Gabapentin enacarbil Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
Beschreibung
Gabapentin enacarbil (GEn) is an actively transported prodrug of gabapentin that provides sustained doseproportional exposure to gabapentin and predictable bioavailability. In April 2011, Gabapentin enacarbil is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of moderate-to-severe primary restless legssyndrome (RLS) in adults.
Gabapentin enacarbil was designed to be recognized as a substrate for two high-capacity nutrient transports, monocarboxylate transporter type 1 and sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter, and to be efficiently cleaved after absorption to give gabapentin. The separated enantiomers of gabapentin enacarbil have similar cleavage rates in human tissues. Preclinical studies showed that gabapentin enacarbil provides good systemic exposure of gabapentin in rats and monkeys.
Verwenden
Gabapentin enacarbil (HORIZANT GlaxoSmithKline/XenoPort) is a prodrug of gabapentin used as an anticonvulsant as well as a treatment for neurogenic pain, with the same mechanism of action as pregabalin.
Definition
ChEBI: A carbamate ester that is the N-[1-(isobutyryloxy)ethoxy]carbonyl derivative of [1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexyl]acetic acid. The prodrug for gabapentin, used for treatment of neuropathic pain and restless legs syndrome.
Pharmakokinetik
Gabapentin enacarbil is an acyloxyalkylcarbamate prodrug of analgesic and anticonvulsant drug gabapentin which has problematic pharmacokinetic properties, including short half-life, saturable absorption, high inter-patient variability, and lack of linear dose–response relationship. Gabapentin enacarbil was designed to be absorbed throughout the entire length of the gastrointestinal tract, and its absorption is mediated by high-capacity nutrient transporters, including monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT-1) and sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter (SMVT). Prodrug modification produced an extended release of gabapentin with twofold improved, more predictable, and dose-proportional oral bioavailability in humans. During and after its absorption, gabapentin enacarbil is efficiently hydrolyzed by nonspecific esterases to yield gabapentin. Currently, gabapentin enacarbil is commercially available for the treatment of restless legs syndrome and post-herpetic neuralgia of adults.
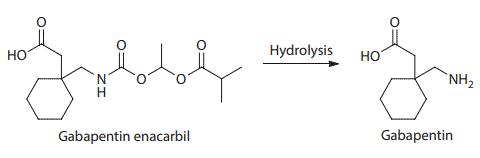
Structure and hydrolysis of gabapentin enacarbil to the active gabapentin
Clinical Use
Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin (Neurontin,
Pfizer) which binds to the a2-d subunit of L-type voltage-regulated
calcium channels, reducing the release of several neurotransmitters.
122,123 Gabapentin enacarbil was discovered at XenoPort, codeveloped
with GlaxoSmithKline, is marketed under the brand
name Horizant, and is approved for the treatment of moderate
to severe restless leg syndrome. Gabapentin enacarbil was designed
to increase the absorption of gabapentin through the interaction with sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter (SMVT)
and monocarboxylate transporter type 1 (MCT-1). As a result, the
drug demonstrated much better oral bioavailability and more consistent
exposure compared to the parent.
Gabapentin enacarbil Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

