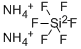????? ??? C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
Ammonium hexafluorosilicate is a white crystalline
powder. Odorless.
??? ??
d 2.01 g cm?3; decomposes prior to melting;
odorless.
??
Ammonium hexafluorosilicate is used as a disinfectant and analytical reagent. It finds application in etching glass, metal casting, and electroplating. It is also employed as a wood preservative agent and mothproofing agent in textiles. It plays a useful application in soldering flux. It is also used to arrest caries treatment without discoloration on demineralized primary tooth enamel.
?? ??
By reacting crude quartz with ammonium fluoride or ammonium hydrodifluoride or a mixture thereof in an aqueous medium when heated from 50 ° to 110 ° C. to form ammonium hexafluorosilicate, separating it from unreacted quartz and insoluble impurities by known methods (filtration or centrifugation) and subsequent concentration and cooling of the mother liquor for crystallization of Ammonium hexafluorosilicate.
?? ??
A white crystalline solid. Noncombustible. Corrodes aluminum. Used as a disinfectant, in etching glass, metal casting, and electroplating.
??? ?? ??
Water soluble.
?? ???
Salts, basic, such as Ammonium hexafluorosilicate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible.
???
Very toxic; fatal.
????
Inhalation of dust can cause pulmonary irritation and can be fatal in some cases. Ingestion may be fatal. Contact with dust causes irritation of eyes and irritation or ulceration of skin.
????
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating hydrogen fluoride, silicon tetrafluoride, and oxides of nitrogen may form in fires.
??? ??
This material is used as a pesticide
and miticide, wood preservative, soldering flux; light metal
casting; and in the etching of glass.
?? ??
UN2856 Fluorosilicates, n.o.s., Hazard Class:
6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name
Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the salt from water (2mL/g). After 3 recrystallisations, the Technical grade salt has Li, Na, K and Fe at 0.3, 0.2, 0.1 and 1.0 ppm respectively.
? ???
Aqueous solution is highly corrosive.
Contact with acids reacts to form hydrogen fluoride,
which is a highly corrosive and forms a toxic gas.
Corrosive to aluminum. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates,
nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates,
chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires
or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong
bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Ammonium fluorosilicate
reacts with water to form
hydrofluoric acid, a source of fluoride ions. Unlike other
halide ions, the fluoride ion is highly reactive, acting as a
weak base and participating in some unique reactions. In
particular, fluorides react strongly with compounds containing
calcium, magnesium, or silicon ions, which means
that solutions containing soluble fluorides are corrosive to
both living tissue and glass. Hydrofluoric acid can cause
severe chemical burns and is one of the few materials that
can etch glass. It is also a toxic gas in its anhydrous
form.
??? ??
Consult with environmental
regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal
practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant
(≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing
storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Incineration.
????? ??? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??