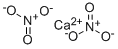Calcium nitrate
- CAS No.
- 10124-37-5
- Chemical Name:
- Calcium nitrate
- Synonyms
- CA(NO3)2;Calcium nitrate anhydrous;synfat1006;nitrocalcite;Calciumnitrat;limesaltpeter;norgesaltpeter;norwaysaltpeter;CALCIUM NITRATE;calciumsaltpeter
- CBNumber:
- CB4315083
- Molecular Formula:
- CaN2O6
- Molecular Weight:
- 164.09
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00010899
- MOL File:
- 10124-37-5.mol
| Melting point | 561°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 130-140 °C |
| Density | 2.36 |
| solubility | soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone |
| form | Liquid |
| color | white cubic crystals, crystalline; hygroscopic |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| LogP | -0.129 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10124-37-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Indirect Additives used in Food Contact Substances | CALCIUM NITRATE |
| FDA 21 CFR | 175.105 |
| FDA UNII | NF52F38N1N |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium nitrate (10124-37-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H319-H315 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313P-P264-P280-P302+P352-P321-P332+P313-P362 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38-36/38 |
| Safety Statements | 24/25-36/37-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 1454 |
| WGK Germany | - |
| HazardClass | 5.1 |
| PackingGroup | III |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 10124-37-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Calcium nitrate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Calcium nitrate has the molecular formula of
Ca(NO3)2 and the molecular weight of 164.0935 g/mol.
Its CAS number is 10124-37-5. Calcium nitrate may be
prepared by the reaction of nitric acid with calcium
carbonate or calcium sulfide:
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 ? Ca(NO3)2 + CO +H2O
CaS + 2HNO3 ? Ca(NO3)2 +H2S
It is very soluble and forms a tetrahydrate, Ca(NO3)
2·4H2O if the solution is evaporated to dryness.
The CAS number of the anhydrate is 10124-37-5 while
that of the tetrahydrate is 13477-34-4. As with the beryllium
nitrate salts, variation of the nitric acid concentration
affects the type of hydrate produced. The
trihydrate is known (CAS number 10124-37-5) but not
the monohydrate. The anhydrate is a white cubic crystal
that is hygroscopic; its density is 2.504 g/cm3 and it
melts at 561°C. This salt is highly soluble in water and
also dissolves in alcohols and acetone. The tetrahydrate
melts in its own waters of hydration at 42.7°C and loses
4H2O molecules at 132°C. It decomposes to form
nitrogen oxides and CaO similar to the behavior of the
other alkaline earth nitrates. The anhydrous salt is
soluble at 121.2 g/100 ml at 20°C and 271.2 g/100 ml
at 40°C.
Chemical Properties
White, deliquescent mass. Soluble in water, alcohol, and acetone.
Physical properties
White cubic crystal; hygroscopic; density 2.50g/cm3; melts at 561°C; highly soluble in water; also dissolves in alcohols and acetone.
Uses
Calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2] is known as Norwegian saltpeter. It is a strong oxidizer (because of the NO3) that is flammable in the presence of organic materials (such as hands). It explodes when given a hard shock. It is used in fireworks, matches, and fertilizers.
Uses
Calcium nitrate is mainly used as a component in fertilizers. Nitrocalcite is the name for a mineral which is a hydrated calcium nitrate that forms as an efflorescence in places where manure contacts limestone (or concrete) in a dry environment such as caverns or stables.Calcium nitrate is used in explosives, matches and pyrotechnics. Other applications are in the manufacture of incandescent mantle; and as an additive to diesel fuel for corrosion inhibition.This calciumnitrate is useful as an oxidizer but its hygroscopic nature, results in extreme deliquescence in air. Calcium nitrate is mainly used as a flocculent in rubber latex and in refrigerant manufacture. And it is also employed in oil exploratory wells and sewage treatment. In agriculture, it is used in hydroponic culture and as a fast-effective fertilizer for acid soil. It can also be used to make fireworks, to produce explosives in national defense industry, and to paint negative poles in the electronic instrument industry. It is also a raw material in making other nitrates. It is this usage that calcium nitrate finds most of its employment in industry, other than its use in agriculture. Calcium nitrate is a strong oxidizing agent. Mixing it with organic substances such as fuel oil or hydrocarbons or other oxidizable compounds can cause an explosion. Calcium nitrate has been evaluated as a component for heat storage devices.
Uses
In explosives, fertilizers, matches, pyrotechnics; manufacture of incandescent mantles, radio tubes, HNO3; corrosion inhibitor in diesel fuels.
