Pyrimidine is a six-membered aromatic heterocyclic compound containing two nitrogen atoms on meta-position. Due to the conjugated double bonds pyrimidine has a special UV spectrum. Pyrimidine is a colorless crystal, the melting point of which is 22 ℃. It’s soluble in water. It’s a weaker alkaline than pyridine so that it’s less prone to electrophilic substitution reactions than pyridine, but more prone to nucleophilic substitution. Pyrimidine derivatives are widely distributed in nature, e.g. vitamin B1, uracil, thymine, and cytosine contain the pyrimidine structure.
Nucleic acid contains several important pyrimidine derivatives as important bases.
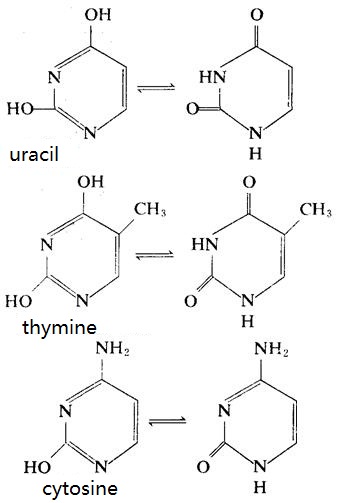
DNA mainly contains cytosine and thymine and RNA mainly contains cytosine and uracil. Some nucleic acids also contain a small amount of pyrimidine modified bases, for example:

Pyrimidine base is one of the chemical compositions of nucleotides, consisting of carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and other elements. Pyrimidine bases include uracil, cytosine and thymine, wherein cytosine and uracil constitute the bases in ribonucleic acid molecule, thymine and cytosine bases constituting the DNA molecule. Pyrimidine base has a strong absorption of ultraviolet light of 250 ~ 280nm. The synthesis raw materials originate from carbamoyl phosphate and aspartic acid. Pyrimidine base can be metabolized into carbon dioxide, β-alanine and βammonia isobutyrate and other substances. Due to congenital factors or taking certain medications, some patients suffer from metabolic disorder of pyrimidine bases, which causes orotic aciduria.