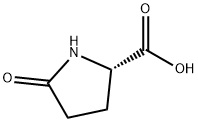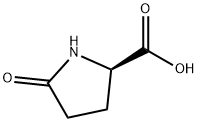
D-Pyroglutamic acid synthesis
- Product Name:D-Pyroglutamic acid
- CAS Number:4042-36-8
- Molecular formula:C5H7NO3
- Molecular Weight:129.11
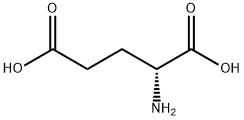
6893-26-1
465 suppliers
$6.00/10g

4042-36-8
394 suppliers
$6.00/5g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with D-glutamate cyclase from mouse in methanol; pH=8 at 37; for 1 h;Kinetics;Enzymatic reaction;
Steps:
2.4. Enzyme activity assays
The catalytic activity of DGLUCY was determined by measuring theformation of 5-oxo-D-Pro from D-Glu as described previously [1] withsome modifications. Specifically, an appropriate amount (100 μg) ofpurified enzyme was added to a reaction mixture (at a final concentrationof ~10 μM) containing 50mM borate buffer (pH 8.0), 1mMdithiothreitol and 10mM D-Glu in a final volume of 150 μL. The reactionmixture was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min prior to addition of600 μL methanol to stop the reaction. The mixture was incubated at-80 °C for 1 h and centrifuged at 20,000×g for 10 min at 4 °C to removeprecipitated proteins. The supernatant (600 μL) was then filteredthrough a 0.45 μm Millex-LH filter (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA), and a100 μL aliquot of the filtrate was evaporated to dryness. Subsequently, a65 μL aliquot of 2-propanol was added to the residue to dissolve 5-oxo-D-Pro but not D-Glu, and the suspension was vigorously vortexed for20 s, sonicated in a water bath for 5 min and vigorously vortexed foranother 20 s to extract the 5-oxo-D-Pro product. The suspension wasthen centrifuged at 20,000×g for 5 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant(60 μL) was transferred to a fresh 1.5 mL microtube. The original pelletwas then vigorously vortexed in 65 μL 2-propanol again for 20 s to further extract the 5-oxo-D-Pro product. The suspension was then centrifugedat 20,000×g for 5 min at 4 °C and the supernatant (60 μL) wastransferred to a fresh 1.5 mL microtube. The extraction procedure wasrepeated one more time and supernatants were combined. The combined180 μL supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm Millex-LHfilter, and an 80 μL aliquot of the filtrate was mixed with 100 μL of10mM L-Trp-OMe in acetonitrile/methanol (90:10 v/v) and 20 μL of50mM EDC in acetonitrile/methanol (90:10 v/v) to derivatise aminoacids in the mixture (Fig. 1B). After incubation at 65 °C for 1 h, thesolution was filtered through a 0.45 μm Millex-LH filter, and a 5 μLsample was injected into a Jasco chromatographic system comprising amodel PU-2089 pump, a model UV-2075 UV-visible detector and amodel 807-IT integrator (Jasco Corp., Tokyo, Japan). Amino acid derivativeswere then separated on an octadecylsilyl silica gel column(Mightysil RP-18GP, 150×4.6mm internal diameter; Kanto ChemicalCo., Tokyo, Japan) with isocratic elution at a flow rate of 1 mL/min.The mobile phase comprised 50mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.0)/methanol (72:28 v/v), and spectrophotometric determination wasperformed at 278 nm. The amount of 5-oxo-D-Pro was determined fromthe peak area in the chromatogram. Under these conditions, similarchromatograms to those reported in our previous study [1] were obtained,and 5-oxo-D-Pro was clearly separated from 5-oxo-L-Pro(Fig. 1C-E). To verify the formation of 5-oxo-D-Pro from D-Glu, thefraction corresponding to the 5-oxo-D-Pro peak was isolated and evaporatedto dryness, and a sample of the residue was dissolved in 50 μLdistilled water and subjected to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry(LC-MS) analysis using a JMS-T100LP time-of-flight mass spectrometer(JEOL Ltd, Tokyo, Japan) connected to a 1200 Series LCsystem (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clare, CA, USA). An octadecylsilylsilica gel column (Capcell Core C18, 50 × 2.1 mm internal diameter;Osaka Soda, Osaka, Japan) was used at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min, witha gradient comprising solution A (acetonitrile containing 0.1% [v/v]formic acid) and solution B (distilled water containing 0.1% [v/v]formic acid) as follows: 0-8 min, 5%-100% solution A; 8-10 min, 100%solution A. MS analysis was performed in positive ion mode, and cationicforms of the derivatised product, [M + H]+ and [M + Na]+ (m/z=330.1434 and 352.1269, respectively), were observed in the massspectrum (Fig. 1F), confirming the identity of 5-oxo-D-Pro.
References:
Katane, Masumi;Ariyoshi, Makoto;Tateishi, Shuhei;Koiwai, Sachi;Takaku, Kaoruko;Nagai, Kenichiro;Nakayama, Kazuki;Saitoh, Yasuaki;Miyamoto, Tetsuya;Sekine, Masae;Mita, Masashi;Hamase, Kenji;Matoba, Satoaki;Homma, Hiroshi [Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,2018,vol. 654,p. 10 - 18]
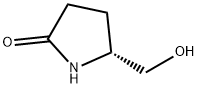
66673-40-3
231 suppliers
$5.00/250mg

4042-36-8
394 suppliers
$6.00/5g
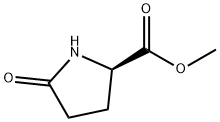
64700-65-8
85 suppliers
$27.50/1g

4042-36-8
394 suppliers
$6.00/5g
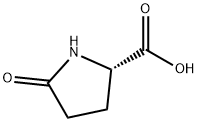
98-79-3
617 suppliers
$5.00/25g

4042-36-8
394 suppliers
$6.00/5g