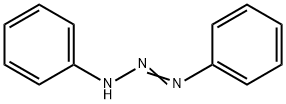
1,3-??????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
Diazoaminobenzene (DAAB) is an aromatic amine that is
a suspected carcinogen. It is harmful if inhaled, ingested, or
absorbed through the skin. It causes skin irritation and severe
irritation to eyes. DAAB can be made by diazotizing aniline
dissolved in hydrochloric acid with sodium nitrite and then
adding a concentrated solution of sodium acetate. DAAB is
listed in the US Environmental Protection Agency’s Toxic
Substances Control Act Inventory. DAAB has three major use
areas: intermediate, complexing agent, and polymer additive.
Use as an intermediate is reported in several industry sectors,
including organic synthesis, dye manufacture, and agrochemical
manufacture (insecticides). DAAB is also a versatile metal
complexing agent. A series of metabolism studies in rodents
and human liver slices, electron spin resonance spectroscopy
studies, short-term dermal toxicity studies in rodents, and acute
bone marrow micronucleus studies in mice demonstrated that
DAAB is metabolized and shares similar genotoxic and toxicological
properties to the known human carcinogen, benzene,
and the known rodent carcinogen, aniline.
??? ??
ochre powder
??
Diazoaminobenzene is used as a chemical intermediate, complexing agent, and polymer additive (Mathews and De Costa 1999). It has uses associated with organic synthesis and dye and insecticide manufacture (Lewis 1997), and it is an effective dopant for laser ablation (micro-machining) of polymethylmethacrylate (Bolle et al. 1990). Diazoaminobenzene has been identified as a low-level contaminant in the dyes D&C red no. 33, FD&C yellow no. 5 (tartrazine), and FD&C yellow no. 6; all three are permitted for use in drugs and cosmetics, and the latter two are permitted in food (FDA 2010).
?? ??
Orange solid.
??? ?? ??
Dust can be explosive when suspended in air at specific concentrations. Insoluble in water.
?? ???
1,3-DIPHENYLTRIAZENE is an azo compound. Azo, diazo, azido compounds can detonate. This applies in particular to organic azides that have been sensitized by the addition of metal salts or strong acids. Toxic gases are formed by mixing materials of this class with acids, aldehydes, amides, carbamates, cyanides, inorganic fluorides, halogenated organics, isocyanates, ketones, metals, nitrides, peroxides, phenols, epoxides, acyl halides, and strong oxidizing or reducing agents. Flammable gases are formed by mixing materials in this group with alkali metals. Explosive combination can occur with strong oxidizing agents, metal salts, peroxides, and sulfides. 1,3-DIPHENYLTRIAZENE explodes when heated to above 150°C. A mixture of the triazine and acetic anhydride exploded violently upon warming, Ber., 1891, 24, 4160.
????
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: 1,3-DIPHENYLTRIAZENE may explode if subjected to severe shock or heat.
????
Flash point data for 1,3-DIPHENYLTRIAZENE are not available, however, 1,3-DIPHENYLTRIAZENE is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Questionable
carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic
data. Mutation data reported. Strongly
explosive when shocked or heated to 98'C.
Mixture with acetic anhydride explodes
when warmed. When heated to
decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx,.
Carcinogenicity
Diazoaminobenzene is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on (1) evidence from studies in experimental animals andwith human tissue demonstrating that diazoaminobenzene is metabolized to benzene, a known human carcinogen, and (2) evidence that diazoaminobenzene causes genetic damage. Studies in rats and mice have shown that the metabolism of diazoaminobenzene to benzene is quantitative. Benzene was listed in the First Annual Report onCarcinogens in 1980 based on human epidemiological studies dem-causes cancer at numerous tissue sites in rodents.
????
DAAB is a respiratory tract, skin, and eye irritant. DAAB yields
benzene and aniline as metabolites. The proposed metabolic
pathway forDAAB is that it is cleaved reductively by liver enzymes
or gut flora to form aniline, benzene, and nitrogen. DAAB
metabolism also results in the formation of a reactive phenyl
radical, which could account for an additional risk of toxicity or
carcinogenicity. The erythrocyte and lymphoid systems are major
targets of DAAB toxicity. Induction of lymphoid atrophy of the
thymus and other lymphoid tissues were observed, as well as
methemoglobin formation, accompanying anemia, increased
spleen weights, and regenerative hematopoiesis. Analysis of
organ weights indicated possible chemical-related effects in the
thymus, heart, spleen, kidney, and liver of rats and/or mice.
Increases in the incidences of several skin lesions, including
hyperplasia of the epidermis and hair follicles, and inflammation
in rats and mice and ulceration in female mice were observed.
1,3-??????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??