Malons?ure Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
WEISSE KRISTALLE.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Mittelstarke S?ure in w?ssriger L?sung. Reagiert mit starken Oxidationsmitteln.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2005).
MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation und durch Verschlucken.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfung bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine gesundheitssch?dliche Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch beim Dispergieren schnell erreicht werden.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz reizt die Haut und reizt stark die Augen und die Atemwege.
LECKAGE
Verschüttetes Material in abgedeckten Beh?ltern sammeln. Dann mit viel Wasser wegspülen.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R20/22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen und Verschlucken.
R41:Gefahr ernster Augensch?den.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
C3H4O4. Farbloses, feinkristallines Pulver, fast geruchlos. Hygroskopisch, feuchtigkeitsempfindlich und brennbar.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Gesundheitsschädlich beim Verschlucken. Reizt die Augen, Haut und Schleimhäute.
Zersetzung oberhalb 140鳦 unter Freisetzung von Essigsäure.
LD50 (oral, Ratte) 1310 mg/kg
Nicht ins Abwasser gelangen lassen.
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Lagerung trocken unter 15鳦.
Schutzhandschuhe als kurzzeitiger Staubschutz.
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Staubentwicklung und Substanzkontakt vermeiden. Trocken aufnehmen. Der Entsorgung zuführen. Nachreinigen.
Kohlendioxid, Wassernebel, Pulver, Schaum.
Brennbar.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser abwaschen.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser bei geöffnetem Lidspalt mindestens 10 Minuten ausspülen. Augenarzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft.
Nach Verschlucken: Viel Wasser trinken lassen, Erbrechen auslösen. Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung entfernen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
In Wasser lösen, neutralisieren, dann in wässrige Lösemittelabfälle.
Beschreibung
Malonic acid (MA), also known as propanedioic acid, is a dicarboxylic acid with structure CH2(COOH)2. It have three kinds of crystal forms, of which two are triclinic, and one is monoclinic. That crystallized from ethanol is white triclinic crystals.It decomposes to acetic acid and carbon dioxide at 140℃. It does not decompose at 1.067×103~1.333×103Pa vacuum, but directly sublimates. The ionised form of malonic acid, as well as its esters and salts, are known as malonates. For example, diethyl malonate is malonic acid's ethyl ester. The name originates from Latin malum, meaning apple.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Malonic acid is a white crystalline solid that decomposes at approximately 135°C. It has high solubility in water and oxygenated solvents and exhibits greater acidity than acetic acid, which has a pK value of 4.75. The pKa values for the loss of its first and second protons are 2.83 and 5.69, respectively. It is slightly soluble in pyridine. It can decompose to formic acid and carbon dioxide in case of potassium permanganate. Since that malonic acid generates carbon dioxide and water after heated without pollution problems, it can be directly used as aluminum surface treatment agent.
Verwenden
Malonic acid is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of barbiturates and other pharmaceuticals. It is a component used as a stabilizer in many high-end cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Malonic acid is also used as building block in chemical synthesis, specifically to introduce the molecular group -CH2-COOH. It is used for the introduction of an acetic acid moiety under mild conditions by Knoevenagel condensation and subsequent decarboxylation.
Definition
ChEBI: Malonic acid is an alpha,omega-dicarboxylic acid in which the two carboxy groups are separated by a single methylene group. It has a role as a human metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a malonate(1-).
synthetische
Malonic acid is usually produced from chloroacetic acid.
Reaction: The chloroacetic acid is added to the reaction kettle by adding sodium carbonate aqueous solution to generate sodium chloroacetate aqueous solution, and then 30% sodium cyanide solution is slowly added dropwise, and the reaction is carried out at a predetermined temperature to generate sodium cyanoacetate. After the cyanation reaction is completed, add sodium hydroxide for heating and hydrolysis to generate sodium malonate solution, concentrate, then dropwise add sulfuric acid for acidification to generate malonic acid, filter and dry to obtain the product.
