| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Imidazolidine | [CAS]
504-74-5 | [Synonyms]
mizuolin
imidazoline
Imidazolidine
1,3-Diazacyclopentane
Oil soluble imidazoline
Imidazolidine ISO 9001:2015 REACH | [EINECS(EC#)]
263-058-8 | [Molecular Formula]
C3H8N2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD19216513 | [MOL File]
504-74-5.mol | [Molecular Weight]
72.11 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
68.2-68.8 °C | [Boiling point ]
92.8±8.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
0.892±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature | [pka]
10.33±0.20(Predicted) | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C3H8N2/c1-2-5-3-4-1/h4-5H,1-3H2 | [InChIKey]
WRYCSMQKUKOKBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
C1NCCN1 | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Imidazolidine (504-74-5) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
The imidazolines, was
discovered at American Cyanamid in the early 1980s.
Extensive research has led to the development of
four commercial compounds: imazapyr, imazamethabenzmethyl,
imazethapyr, and imazaquin. Like
the sulfonylureas, the imidazolines are extremely active
at low rates. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Imidazolidine is a saturated organic heteromonocyclic parent, a member of imidazolidines and an azacycloalkane. | [Synthesis]
Imidazolidine is produced by a cyclocondensation reaction between ethylenediamine and an aldehyde. The yield is 70 %. The reaction conditions are that one of the amino groups of ethylenediamine is present using the secondary amine form.
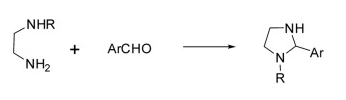
Synthesis of Imidazolidine derivatives including:
(1) Synthesis of 1,3-dibenzyl-2-arylimidazolidine
It is divided into three steps: the first step is the condensation of ethylenediamine with aldehyde in dry benzene to obtain N,N′-dibenzylidene-1,2-diamine, and the second step is the reduction of N,N′-dibenzylidene ethylenediamine to N,N′-dibenzylidene ethylenediamine in ethanol with sodium borohydride. The substituted diamine was condensed with an aryl aldehyde in the final step to give 1,3-dibenzyl-2-arylimidazolidine.
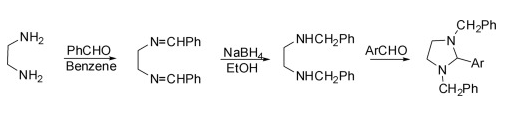
(2)Synthesis of 2-iminoimidazolidine
Method: Ethylenediamine reacts with cyanobromide to form 2-iminoimidazolidine by substitution-cyclisation.

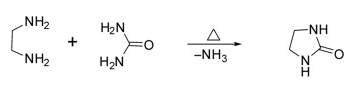
(3) Synthesis of Imidazolidin-2-one
Methods: Imidazolidin-2-one was prepared by heating ethylenediamine and urea with 75% yield.
 | [Structure and conformation]
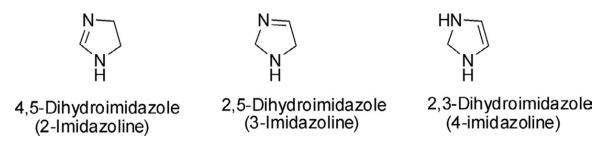
Dihydroimidazole is a five-membered, nonplanar, and nonaromatic heterocycle, derived by the partial reduction of one of the two double bonds of the imidazole ring. The dihydroimidazoles are also referred to as imidazolines and there are three possible regioisomeric forms: 4,5-dihydroimidazole (2-imidazoline), 2,5-dihydroimidazole
(3-imidazoline), and 2,3- dihydroimidazole (4-imidazoline). The 2- and 3-imidazolines contain an imine center, while
4-imidazoline contains an alkene substructure. Among these three isomeric forms, the chemistry of 2-imidazoline is
more developed than 3- and 4-imidazolines.
 |
|
|