4,4'-Isopropylidendiphenol Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
WEISSE KRISTALLE.
PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Staubexplosion der pulverisierten oder granulierten Substanz in Gemischen mit Luft m?glich.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Reagiert sehr heftig mit S?ureanhydriden, S?urechloriden, starken Basen und starken Oxidationsmitteln.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2005).
MAK: 5 mg/m?(Einatembare Fraktion); Spitzenbegrenzung: überschreitungsfaktor I(1); Photosensibilisierung; Schwangerschaft: Gruppe C; (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation des Aerosols und durch Verschlucken.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfen bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine bel?stigende Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch schnell erreicht werden.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz reizt die Augen, die Haut und die Atemwege.
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
Wiederholter oder andauernder Kontakt kann zu Hautsensibilisierung führen.
LECKAGE
Verschüttetes Material in abdichtbaren Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste sorgf?ltig sammeln. An sicheren Ort bringen. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P2-Filter für sch?dliche Partikel.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R37:Reizt die Atmungsorgane.
R41:Gefahr ernster Augensch?den.
R43:Sensibilisierung durch Hautkontakt m?glich.
R62:Kann m?glicherweise die Fortpflanzungsf?higkeit beeintr?chtigen.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36/37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung,Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S46:Bei Verschlucken sofort ?rztlichen Rat einholen und Verpackung oder Etikett vorzeigen.
S39:Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
Beschreibung
Reports of bisphenol-
A sensitization, particularly in workers at epoxy
resin plants, are controversial. Bisphenol-A was also
reported as an allergen in fiberglass, semisynthetic
waxes, footwear and dental materials.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Bisphenol A is a white or tan crystals or flakes with a mild phenolic odor and a very low vapor pressure (ECB, 2003). It is mildly soluble in water. It is not considered to be an explosive in the conventional sense but can pose a hazard as a finely powdered material in air (ECB, 2003). It is not considered to be a chemical oxidizer.
History
Bisphenol A (BPA) was first synthesized in 1891, but it was not used widely until applications in the plastics industry were identified in the 1950s (University of Minnesota, 2008). While the most prominent use of BPA is in the manufacture of polycarbonate plastic and epoxy resins, it is also used in the production and processing of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and modified polyamide and in the manufacture of carbonless and thermal paper, wood filler, adhesives, printing inks, surface coatings, polyurethane, brake fluid, resin-based dental composites and sealants, flame retardants, paints, and tires (ECB, 2003; EFSA, 2006).

Verwenden
Bisphenol A (BPA) is used as the constitutional monomer or the monomeric building block of polycarbonate plastics, either by trans-esterification with diphenyl carbonate or via the interfacial process with a monohydroxylic phenol. Together with epichlorohydrin, BPA is also used as a major component of epoxy resins. Bisphenol A-polycarbonate plastics are in turn used in the manufacture of plastic food containers such as reusable water bottles, while epoxy resins are used as inner linings of tin cans. In addition, BPA is also used as an additive in other plastics and polymers, particularly as an antioxidant or stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride, printer ink, and in some other products.
synthetische
The formation of bisphenol A is thought to proceed as follows:
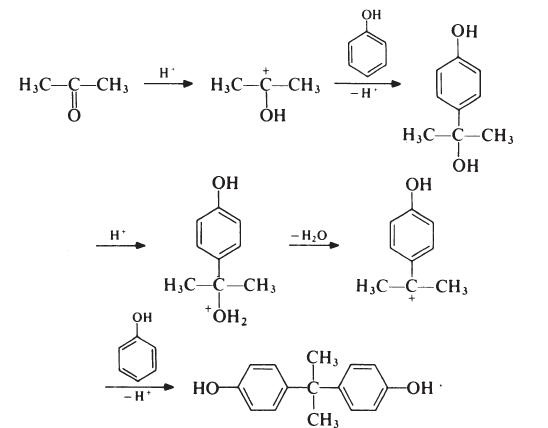
Although the reaction theoretically requires the molar ratio of reactants to be
2: 1, an improved yield of bisphenol A is obtained if additional phenol is
present; the optimum molar ratio is 4: 1. In a typical process, the phenol and
acetone are mixed and warmed to 50??C. Hydrogen chloride (catalyst) is
passed into the mixture for about 8 hours, during which period the temperature
is kept below 70??C to suppress the formation of isomeric products.
