5058-13-9
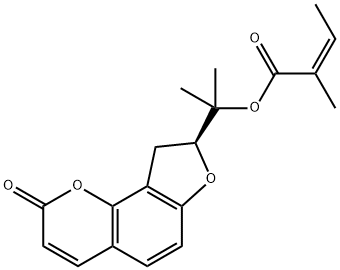 5058-13-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
5058-13-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
二氫山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸酯
氫歐山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸酯
二氫歐山芹當(dāng)歸酸酯
二氫歐山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸脂
二氫歐山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸酯
二氫歐山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸酯對(duì)照品,
二氫歐山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸酯(標(biāo)準(zhǔn)品)
二氫歐山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸酯, 來(lái)源于獨(dú)活
二氫歐山芹醇當(dāng)歸酸酯(分析標(biāo)準(zhǔn)品)
ColuMbianin
Columbianadin
Columbianetin angelate
Columbianadin 5058-13-9
Columbianadin Columbianadin
Columbianadin, 98%, from Angelica pubescens Maxim.f. biserrata Shan et Yuan
2-[(8S)-2-oxo-8,9-dihydrofuro[2,3-h]chromen-8-yl]propan-2-yl (Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate
(S)-2-(2-oxo-8,9-dihydro-2H-furo[2,3-h]chromen-8-yl)propan-2-yl (Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate
(S)-8-[1-[(Z)-2-Methyl-2-butenoyloxy]-1-methylethyl]-8,9-dihydro-2H-furo[2,3-h]-1-benzopyran-2-one
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
常見(jiàn)問(wèn)題列表
Apoptosis
Columbianadin (CBN) effectively suppresses the growth of colon cancer cells. Low concentration (up to 25 μM) of Columbianadin induces apoptosis, and high concentration (50 μM) of Columbianadin induces necroptosis. The induction of apoptosis by Columbianadin is correlated with the modulation of caspase-9, caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, Bim and Bid, and the induction of necroptosis is related with RIP-3, and caspase-8. In addition, Columbianadin induces the accumulation of ROS and imbalance in the intracellular antioxidant enzymes such as SOD-1, SOD-2, catalase and GPx-1. Columbianadin shows the most effective growth inhibitory activity against human colorectal cancer cells. Accordingly, further study is performed using HCT116 cells to give the detailed growth-inhibitory mechanism of action mediated by Columbianadin. The cells treated with various concentrations of Columbianadin (0-100 μM) exhibit a dose- and time-dependent growth inhibition with an IC 50 value of 47.2 and 32.4 μM after 48 and 72 h incubation, respectively. Treatment of various concentrations (12.5, 25, and 50 μM) of Columbianadin for 48 h in HCT116 cells decreases the number of cells and increases the floating cells. Apparent morphological changes with round-shape and dying cells are also observed at 25 and 50 μM Columbianadin -treated cells.
The analysis method is successfully applied to a tissue distribution study of Columbianadin (CBN) and Columbianetin (CBT) after intravenous administration of Columbianadin to rats. The results of this study indicated that Columbianadin can be detected in all of the selected tissues after i.v. administration. Columbianadin is distributed to rat tissues rapidly and can be metabolized to CBT in most detected tissues. Of the detected tissues, heart had the highest uptake of Columbianadin, which suggests that heart might be one of the main target tissues of Columbianadin .