Definition
calcium nitrate: A white deliquescentcompound, Ca(NO3)2, that isvery soluble in water; cubic; r.d. 2.50;m.p. 561°C. It can be prepared byneutralizing nitric acid with calciumcarbonate and crystallizing it fromsolution as the tetrahydrateCa(NO3)2.4H2O, which exists in twomonoclinic crystalline forms (α, r.d.1.9; β, r.d. 1.82). There is also a trihydrate,Ca(NO3)2.3H2O. The anhydroussalt can be obtained from the hydrateby heating but it decomposeson strong heating to give the oxide,nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen. Calciumnitrate is sometimes used as anitrogenous fertilizer.
Definition
ChEBI: Inorganic nitrate salt of calcium.
Preparation
Calcium nitrate may be prepared by the reaction of nitric acid with calcium carbonate or calcium sulfide:
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 →Ca(NO3)2 + CO + H2O
CaS + 2HNO3 →Ca(NO3)2 + H2S
General Description
White to light gray granular solid. May be either the anhydrous compound or the tetrahydrate. Used in fertilizers, explosives and pyrotechnics.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
An oxidizing agent. Noncombustible but accelerates the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in the fire or the combustible material is finely divided an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. May explode if shocked or heated [Hawley]. Heating causes release of toxic oxides of nitrogen. Mixtures with alkyl esters may explode owing to the formation of alkyl nitrates; mixtures with phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick 1979 p. 108-109].
Hazard
Strong oxidizer, dangerous fire risk in con- tact with organic materials, may explode if shocked or heated.
Health Hazard
Dust causes mild irritation of eyes.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Nitrocalcite is another name for calcium nitrate. It was
the first chemical nitrogenous fertilizer to be marketed.
Nitro-carbonic process for calcium carbonate
In manufacturing nitrophosphate fertilizers by Odda
process, calcium nitrate is left behind in the solution. It is
highly hygroscopic and is thus very inconvenient to use
as a fertilizer. It has, therefore, to be removed or
modified to some other form, which is done by the nitrocarbonic
process. The process converts calcium nitrate to
calcium carbonate by injecting carbon dioxide into the
calcium nitrate solution.
Agricultural Uses
Calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2], also known as lime nitrate,
nitrocalcite, lime saltpeter and Norwegian saltpeter,
was the first chemical nitrogenous fertilizer to be
marketed.
Calcium nitrate fertilizer absorbs considerable
amount of water, which makes it somewhat difficult to
handle. It contains 15 % nitrogen and 21 % calcium. In a
prilled form, it becomes suitable for bulk mixing and the
powdered form is useful in sprays.
Calcium nitrate controls the blossom-end rot of
tomatoes and is used in Europe as a major source of
nitrogen.
Calcium nitrate used on saline soils displaces sodium
with calcium. In addition, calcium nitrate is a non-acid
forming fertilizer and improves physical properties of
acidic and exhausted soils. However, its advantage as a
fertilizer is offset by its extreme hygroscopic nature. This
calls for its production in air-conditioned plants and the
use of sealed moisture proof bags.
Calcium nitrate, in addition to its usage as a fertilizer,
finds application in explosives, pyrotechnics, and
inorganic chemical operations.
Safety Profile
A poison by ingestion. An irritant. A strong oxidant. Forms powerfully explosive mixtures with aluminum + ammonium nitrate + formamide + water, ammonium nitrate + hydrocarbon oils, ammonium nitrate + water-soluble fuels, and organic materials. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also NITRATES and CALCIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
It is used to make explosives, fertilizers, matches, fireworks, and other industrial products.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heartaction has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility.When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Donot make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: Treat for methemoglobinemia.Spectrophotometry may be required for precise determination of levels of methemoglobin in urine.
storage
lor Code—Yellow: Reactive Hazard; Store in alocation separate from other materials, especially flam?mables and combustibles. Prior to working with Calcium540 Calcium nitratenitrate you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from flammables (such as fuel) orcombustibles (such as wood, paper, and oil). Calciumnitrate may explode if shocked or heated. See OSHAStandard 1910.104 and NFPA 43A Code for the Storage ofLiquid and Solid Oxidizers for detailed handling and storageregulations.
Shipping
Calcium nitrate must be labeled“OXIDIZER.” It falls in Hazard Class 5.1 and PackingGroup III.
Incompatibilities
A strong oxidizer. Incompatible withcombustible materials, reducing agents, organics and otheroxidizable materials, chemically active metals, aluminumnitrate, ammonium nitrate.