Bisphenol A precipitates and is filtered off and washed with toluene to remove
unreacted phenol (which is recovered). The product is then recrystallized from
aqueous ethanol. Since epoxy resins are oflow molecular weight and because
colour is not normally particularly important, the purity of bisphenol A used
in resin production is not critical. Material with a p,p'-isomer content of
95-98% is usually satisfactory; the principal impurities in such material are
o,p'- and o,o'-isomers.
Definition
ChEBI: A bisphenol that is 4,4'-methanediyldiphenol in which the methylene hydrogens are replaced by two methyl groups.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
White to light brown flakes or powder. Has a weak medicine odor. Sinks in water.
Air & Water Reaktionen
The finely powdered resin is a significant dust explosion hazard. Insoluble in water.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
Bisphenol A is incompatible with strong oxidizers. Bisphenol A is also incompatible with strong bases, acid chlorides and acid anhydrides.
Hazard
Poison; moderately toxic; teratogen;
irritant.
Health Hazard
Dusts irritating to upper respiratory passages; may cause sneezing.
Brandgefahr
Bisphenol A is combustible. Bisphenol A may form explosive dust clouds. Static electricity can cause its dust to explode.
Kontakt-Allergie
Bisphenol A is used with epichlorhydrin for the
synthesis of epoxy resins bisphenol-A type, for
unsaturated polyester and polycarbonate resins, and
epoxy di(meth)acrylates. In epoxy resins, it leads to
bisphenol-A diglycidyl ether, which is the monomer
of bisphenol-A-based epoxy resins. Reports of
bisphenol-A sensitization are rare and concern
workers at epoxy resin plants, after contact with
fiber glass, semi-synthetic waxes, footwear, and
dental materials. It is also a possible sensitizer in
vinyl gloves.
m?gliche Exposition
Workers engaged in the manufacture
of epoxy, polysulfone, polycarbonate and certain polyester
resins. It is also used in flame retardants, rubber chemicals,
and as a fungicide. Bisphenol A (BP A), an environmental
estrogen, is found in a wide variety of products, including
polycarbonate bottles food and drink containers. According
to 2008 research conducted at University of Cincinnati,
when it comes to BPA, it’s not whether polycarbonate
bottles are new or old but the liquid’s temperature that
has the greatest impact on how much BPA is released.
When exposed to boiling hot water, BPA was released
55 times more rapidly than exposure to cold water.
Environmental Fate
Bisphenol A can be released into the environment during the production, processing, and use of BPA-containing materials, although levels in environmental samples are generally very low or undetectable (ECB, 2003). This is because BPA has low volatility and a short half-life in the atmosphere, is rapidly biodegraded in water, and is not expected to be stable, mobile, or bioavailable from soils (ECB, 2003; Cousins et al., 2002).
Most environmental releases of BPA are during the manufacture of BPA-containing products when residual BPA in wastewater is released from treatment plants into receiving streams (Cousins et al., 2002). BPA's half-life in soil and water is in the order of 4.5 days while in air it is <1 day (Cousins et al., 2002). It has a low bioconcentration factor and is rapidly metabolized in fish, with a half-life of <1 day (Cousins et al., 2002).
Versand/Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances,
solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9—Miscellaneous
hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
l?uterung methode
Crystallise bisphenol from acetic acid/water (1:1). It is used for making polycarbonate bottles and leaches out slowly on heating. It is a known “estrogenic chemical” shown to disrupt chemical signaling in the complex network of glands, hormones and cell receptors which make up the endocrine system. It causes low sperm count and damages the ecosystem by the feminisation of fish, reptiles and birds. [cf Chapter 1, p 3, Beilstein 6 IV 6717.]
Inkompatibilit?ten
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates,
nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine,
bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions.
Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases,
strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, acid chlorides and acid
anhydrides.
4,4'-Isopropylidendiphenol Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Stirring vessel
Aceton
Phenolic epoxy resin
Phenol
Polycarbonate
Schwefelsure
o-[1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl]phenol
3-Penten-2-one, 4-hydroxy-, (3Z)-
1H-Inden-5-ol, 2,3-dihydro-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,3,3-trimethyl-
Phenol, 4-(3,4-dihydro-2,4,4-trimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-2-yl)-
Downstream Produkte

