| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
2,5-DICHLORO-4,6-DIMETHYLNICOTINONITRILE | [CAS]
91591-63-8 | [Synonyms]
2,5-DICHLORO-4,6-DIMETHYLNICOTINONITRILE
3-Cyano-2,5-dichloro-4,6-dimethylpyridine
2,5-Dichloro-4,6-dimethylnicotinonitrile 95+%
2,5-DICHLORO-4,6-DIMETHYLPYRIDINE-3-CARBONITRILE
2,5-Dichloro-4,6-diMethyl-3-pyridinecarbonitrile
3-Pyridinecarbonitrile,2,5-dichloro-4,6-dimethyl-
2,5-Dichloro-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carbonitrile, 3-Cyano-2,5-dichloro-4,6-dimethylpyridine | [Molecular Formula]
C8H6Cl2N2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00052631 | [MOL File]
91591-63-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
201.05 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
82 °C | [Boiling point ]
304.6±37.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.36 | [storage temp. ]
Inert atmosphere,2-8°C | [pka]
-2.79±0.10(Predicted) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
2,5-Dichloro-4,6-dimethyl-3-pyridinecarbonitrile, can be used for the synthesis of a selective muscarinic receptor 4 (M4) positive allosteric modulator called ML253, which is a potent and brain penetrant compound that is active in a preclinical model of schizophrenia. | [Synthesis]
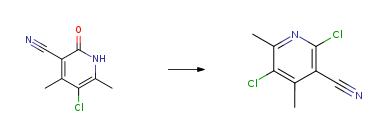
Phosphoryl chloride (973.2g), tetramethylammonium chloride (67.3g) and compound of Preparation 2 (227.1g) were added to dichloromethane (500g). The suspension was heated to 85°C and stirred for 5 hours. Excess of phosphoryl chloride was removed by distillation in vacuo. The reaction mixture was cooled below 30 °C and diluted with dichloromethane. The resulting solution was added to water (1350g) at room temperature and stirred for 30 minutes. The lower organic phase was separate and the aqueous phase extracted with dichloromethane. The organic phases were combined, washed with water and then treated with charcoal. The charcoal was filtered and a solvent swap to heptane was performed by distillation at atmospheric pressure. The solution was filtered at 50 °C and then cooled to 30 °C. On further cooling to 0°C crystals were obtained. These were isolated by filtration, washed twice with heptane. After drying at 50°C the desired product was obtained typically at 88-91 % . The above process was repeated with a reduction in dichloromethane during crystallisation and adding some methanol. The resulting plate-like crystals were more easily transferred for subsequent use. |
|
|