Acetanilid Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S22:Staub nicht einatmen.
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
C8H9NO; Farb- und geruchlose Kristalle.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Acetanilid zersetzt sich mit Alkalien unter Bildung von Anilin. Als Zersetzungsprodukte können Stickoxide, Kohlenmonoxid und Kohlendioxid entstehen.
Acetanilid ist gesundheitsschädlich beim Verschlucken. Es ist geringer toxisch als Anilin, verursacht aber in hohen Dosen nach oraler oder inhalativer Einnahme die gleichen Symptome: Übelkeit, Bauchschmerzen, Krämpfe, Herzrhythmusstörungen, Cyanose infolge von Methämoglobinämie und als Folge davon zunehmende Atemnot, oft begleitet von zentralnervösen Erscheinungen. Dies führt bei höheren Dosen zu Kreislaufversagen und Koma. 4g können für den Menschen ttödlich wirken. Nach Hautkontakt sind Dermatitiden oder Ekzeme möglich. Bei der Aufnahme der Substanz über einen längeren Zeitraum kann es zu Blutbildveränderungen kommen.
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Gummi-Schutzhandschuhe (nur als kurzzeitiger Spritz- und Staubschutz).
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Verschüttetes Acetanilid ist vorsichtig mechanisch aufzunehmen und in dicht schließenden Gefäßen zu sammeln.
Wasser, Kohlendioxid, Schaum oder Trockenlöschmittel.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Sofort mit viel Wasser und Seife waschen, besser Reinigung mit PEG 300/Ethanol-Gemisch (2:1) oder PEG 400 und anschließende Spülung mit Wasser.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mindestens 15 Minuten mit reichlich Wasser spülen. Augenarzt ist hinzuziehen.
Nach Einatmen: Sofort an die frische Luft bringen.
Nach Verschlucken: Viel Wasser trinken lassen. Arzt ist hinzuziehen.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung sofort ausziehen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Als Sondermüll entsorgen.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Acetanilide, also known as Nphenylacetamide, acetanil, or acetanilide is a white to gray solid with molecular formula CH3CONHC6H5. It is an odorless colorless, glossy, crystalline powder or flakes. Acetanilide was the first aniline derivative found to possess analgesic as well as antipyretic properties and was quickly introduced into medical practice (Weast, 1981; Gnanasambandan et al., 2014). Later, it was established that in the human body it is mostly metabolized to paracetamol, this compound being responsible for the analgesic and antipyretic properties of acetanilide (Bertolini et al., 2006; Gnanasambandan et al., 2014). In addition, it was discovered that it has unacceptable toxic effects, so that acetanilide is no longer used as a drug.

Acetanilide is mainly used as an intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and dyes, as an additive for hydrogen peroxide and cellulose ester varnishes, and as a plasticizer in polymer industry as well as accelerator in the rubber industry.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
White glossy flake crystal or white crystalline powder. Slightly soluble in cold water, soluble in hot water, methanol, ethanol, ether, chloroform, acetone, glycerol and benzene.
History
The department of internal medicine at the University of Strassburg in the 1880s was noted for its investigations into intestinal worms. Adolf Kussmaul, the director, asked two young assistants, Arnold Cahn and Paul Hepp, to treat patients with naphthalene as it had been used elsewhere as an internal antiseptic. The young doctors were disappointed with the initial results, but Hepp persevered with the naphthalene treatment in a patient suffering from a variety of complaints besides worms. Surprisingly, the fever chart revealed a pronounced antipyretic effect from this treatment. This had not been observed before, but further investigation revealed that Hepp had wrongly been supplied by Kopp’s Pharmacy in Strassburg with acetanilide instead of naphthalene! Cahn and Hepp lost no time in publishing a report on their discovery of a new antipyretic.
For many years after its discovery in 1886, Acetanilide was used as an alternative to aspirin (i.e. acetyl salicylate) - an analgesic (painkiller) and antipyretic (fever reducing) drug to relieve e.g. headache, menstrual pain, and rheumatic pain. Under the name “Acetanilide” it formerly appeared in the formula of a number of patent medicines and over the counter drugs. In 1948, Julius Axelrod and Bernard Brodie discovered that Acetanilide is much more toxic in these applications than other drugs, causing methemoglobinemia and ultimately causing damage to the liver and kidneys. Thus, Acetanilide has largely been replaced by less toxic drugs, in particular acetaminophen (i.e. paracetamol), which is a metabolite of Acetanilide and whose use Axelrod and Brodie suggested in the same study.
