25843-45-2
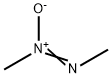 25843-45-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
25843-45-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
氧化偶氮基甲烷
AOM氧化偶氮甲烷
偶氮甲烷(AOM)
結(jié)腸癌造模誘導(dǎo)劑氧化偶氮甲烷
PERFEMIKER]氧化偶氮甲烷,95%
AZOXYMETHANE
azoxy-methan
CH3N=N(→O)CH3
Methane, azoxy-
ONN-Azoxydimethane
Dimethyldiazene 1-oxide
Azoxymethane DISCONTINUED
1,2-Dimethyldiazene 1-oxide
(Z)-1,2-diMethyldiazene oxide
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
安全數(shù)據(jù)
常見問題列表
Azoxymethane is a colon carcinogen which leads to the formation of DNA adducts. On an equal protein basis, hepatic microsomes are much more active than SI and colon microsomes in NADPH-dependent Azoxymethane bioactivation and N 7 -mG adduct formation. Hepatic microsomes show the highest activity in the hydroxylation of Azoxymethane, followed by SI and colon microsomes.
Regardless of the strain, the amounts of O 6 -mG and N 7 -mG produced by Azoxymethane are highest in the liver, followed by proximal and distal colons, which have similar levels, and then by duodenum, jejunum and ileum. Results indicate that the Azoxymethane-induced DNA adduct formation in the SI and colon does not depend on bioactivation by hepatic P450 enzymes. Irrespective of the mouse strain, no aberrant crypt foci (ACF) is detected in the colons of saline-treated mice; in contrast, colonic ACF is detected in all three strains of Azoxymethane-treated mice. The Azoxymethane-treated athymic mice have approximately an 11-fold lower tumor incidence than similarly treated WT animals.


