75899-68-2
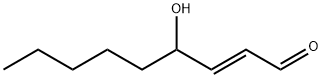 75899-68-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
75899-68-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報(bào)價(jià)日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號(hào) | 產(chǎn)品名稱(chēng) | CAS號(hào) | 包裝 | 價(jià)格 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-113466 | 4-羥基壬烯醛 4-Hydroxynonenal | 75899-68-2 | 1 mg | 480元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-113466 | 4-羥基壬烯醛 4-Hydroxynonenal | 75899-68-2 | 5 mg | 1200元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-113466 | 4-羥基壬烯醛 4-Hydroxynonenal | 75899-68-2 | 10 mM * 1 mLin DMSO | 1320元 |
常見(jiàn)問(wèn)題列表
|
Human Endogenous Metabolite
|
4-Hydroxynonenal is both a substrate and an inhibitor of ALDH2; inhibition of ALDH2 by 4-Hydroxynonenal is reversible at low concentration and become irreversible when the concentration of 4-HNE reaches 10 μM.
4-Hydroxynonenal can induce antioxidant defense mechanisms to restrain its own production and to enhance the cellular protection against oxidative stress.
4-Hydroxynonenal, the product of lipid peroxidation, is mutagenic and genotoxic in viruses, bacteria and mammalian cells. It reacts with all four DNA bases but with different efficiency: G >C > A >T. 4-Hydroxynonenal-dG represents the best biomarker of the genotoxic effects of 4-Hydroxynonenal and these adducts are primarily found in nuclear DNA. A classic example of etiological relevance of 4-Hydroxynonenal-dG in human cancers is 4-Hydroxynonenal-dG induced p53 mutation. 4-Hydroxynonenal-dG adducts were preferentially formed at the third base of codon 249 in the p53 gene, causing gene mutation and affecting diverse biological processes including cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, DNA repair, and differentiation.
Following 24 h after fluid percussion injury (FPI), the mouse brain tissue is analyzed for the expression level of NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE. Both wild-type (Nrf2 +/+ ) and Nrf2-deficient mice (Nrf2 ?/? ) results in increased expression of 4-Hydroxynonenal following 15 psi injury (moderate injury) when compared to uninjured Nrf2 +/+ and Nrf2 ?/? mice. Similar to iNOS result, in Nrf2 ?/? KO mice, the expression level of 4-Hydroxynonenal is significantly high when compared to corresponding injured and uninjured Nrf2 +/+ WT animals.

