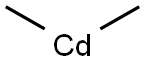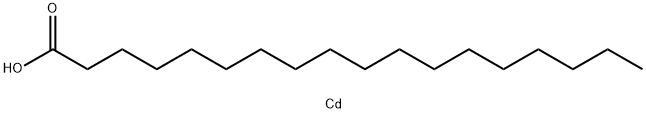
Cadmium stearate synthesis
- Product Name:Cadmium stearate
- CAS Number:2223-93-0
- Molecular formula:C18H36CdO2
- Molecular Weight:396.9
Yield: 96.3%
Reaction Conditions:
in benzene
Steps:
5
Example 5 Synthesis of Cd(Stearate)2 ; Within the glove box, a 500 mL three-neck round bottom flask was loaded with a stir bar and approximately 29.6 mmoles of Stearic Acid (8.4150 g). A glass stopper was connected to one neck, a 45 degree medium grain scintered frit with a 300 mL one-neck round bottom flask was connected to another neck and finally a high-vacuum line adapter was connected to the third neck. The reaction vessel was removed from glove box and immediately connected to the high-vacuum line. After a vacuum was established, approximately 200-250 mL of dry benzene was distilled into the reaction flask. Then the flask was transferred to a Schlenk line and backfilled with Argon. The glass stopper was replaced with a reflux condenser and the high-vacuum line adapter was replaced with a pressure-equalizing addition funnel capped with a rubber septa. The entire time an argon rich atmosphere was maintained, the exclusion of water and oxygen was the main priority. Before starting the reaction, a mark was placed on the pressure-equalizing addition funnel measuring 28 ml. Then via cannula transfer, about 28 mL of CdMe2 (14.0 mmoles) was added to the addition funnel. Once completed, the CdMe2 solution was slowly added to the reaction mixture over a period of 30-45 minutes. Throughout the addition the evolution of a gas is evident (Methane). Upon complete addition of the CdMe2 solution, the reaction vessel was set-up back to the original condition with high-vacuum line adapter and glass stopper and continuously stirred under a mild argon bubble. After 2 hours of stirring, a slight vacuum was established on the Schlenk line. Then the entire apparatus was place on the high-vacuum line where approximately half of the solvent was removed via flask to flask distillation. Then the resulting reaction mixture was filtered through frit and the volatile components were distilled back onto the crude product. This was repeated for a total of three times. Once completed, the remaining volatile components were removed on the high-vacuum line via flask to flask distillation. The product was left under dynamic vacuum overnight at which point the fine white powder was taken into the glove box and used. Yield 96.3%, 1H NMR (d6-benzene) T 55° C.: δ 7.15 (benzene), δ 2.04 (br, 2H), δ 1.49 (br, 2H), δ 1.29 (br, 20H), δ 0.903 (br, 3H).
References:
Lucey, Derrick W.;MacRae, David J.;Prasad, Paras N.;Beachley, Orville T. US2007/49765, 2007, A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 6

57-11-4
1230 suppliers
$6.00/100g
10108-64-2
186 suppliers
$10.00/5g

2223-93-0
136 suppliers
inquiry

543-90-8
131 suppliers
$60.00/25 gm

57-11-4
1230 suppliers
$6.00/100g

2223-93-0
136 suppliers
inquiry

57-11-4
1230 suppliers
$6.00/100g
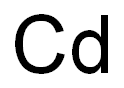
7440-43-9
234 suppliers
$34.00/50g

2223-93-0
136 suppliers
inquiry