Silane Reduction of Ketones
Nov 25,2022
Silanes have been used for the reduction of ketones to alcohols with excellent results. The reduction of ketones or aldehydes in the presence of acetonitrile and an acid provides an alkyl acetamide. The comparable reduction of aldehydes to alkyl acetamides is also possible.

In a similar manner, the reduction of ketones and aldehydes to esters has been reported. This reaction is always accompanied with the formation of the symmetrical ether.

The reduction of aryl ketones (acetophenone derivatives) to the methylene is readily accomplished. Triethylsilane with titanium tetrachloride works best for this transformation, though other systems also work well.

The selective reduction of aryl ketones to alcohols over dialkyl ketones can be carried out with phenyldimethylsilane in the presence of cuprous chloride or cuprous acetate. Cyclic ethers can be formed in the reduction of diketones or hydroxyketones. Epoxy ketones can lead to ethers as well.

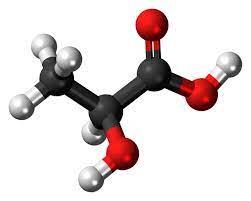
The reductive halogenation of ketones has been shown. Thus, acetophenone derivatives are converted to benzylic halides. An ynone was converted to the propargyl chloride in good yield.
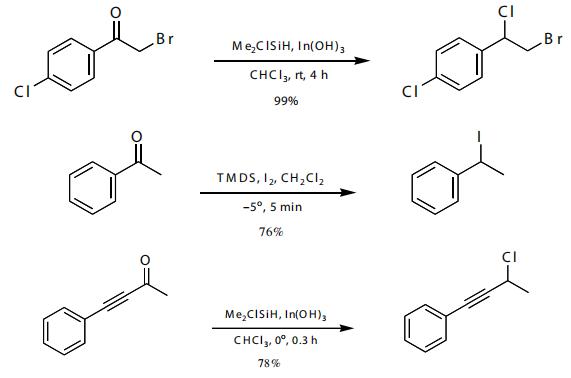
The reduction of aliphatic ketones to the methylene is best accomplished with the tris(pentaflfl uorophenyl)borane catalyst.
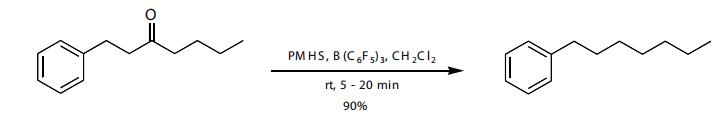
Dimethyl(diethylamino)silane served as the reducing agent and the amine source in the reductive amination of acetophenone.
The reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones can occur in a 1,2- or 1,4-fashion.
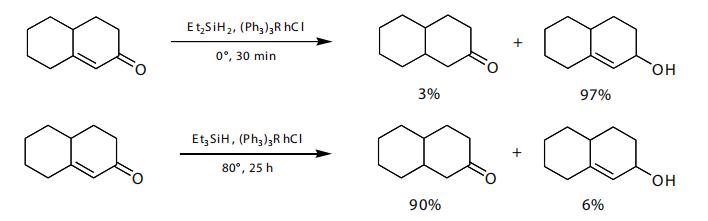
Some selectivity was seen in the reduction of an enone in the presence of a ketal and an acid, allyl alcohol, and halide.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion