1062169-56-5
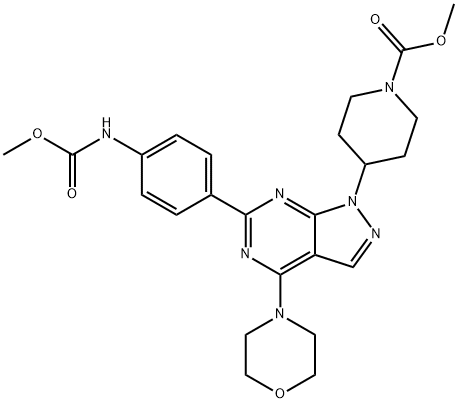 1062169-56-5 結(jié)構(gòu)式
1062169-56-5 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
4-[6-[4-[(甲氧羰基)氨基]苯基]-4-(4-嗎啉基)-1H-吡唑并[3,4-D]嘧啶-1-基]-1-哌啶羧酸甲酯
WYE-354
WYE-354 USP/EP/BP
WYE-354 (Degrasyn)
WYE-354
WYE 354
WYE354
Methyl 4-(6-(4-(methoxycarbonylamino)phenyl)-4-morpholino-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl)pip
methyl 4-[6-[4-(methoxycarbonylamino)phenyl]-4-morpholin-4-ylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]piperidine-1-carboxylate
4-[6-[4-[(Methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl]-4-(4-morpholinyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid methyl ester
1-Piperidinecarboxylic acid, 4-[6-[4-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl]-4-(4-morpholinyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]-, methyl ester
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
應(yīng)用領(lǐng)域
常見問題列表
|
mTOR 5 nM (IC 50 ) |
mTORC1
|
mTORC2
|
PI3K alpha 1.89 μM (IC 50 ) |
PI3K gamma 7.37 μM (IC 50 ) |
Autophagy
|
In the DELFIA measuring His6-S6K1 T389 phosphorylation, WYE-354 inhibits recombinant mTOR enzyme with an IC 50 of 5 nM. Cell viability is analyzed by MTS assay. G-415 and TGBC-2TKB cell lines are treated with increasing concentrations of WYE-354 (0.1, 1, 5 and 10 μM) for 24, 48, and 72 hours. WYE-354 significantly reduces cell viability starting at a 1 μM concentration after a 24 hours exposure, in both studied cell lines (P<0.001). A decrease in cell viability is not observed at a dose of 100 nM, except for the TGBC-2TKB cell line after 72 hours of treatment.
The effect of Rapamycin and WYE-354 on tumor growth is evaluated in xenograft GBC tumor models. 2×10 6 or 5×10 6 cells of G-415 or TGBC2TKB, respectively, are xenotransplanted into NOD-SCID mice subcutaneously. When tumors reach an average volume of 100 mm 3 , the mice are treated either with Rapamycin or WYE354. Rapamycin is administered i.p. at a concentration of 10 mg/kg, daily for 5 days per week for 3 weeks, while WYE-354 is administrated at a daily i.p. dose of 50 mg/kg for 5 days. Mice are sacrificed 30 days after the initiation of the treatments and an autopsy is performed that include removal of the entire tumor area. Mice treated with WYE-354 exhibit 68.6% and 52.4% reduction in average tumor size (P<0.01; P<0.01), as well as 82.9% and 45.5% (P<0.01; ns) reduction in tumor weight, respectively.