5-Heptylresorcin Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
Verwenden
5-Heptylresorcinol and other alkylhydroxybenzenes have been used to study the protective effect in Saccharomyces cerevisiae against oxidative and radiation-caused damage.
Definition
5-Heptylresorcinol is one of the main volatile compounds present in F. japonicum stem oils (6.5%) which presented apparent antioxidant and antibacterial capacities[1]. It is a cannabinoid compound related to the structure of cannabinoids, which has been shown to have cannabinoid effects in animals and humans.
Synthese
To a solution of 1-heptyl-3,5-dimethoxy-Benzene (388 mg, 1.41 mmol) in dry CH2Cl2 (47 mL) at -78 °C under an argon atmosphere was added boron tribromide (3.4 mL, 1 M solution in CH2Cl2). Following this addition, the reaction temperature was gradually raised over a period of 3 h to 0 °C, and the stirring continued at that temperature until the reaction was completed (28 h). Unreacted boron tribromide was destroyed by adding methanol at -78 °C. The resulting mixture was warmed at room temperature and stirred for 40 min, and the volatiles were removed in vacuo. The residue was diluted with EtOAc and washed with saturated NaHCO3 solution, water, and brine. The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. Purification by flash column chromatography (45% diethyl etherpetroleum ether) afforded 340 mg (97% yield) of the compound as a slightly brown viscous oil: 5-Heptylresorcinol (. The synthesis was carried out as described for 5-Heptylresorcinol by using 15 (1.18 g, 5 mmol) and boron tribromide (11 mL, 11 mmol, 1 M solution in CH2Cl2) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (40 mL): yield 91% (0.95 g); slightly brown solid; mp 53-54 °C (lit.63 mp 55-56 °C); spectral and analytical data were reported previously.
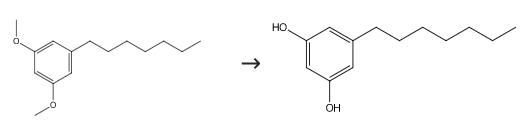
5-Heptylresorcin Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