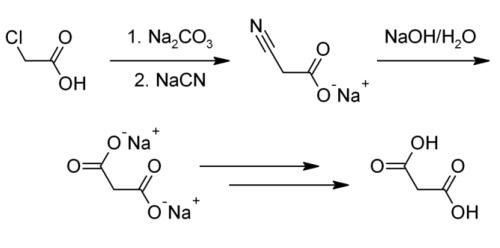
This method often does not produce a pure enough product or the pure product has an extremely low yield. Industrially, malonic acid is also produced by hydrolyzing dimethyl malonate or diethyl malonate. This manufacturing method is able to bring about a higher yield and purity, but the organic synthesis of malonic acid through these processes is extremely costly and environmentally hazardous.
Application
Malonic acid is acts as a building block in organic synthesis. It is also useful as a precursor for polyesters and alkyd resins, which is used in coating applications, thereby protecting against UV light, corrosion and oxidation. It acts as a cross linker in the coating industry and surgical adhesive. It finds application in the production of specialty chemicals, flavors and fragrances, polymer cross linkers and pharmaceuticals.
Reaktionen
In a well - known reaction, malonic acid condenses with urea to form barbituric acid. Malonic acid is also frequently used as an enolate in Knoevenagel condensations or condensed with acetone to form Meldrum's acid. The esters of malonic acid are also used as a - CH2COOH synthon in the malonic ester synthesis.
Biologische Funktion
Malonic acid is the classic example of a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (complex II), in the respiratory electron transport chain.It binds to the active site of the enzyme without reacting, competing with the usual substrate succinate but lacking the ?CH2CH2? group required for dehydrogenation. This observation was used to deduce the structure of the active site in succinate dehydrogenase.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
White crystals or crystalline powder. Sublimes in vacuum.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Water soluble.
Hazard
Strong irritant.
Brandgefahr
Flash point data for Malonic acid are not available; however, Malonic acid is probably combustible.
Biotechnological Applications
The calcium salt of malonic acid occurs in high concentrations in beetroot. It exists in its normal state as white crystals. Malonic acid is the classic example of a competitive inhibitor: It acts against succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) in the respiratory electron transport chain.
l?uterung methode
Crystallise malonic acid from *benzene/diethyl ether (1:1) containing 5% of pet ether (b 60-80o), wash with diethyl ether, then recrystallise it from H2O or acetone. Dry it under vacuum over conc H2SO4. [Beilstein 2 IV 1874.]
Malons?ure Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
4-(MORPHOLIN-4-YLMETHYL)-1,3-THIAZOL-2-AMINE
Diethylmesoxalat
3,4,5-Trimethoxyhydrozimtsure
Tartronsure
Methylnon-2-enoat
2',4',5'-Trimethoxycinnamsure
4-CHLORO-BETA-METHYL-Y-OXO-BENZENEBUTANOIC ACID
Decan-4-olid
5,5-Dimethylcyclohexan-1,3-dion
3-PYRIDIN-2-YL-PROPIONIC ACID H2SO4
(E)-4'-Hydroxy-3'-methoxycinnamsure
trans-Hex-3-ensure
4-BROMO-PYRAN-2-ONE
4-Hydroxy-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-3-carbonsure
6-METHOXY-2-OXO-2H-CHROMENE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID
3-(TRIFLUOROMETHOXY)CINNAMIC ACID
Diethylbutylmalonat
3,3-DIMETHOXYESTR-5(10)-ENE-17 B OL
3-AMINO-3-(2-THIENYL)PROPANOIC ACID
Diethyl(phenylacetyl)malonate
Antifreeze
Diethyl-(1-methylpropyl)malonat
4-ETHOXYCINNAMIC ACID
3',5'-Dimethoxycinnamsure
(1H-INDAZOL-3-YL)-ACETIC ACID
4-Fluorzimtsaeure
3-(2-METHYLPHENYL)PROPIONIC ACID
5-BROMO-2-FLUOROCINNAMIC ACID
3-(3-CHLOROPHENYL)PROPIONIC ACID
3-(p-Tolyl)propionsure
Diethyl butyrylmalonate
trans-3-Methoxyzimtsure
Diethylnitromalonat
3-Pyridinepropionic acid
3-(2-Furyl)acrylsure
3-(1-NAPHTHYL)-PROPIONIC ACID
2-Acetylbenzoesure
3-(3-METHYL-2-THIENYL)ACRYLIC ACID
3-Pyridylacrylsaeure
Diethyl-[(m-chloranilino)methylen]malonat

