| Identification | More | [Name]
OXAMIC ACID | [CAS]
471-47-6 | [Synonyms]
AMINOOXOACETIC ACID
OXALIC ACID MONOAMIDE
OXAMIC ACID
OXAMIDIC ACID
Acetic acid, aminooxo-
aminooxo-aceticaci
Formic acid, (aminocarbonyl)-
Formic acid, carbamoyl-
Glycine, 2-oxo-
Glyoxylic acid, amino-
Oxalamic acid
Oxamate
Oxamate, (aminocarbonyl)-
Oxamic acid Oxalic acid monoamide
Oxamicacid,98%
Aminooxoacetic acid, Oxalic acid monoamide | [EINECS(EC#)]
207-443-0 | [Molecular Formula]
C2H3NO3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00008006 | [Molecular Weight]
89.05 | [MOL File]
471-47-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white crystalline powder | [Melting point ]
207-210 °C (dec.) (lit.) | [Boiling point ]
165.08°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1.6193 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.4264 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C(protect from light) | [solubility ]
DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) | [form ]
Crystalline Powder | [pka]
1.60±0.20(Predicted) | [color ]
White | [Water Solubility ]
Soluble in water 108 mg/mL. | [Merck ]
14,6917 | [BRN ]
1743294 | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C2H3NO3/c3-1(4)2(5)6/h(H2,3,4)(H,5,6) | [InChIKey]
SOWBFZRMHSNYGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
C(O)(=O)C(N)=O | [CAS DataBase Reference]
471-47-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Oxamic acid (471-47-6) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [TSCA ]
Yes | [HS Code ]
29241990 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Oxamic acids also known to as oxalic acid monoamides have emerged as potent precursors for the generation of the carbamoyl radical. Oxamic acids can easily undergo decarboxylation through a single electron oxidation resulting in the generation of the reactive carbamoyl radical, which can then engage in diverse radical reactions or undergo a second single electron oxidation as originally unveiled by Minisci. Oxamic acids are thus versatile intermediates for the synthesis of nitrogen-containing organic molecules[1]. The oxidative decarboxylation of oxamic acids can be mediated through thermal, photochemical, electrochemical or photoelectrochemical means, generating carbamoyl radicals, which may further add to unsaturated systems to provide a broad range of important amides. Oxidative decarboxylation of oxamic acids also offers a straightforward entry for the preparation of urethanes, ureas, and thioureas.
| [Chemical Properties]
white crystalline powder | [Uses]
Oxamic acid is an ozone oxidation product and is used in the synthesis of hydroxybenzimidazoles preparation as potential anti tumor agents targeting human lactate dehydrogenase A.This compound is suitable for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) related research. | [Application]
Oxamic acid (OA) has applications in polymer chemistry. It increases the water solubility of certain polymers, including polyester,epoxide, and acrylic upon binding with them. Oxamic acid can be used as a reactant to prepare 6-phenanthridinecarboxamide by direct C-H carbamoylation reaction using ammonium persulfate in DMSO. It can also be used as an organic ligand to prepare functionalized metal oxide nanoparticles for various biological applications. OA along with p-aminobenzoic acid is used to functionalize Au nanoparticles for the development of a sensor to detect Fe3+ ions by the calorimetric method. | [Definition]
ChEBI: The monoamide of oxalic acid. | [References]
[1] Ikechukwu Martin Ogbu . “Oxamic acids: useful precursors of carbamoyl radicals.” Chemical Communications 58 55 (2022): Pages 7593-7607.
|
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Structure]
The final unit-cell parameters of oxamic acid are a = 9.4989 (6), b = 5.43796 (9), c = 6.8637 (9) ?, β = 107.152 (5), V = 338.772 (10) ?3 , Z = 4. The refinement converged to the figures of merit: Re = 0.01674, Rp = 0.03270, Rwp = 0.05652 and GoF = 3.378 with a good fit between the calculated pattern of the structural model and the experimental pattern. The DFT-D calculations show an excellent reproduction of the experimental structure, validating the correctness of the structure. The non-centrosymmetric nature of the structure was confirmed by SHG measurements. In the crystal structure, the molecules are close to planar and form a complex 2D hydrogen-bonding pattern based on the cyclic amide-acid heterosynthon.
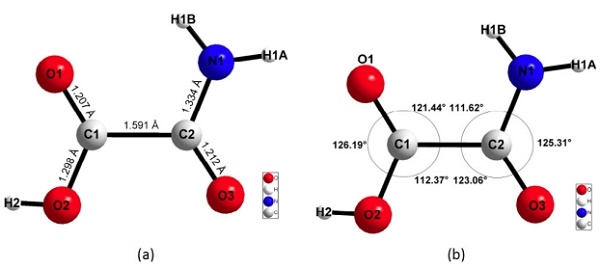
|
|
|