Definition
ChEBI: Acetanilide is a member of the class of acetamides that is acetamide in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is substituted by a phenyl group. It has a role as an analgesic. It is a member of acetamides and an anilide. It is functionally related to an acetic acid.
Application
Acetanilide is used as an inhibitor of hydrogen peroxide decomposition and to stabilize cellulose ester varnishes. It is also used in the intermediation of rubber accelerator synthesis, dyes and dye intermediate synthesis, and camphor synthesis. Acetanilide is used for the production of 4-acetamidobenzenesulfonyl chloride, a key intermediate for the manufacture of the sulfa drugs. It is also a precursor in the synthesis of penicillin and other pharmaceuticals. In the 19th century acetanilide was one of a large number of compounds used as experimental photographic developers.
Acetanilide is used as a EOF (electroosmotic flow) marker in the studies of affinity capillary electrophoresis for drug–protein binding.
Acetanilide undergoes palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction to form ortho-acylacetanilide.
synthetische
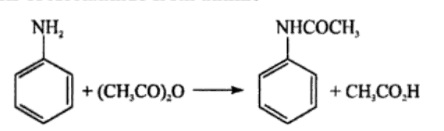
Acetanilide is prepared from aniline by acetylating it with acetic anhydride in presence of glacial acetic acid. Aniline reacts with acetic anhydride to form Acetanilide by nucleophilic substitution reaction and the reaction is called acetylation.
In a 100 ml round bottom flask fitted with a reflux condensor place 5ml of aniline and 10 ml of 1:1 acetic acid and acetic anhydride mixture (5ml acetic acid and 5 ml acetic anhydride). Heat the mixture gently under reflux for 15-20 minutes on oil bath and then pour the contents while still hot with stirring into a 200ml beaker containing 100ml ice cold water. Stir the mixture vigorously to hydrolyse the excess acetic anhydride. After all the acetanilide has precipitated, collct it on buchner funnel and wash with cold water. Recrystallise the crude product from boiling water. If the product is excessively coloured add a pinch of animal charcoal to hot water and filter hot through glass wool/ cotton plug. Pure colourless crystals of acetanilide melts at 114°C (5-5.5g).
Weltgesundheitsorganisation (WHO)
Acetanilide, a para-aminophenol derivative with analgesic,
antipyretic and weak antiinflammatory activity, was introduced into medicine in
1886. It subsequently proved to be excessively myelosuppressive and has been
superseded by safer alternatives.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Acetanilide is a white to gray solid. (NTP, 1992)
Air & Water Reaktionen
Acetanilide is sensitive to prolonged exposure to air . Water insoluble.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
Acetanilide is an amide. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Brandgefahr
Acetanilide is combustible.
m?gliche Exposition
This amide compound is used in rubber industry as accelerator, in plastics industry as cellulose ester stabilizer, in pharmaceutical manufacture, stabilizer for hydrogen peroxide, azo dye manufacture
Versand/Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
l?uterung methode
Recrystallise acetanilide from water, aqueous EtOH, *benzene or toluene. [Beilstein 12 IV 373.]
Inkompatibilit?ten
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, alkyl nitrates, alkalis (liberate aniline), chloral hydrate, phenols, ferric salts
Waste disposal
Add to flammable solvents (alcohol or benzene) and incinerate. Oxides of nitrogenmay be scrubbed from combustion gases with alkaline solution
Acetanilid Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Salazosulfapyridin
Sulfachinoralin
Disperse Blue 301
Asulam
2-Naphthacencarboxamid, 4-(Dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-, Monohydrochlorid, [4S-(4α,4aα,5α,5aα,6α,12aα)]-
m-Phenetidin
METHYL 4-(4-(BIS(2-HYDROXYETHYL)AMINO)PHENYL)BUTYRATE
Sulfanilamid
2-[(p-Aminophenyl)sulfonyl]ethylhydrogensulfat
2-[(4-Methyl-2-nitrophenyl)azo]-3-oxo-N-phenylbutyramid
4'-Aminoacetanilid
4'-Aminoacetophenon
4-Amino-3-nitrophenol
4-(4-Aminophenyl)butyric acid
METHYL 4-(4-(BIS(2-CHLOROETHYL)AMINO)PHENYL)BUTYRATE
9,9-Bis(4-aminophenyl)fluorene
2-MORPHOLIN-4-YL-1,3-THIAZOL-4(5H)-ONE
4-(4-IODO-PHENYL)-4-OXO-BUTYRIC ACID
4-Methoxy-N-phenyl-o-toluidin

