is a general term used to describe any kind of calcareous material or finely divided form of limestone and dolomite. In more strict chemical terms, lime is calcinated limestone known as calcium oxide (CaO), quicklime or unslaked lime.The slaked or hydrated lime Ca(OH)2 is the form of lime primarily used in mineral flotation. Production of high-calcium lime is based on calcination of limestone at a temperature of 1100–1300 °C in kilns.CaCO3+heat--->CaO+CO2 For high-magnesium (dolomitic) limestone, the calcination reaction (at 1000–1200 °C) is CaCO3·MgCO3 (limestone) + heat--->CaOMgO (quicklime-2CO2)
Safety Profile
A caustic and irritating material. See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS. A common air contaminant. A powerful caustic to living tissue. The powdered oxide may react explosively with water. Mixtures with ethanol may igmte if heated and thus can cause an air-vapor explosion. Violent reaction with (I3203 + CaCl2) interhalogens (e.g., BF3, CIF3), F2, HF, P2O5 + heat, water. Incandescent reaction with liquid HF. Incompatible with phosphoms(V) oxide.??? ??
Calcium oxide is used as a refractory material; a binding agent in bricks; plaster, mortar, stucco, and other building materials. A dehydrating agent, a flux in steel manufacturing, and a labora?? ??
UN1910 Calcium oxide, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.? ???
The water solution is a medium strong base. Reacts with water, forming calcium hydroxide and sufficient heat to ignite nearby combustible materials. Reacts violently with acids, halogens, metals.??? ??
Pretreatment involves neutralization with hydrochloric acid to yield calcium chloride. The calcium chloride formed is treated with soda ash to yield the insoluble calcium carbonate. The remaining brine solution may be discharged into sewers and waterways????(???) ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??
????(???) ?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 |
abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8803 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 |
1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12825 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5884 | 58 |
| Yujiang Chemical (Shandong) Co.,Ltd. | +86-17736087130 +86-18633844644 |
catherine@yjchem.com.cn | China | 994 | 58 |
| Chemson Industrial (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. | 86-21-65208861- 8007 |
sales1@chemson.com.cn | CHINA | 117 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-6139-8061 +86-86-13650506873 |
sales@chemdad.com | China | 39894 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49732 | 58 |
| Beijing CommScope Huiwei Technology Co., Ltd | 86-18810111057 |
summer@kphwchem.com | CHINA | 51 | 58 |