L-(+)-Ergothioneine Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
Beschreibung
L-
(+)-
Ergothioneine is a naturally-
occurring amino acid derived from histidine
via hercynine. Ergothioneine is a stable antioxidant that scavenges and detoxifies free radicals and oxidants, increases intracellular thiol levels, controls nuclear factor-
κB activation, and inhibits inflammatory gene expression. In addition, it inhibits the peroxynitrite-
dependent nitration of nitrotyrosine, blocks oxidative DNA damage and cell death, and prevents the formation of xanthine and hypoxanthine. Ergothioneine is transported by the organic cation/carnitine transporter 1, which has been linked with autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
Chemische Eigenschaften
White Solid
Origin
Ergothioneine was discovered in 1909 by Charles Tanret, a French pharmacist and chemist. Tanret was examining the ergot fungus, which had recently been responsible for destroying crops, and he discovered the compound by using a purification process. The amino acid name ergothioneine originates from this fungus. Though this discovery is relatively recent, scientists speculate that ergothioneine may have originated from ancient earth. Due to its anaerobic nature (it does not require oxygen to function), it may have manifested in the earth's oxygen-free atmosphere more than three billion years ago While ergothioneine is not classified as one of the nine essential amino acids.
benefits
L-(+)-Ergothioneine is a natural antioxidant, which has various physiological functions such as scavenging free radicals, detoxification, maintaining DNA biosynthesis, normal cell growth and cellular immunity.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
L-(+)-Ergothioneine (ERG) is a substance that cannot be synthesized by humans and must be obtained from food. It has cytoprotective and antioxidant properties.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
L-(+)-Ergothioneine (ET) is a sulfur-containing amino acid, which is only produced by
Actinomycetales bacteria and non-yeast like fungi belonging to the division
Basidiomycota and
Ascomycota. It was originally isolated from
Claviceps purpurea or rye ergot. It is obtained from L-histidine, which is converted into betaine form called hercynine. It is found in both animals and plants, and mammals usually obtain it from their diet, e.g. through mushrooms or oats. It is tautomeric in nature, and in neutral aqueous solution exists in thione form.
Synthese
L-(+)-Ergothioneine is prepared by the reaction of hercynine. The steps are as follows:
15g of compound was added to 150ml of water, and 15.6g of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added, add 10.9g dibromohydantoin, stir for 20min, add D-cysteine, Continue to stir for 1 hour, add sodium thiosulfate, raise the temperature to 90-100°C, and continue the reaction for 15 hours. After the reaction, cool down and filter, adjust the pH to neutral, desalt, concentrate, crystallize with 5ml of water and 75ml of isopropanol, and dissolve the solid Filter and dry at 70-80°C to obtain 88% ergothioneine product with a yield of 81%.
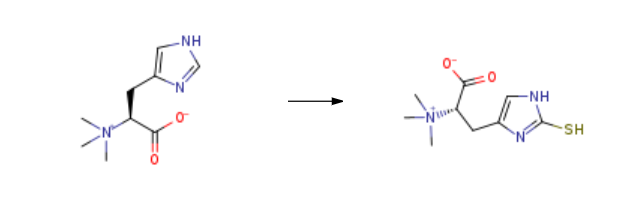
L-(+)-Ergothioneine Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

