Strontiumcarbonat Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
WEISSES GERUCHLOSES PULVER.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Reagiert mit S?uren.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt.
MAK: IIb (nicht festgelegt, aber Informationen vorhanden) (DFG 2006).
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Eine bel?stigende Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann schnell erreicht werden.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Kann mechanische Reizungen der Augen und der Atemwege verursachen.
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
(Siehe ANMERKUNGEN.)
LECKAGE
Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t mit Partikelfilter entsprechend der Arbeitsplatzkonzentration des Stoffes. Verschüttetes Material in Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern.
Beschreibung
Strontium carbonate has the formula of SrCO
3 and
the molecular weight of 147.6326 g/mol. Strontium carbonate occurs in nature as the mineral “strontianite”. The name strontianite
comes from a famous location for the mineral,
Strontian, Scotland. Strontianite is strontium carbonate
as found naturally. It occurs as white or slightly gray orthorhombic
crystals with a refractive index of 1.518. The
unit-cell parameters are: a = 5.107 ? , b = 8.414 ? ,
c = 6.029 ? , Z = 4; V = 259.07 ? 3, Den(Calc) = 3.78. The
crystal system is orthorhombic with space group Pmcn
and point group 2/m, 2/m, 2/m. Strontium carbonate
has only one stable form (aragonite-type structure) and
temperature of precipitation has no effect on crystal
form, unlike that of calcium or magnesium carbonates.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Strontium carbonate is a milky white free flowing powder. It is little more insoluble (Ksol=10-8.8) than calcium carbonate (Ksol=10-8.07), so it should not be surprising that under appropriate conditions Sr2+ can be precipitated by biogenic carbonate.
Chemische Eigenschaften
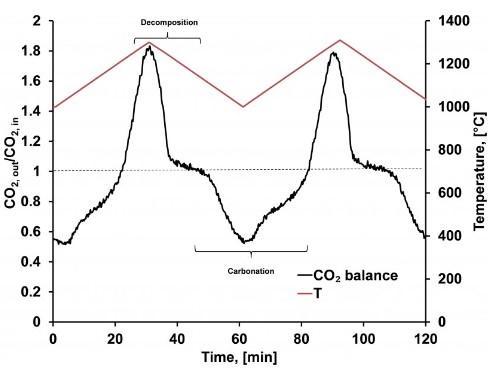
Heating strontium carbonate up from 1000°C to 1300°C causes the compound to undergo a decomposition reaction which results in the capture of thermal energy, shown here as the peak in the black curve occurring between Time = 20 and Time = 40 minutes. Cooling the system back down to 1000°C leads to reconstitution of the starting material in a carbonation reaction thereby releasing the stored thermal energy, a process shown as the valley in the black curve between Time = 50 and Time = 80 minutes.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
White orthorhombic crystals; refractive index 1.518; hygroscopic; hardness 3.5 Mohs; density 3.5 g/cm
3; insoluble in water; soluble in dilute acids with liberation of carbon dioxide.
Occurrence
Strontium carbonate occurs in nature as mineral strontianite. The compound is used in pyrotechnics and ceramic ferrites. It also is used in making iridescent glass for color television tubes. Other uses are in refining sugar and preparing other strontium salts.
Verwenden
Strontium carbonate (SrCO3) is used to make radiation-resistant glass and TV picture tubes, as well as pyrotechnics.
Definition
strontianite: A mineral form ofstrontium carbonate, SrCO
3.
synthetische
Strontium carbonate occurs in nature as strontianite
and can be mined from its deposit. It is, however,
usually made commercially from the mineral “celestite”.
Celestite is fused with sodium carbonate at elevated
temperatures or boiled with a solution of ammonium
carbonate.Strontium carbonate is insoluble in water. It precipitates
from the product mixture in the second reaction.
If fused with sodium carbonate, the product mixture is
leached with water. Insoluble carbonate separates from
the water-soluble sodium sulfate.
Vorbereitung Methode
Strontium carbonate, formed (1) by reaction of strontium salt solution and sodium carbonate or bicarbonate solution, (2) by reaction of strontium hydroxide solution and CO2. Strontium carbonate decomposes at 1,200 °C (2,192 °F) to form strontium oxide and CO2, and is dissolved by excess CO2, forming strontium bicarbonate, Sr(HCO3)2, solution.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Strontium carbonate is insoluble in water. It is used predominantly in producing other strontium salts.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Strontianite is a strontium carbonate mineral (SrCO
3). It is the original and principal source of strontium. It often occurs in white masses of radiating fibres, although pale green, yellow, or gray colours are also known. Strontianite forms soft, brittle crystals that are commonly associated with barite, celestine, and calcite in low-temperature veins. Strontianite is used in pyrotechnics to impart a red colour and in sugar refining as a clarifying agent.
Strontiumcarbonat Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

