| Identification | More | [Name]
Diphenylphosphoryl azide | [CAS]
26386-88-9 | [Synonyms]
AZIDOPHOSPHORIC ACID DIPHENYL ESTER
DIPHENYL AZIDOPHOSPHATE
DIPHENYLPHOSPHONIC AZIDE
DIPHENYL PHOSPHORAZIDATE
DIPHENYLPHOSPHORIC AZIDE
DIPHENYLPHOSPHORYL AZIDE
DIPHENYLPHOSPHORYL AZIDE, POLYMER-BOUND
DPPA
DPPA POLYMER-BOUND
LABOTEST-BB LT00453991
(PHO)2PO-N3
PHOSPHORIC ACID DIPHENYL ESTER AZIDE
PS-DPPA
Diphenyl phosphonyl azide
Phosphorazidic acid, diphenyl ester
phosphorazidicacid,diphenylester
Diphenylphosphorazindate(DPPA)
Diphenylphosphonicazide,97%
DPPA polymer-bound, PS-DPPA
DPPA, Phosphoric acid diphenyl ester azide | [EINECS(EC#)]
247-644-0 | [Molecular Formula]
C12H10N3O3P | [MDL Number]
MFCD00001987 | [Molecular Weight]
275.2 | [MOL File]
26386-88-9.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Colorless to yellow liquid | [Boiling point ]
157 °C/0.17 mmHg (lit.) | [density ]
1.277 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
| [refractive index ]
n20/D 1.551(lit.)
| [Fp ]
>230 °F
| [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
Acetonitrile (Slightly), Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Sparingly) | [form ]
Liquid | [color ]
slightly yellow
| [Specific Gravity]
1.277 | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with acids, strong oxidizing agents. | [Water Solubility ]
insoluble | [Hydrolytic Sensitivity]
7: reacts slowly with moisture/water | [Detection Methods]
GC���,NMR | [BRN ]
2058967 | [InChIKey]
SORGEQQSQGNZFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
26386-88-9(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
Diphenylphosphoryl azide(26386-88-9) | [Storage Precautions]
Store under nitrogen |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T | [Risk Statements ]
R23/24/25:Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed .
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show label where possible) . | [RIDADR ]
UN 3278 6.1/PG 2
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [F ]
3-10 | [Hazard Note ]
Toxic/Keep Cold | [TSCA ]
No | [HazardClass ]
6.1 | [PackingGroup ]
III | [HS Code ]
29299000 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
Colorless to yellow liquid | [Uses]
Diphenylphosphonic azide acts as a reagent for the synthesis of peptides and phosphoramidates by reacting with amines. It is also used in the preparation of oligosaccharides linked with carbamate and urea bonds utilizing modified Curtis rearrangement. It is involved in pseudohalogen replacement of the azido group by treatment with nucleophilic reagents, such as water, butanol, ammonia, and various amines. Further, it is used as a hydroazidation catalyst for preparation of organoazides. | [Application]
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) is a well-known azide reagent used in peptide couplings, Curtius rearrangements, and Mitsunobu inversions—is often encountered in pharmaceutical process development because it enables the most direct route to a desired product. Diphenylphosphonic azide acts as a reagent for the synthesis of peptides and phosphoramidates by reacting with amines. It is also used in the preparation of oligosaccharides linked with carbamate and urea bonds utilizing modified Curtis rearrangement. It is involved in pseudohalogen replacement of the azido group by treatment with nucleophilic reagents, such as water, butanol, ammonia, and various amines. Further, it is used as a hydroazidation catalyst for preparation of organoazides. | [Preparation]
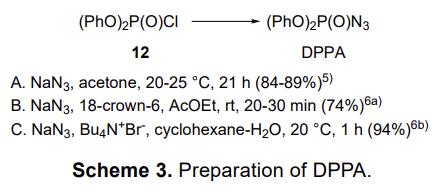
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) is easily prepared in high yield by the reaction of the corresponding chloride with sodium azide in acetone. Combination of sodium azide and 18-crown-6 in the same reaction was reported, and the use of a quaternary ammonium salt as a phase-transfer catalyst in a biphasic phase of water and an organic solvent was also reported to be effective, as shown in Scheme 3.
Diphenyl Phosphorazidate (DPPA) - More Than Three Decades Later
Takayuki Shioiri
Graduate School of Environmental and Human Sciences, Meijo University | [Reactions]
Diphenylphosphoryl azide, originally developed by Yamada in 1972, has shown significant synthetic versatility, being used in isocyanate synthesis, especially in the Curtius rearrangement, stereospecific conversion of alcohol into azide, as a coupling reagent in macrolactamization[4], in allylic amine synthesis, and in aziridination reactions. Diphenylphosphoryl azide, also called DPPA, diphenyl phosphorazidate or phosphoric acid diphenyl ester azide, is a colorless liquid with high boiling point (157 °C/0.17 mmHg), and can be easily prepared by the reaction between diphenylphosphoryl chloride and sodium azide in acetone in high yield. The Waldvogel group developed a reliable protocol for the large-scale (100 g) synthesis of DPPA, including purification by reduced-pressure distillation (Picture 1). A polymer-supported form of the reagent has also been developed using phenol resin by the Taylor group.
 | [reaction suitability]
reaction type: click chemistry | [Mechanism of action]
Diphenyl phosphoryl azide is used in the aziridination of olefins catalyzed by colbalt-tetraphenylporphyrin. It is also used as the activating agent in the preparation of macrocyclic lactams and of an aldose reductase inhibitor.
|
|
|