| Identification | More | [Name]
Tryptamine | [CAS]
61-54-1 | [Synonyms]
1H-INDOLE-3-ETHANAMINE
2-(1H-INDOL-3-YL)ETHANAMINE
2-(1H-INDOL-3-YL)-ETHYLAMINE
2-(3-INDOLYL)ETHYLAMINE
3-(2-AMINOETHYL)-1H-INDOLE
3-(2-AMINOETHYL)INDOLE
3-(BETA-AMINOETHYL) INDOLE
AURORA KA-7834
LABOTEST-BB LTBB000729
RARECHEM AH BS 0131
TIMTEC-BB SBB003963
TRYPTAMINE
(Amino-2 ethyl)-3 indole
(amino-2ethyl)-3indole
3-(2-aminoethyl)-indol
3-Indoleethylamine
beta-(3-Indolyl)ethylamine
Indol-3-ethylamine
Indole, 3-(2-aminoethyl)-
Tryptamin | [EINECS(EC#)]
200-510-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C10H12N2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00005661 | [Molecular Weight]
160.22 | [MOL File]
61-54-1.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
White to Orange Crystalline Powder | [Melting point ]
113-116 °C (lit.) | [Boiling point ]
137 °C/0.15 mmHg (lit.) | [density ]
0.9787 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.6210 (estimate) | [Fp ]
185 °C
| [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
water: soluble1g/L at 20°C | [form ]
crystalline
| [pka]
10.2(at 25℃) | [color ]
white
| [PH]
11.07 (10g/l, H2O, 24.7℃) | [Water Solubility ]
negligible | [Sensitive ]
Air Sensitive | [Usage]
Occurs in plants. | [Detection Methods]
HPLC,NMR | [Merck ]
14,9796 | [BRN ]
125513 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
61-54-1(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
1H-Indole-3-ethanamine(61-54-1) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
61-54-1(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed .
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin .
R41:Risk of serious damage to eyes.
R37/38:Irritating to respiratory system and skin .
R22:Harmful if swallowed. | [Safety Statements ]
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
NL4020000
| [F ]
8-23 | [HazardClass ]
IRRITANT | [HS Code ]
28259080 | [HS Code ]
29339990 |
| Raw materials And Preparation Products | Back Directory | [Raw materials]
1H-Indole-3-propanoic acid, α-amino-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-, (αS)--->L-5-Hydroxytryptophan-->L-KYNURENINE | [Preparation Products]
Vinpocetine-->1,2,3,4-TETRAHYDRO-9H-PYRIDO[3,4-B]INDOLE-->N,N-Dimethyltryptamine-->Vincamine-->N-(p-Coumaroyl) Serotonin-->1-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-2,3,4,9-TETRAHYDRO-1H-B-CARBOLINE-->N-METHYL-N-ISOPROPYLTRYPTAMINE(MIPT)-->TETRAHYDROALSTONINE-->3-Ethylindole-->2-cyano-N-[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]acetamide-->N-(2-INDOL-3-YLETHYL)(4-METHYLPHENYL)FORMAMIDE-->N-(2-INDOL-3-YLETHYL)-3-PHENYLPROP-2-ENAMIDE |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Description]
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid that can be synthesized by decarboxylation of the amino acid tryptophan. Notably, tryptamine can be found in fungi, plants, Amphibia, animals, and microbes.
Tryptamine has an indole ring structure and a fused double ring that is composed of a benzene ring and a pyrrole ring, linked to an amino group by 2-carbon side chain. The indole ring is the vital nucleus of many complex natural products that have significance in drug discovery as well as some synthetic and non-synthetic drugs that are based on tryptamine skeleton.
The chemical’s distinct structure is an approximation to the neurotransmitter serotonin as well-known drugs and hallucinogens. Tryptamine’s significance as psychedelic drugs, neuromodulator, and neurotransmitter is well understood due to its presence in mammalian brain in small amounts.
| [Applications]
Analogs of tryptamine that are typically produced by its synthetic modification play a significant role in individuals due to the introduction of functionalities that are biologically active in its nucleus that may cause changes in the mental and physical status of the human brain.
Substitutions on the indole ring at nitrogen and C-2 of its side chain produce numerous neuroactive compounds ranging from anti-migraine drugs to toxic substances, such as rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan. A small amount of tryptamine is required due to its fatalities and intoxication for several reasons.
| [Plants Containing Tryptamine]
In plants, tryptamine in small amounts acts as a promising phase to the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid in one biosynthetic pathway. N, N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a tryptamine derivative that is an active constituent for the hallucinogenic effect of brew known as the “vine of the souls.” Indigenous Amazonian tribes have traditionally used the drink for therapeutic purposes for effective treatment of some physical maladies and abuse disorders. Magic mushrooms are the most common fungi that contain tryptamine derivatives.
| [Pharmacology]
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), which is a natural derivative of tryptamine is a significant signaling hormone that helps in the modulation and regulation of numerous processes within the central nervous system, for instance, cognition, sleep, temperature regulation, memory, and behavior. The mammalian brain contains small traces of tryptamine, which generally act as a modulator or neurotransmitter by releasing serotonin agents. It is also an enhancer of serotonergic activity. Only one minute is required for tryptamine to produce psychotropic phenomena when used recreationally. It has been associated with fatalities and intoxications for multiple reasons including low toxic concentrations.
|
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
White to Orange Crystalline Powder | [Uses]
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid found in plants. Tryptamine is commonly used in the preparation of biologically active compounds such as neurotransmitters and psychedelics. | [Definition]
ChEBI: An aminoalkylindole consisting of indole having a 2-aminoethyl group at the 3-position. | [Definition]
tryptamine: A naturally occurringalkaloid, C10H12N2, having an indolering system with a –CH2–CH2–NH2side chain in the 3-position of thenitrogen-containing ring. Derivativesof tryptamines have hallucinogeniceffects. An example in psilocybin. | [Preparation]
Tryptamine, a monoamine alkaloid containing an indole ring structure is derived by the decarboxylation of amino acid tryptophan.
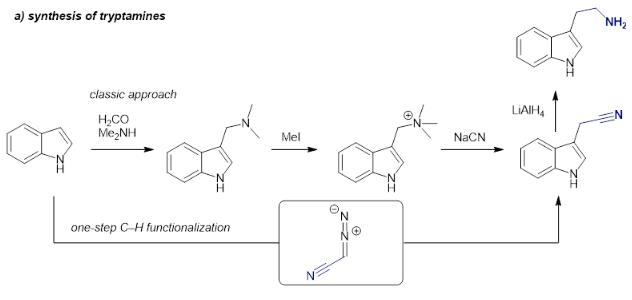
The synthesis of tryptamines is typically conducted following a classic route starting with a Mannich reaction of an indole heterocycle, followed by quaternization of the amine, nucleophilic substitution with highly toxic cyanide and final reduction. | [General Description]
Tryptamines which are usually found in plants, fungi, animals, etc. are categorized under the monoamine alkaloids class of compounds. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Vasoactive; may have a neuromodulator function; biogenic amine formed from the decarboxylation of tryptophan by L-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. | [Purification Methods]
Crystallise tryptamine from *benzene, Et2O (m 114o) or pet ether (m 118o). It has UV: 222n 276, 282 and 291nm (EtOH) and max 226, 275, 281 and 290nm (HCl). [Beilstein 22 II 346, 22 III/IV 4319, 22/10 V 45.] |
|
|