| Identification | More | [Name]
Etodolac | [CAS]
41340-25-4 | [Synonyms]
1,8-DIETHYL-1,3,4,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRANO[3,4-B]INDOLE-1-ACETIC ACID
ETODOLAC
ETODOLIC ACID
1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1,8-diethylpyrano(3,4-b)indole-1-aceticacid
4-b)indole-1-aceticacid,1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1,8-diethyl-pyrano(
4-b]indole-1-aceticacid,1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-pyrano[
ay24236
ultradol
ETODOLAC 8-METHYL ANALOGUE BP(CRM STANDARD)
ETODOLAC, BP STANDARD
ETODOLAC 1-METHYL ANALOGUE BP(CRM STANDARD)
ETODOLAC, ACID DIMER BP STANDARD
ETODOLAC, USP STANDARD
ETODOLAC, RELATED COMPOUND A(±)-8-ETHYL-L-METHYL-1,3,4,9-TETRAHYDROPYRANO[3,4-BETA]-INDOLE-1-ACETIC ACID USP STANDARD
ETODOLAC, EP STANDARD
ETODOLAC, IMPURITY H2-(7-ETHYLINDOL-3-YL)ETHANOL EP STANDARD
1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano-[3,4-6]indole-1-aceticacid
1,8-Diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3.4-b]indoleaceticacid
Etogesic
Lodine | [EINECS(EC#)]
629-689-1 | [Molecular Formula]
C17H21NO3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00133313 | [Molecular Weight]
287.35 | [MOL File]
41340-25-4.mol |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T,Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R23/24/25:Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed .
R40:Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect.
R36:Irritating to the eyes.
R25:Toxic if swallowed.
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S22:Do not breathe dust .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show label where possible) .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36/37:Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves . | [RIDADR ]
3249 | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
UQ0360000
| [HazardClass ]
6.1(b) | [PackingGroup ]
III | [HS Code ]
29349990 |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]
Etodolac (trade name: Lodine), also known as ethoxycolic acid, indoleacetic acid, and rhododine, is a new generation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug highly selective to COX-2. This product is a weak acidic drug, existing in a molecular form under the condition of lower pH value which is conducive to drug absorption. This product is widely used in the clinical treatment of postoperative pain. It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, being able to relieve the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, delaying the pathological changes caused by arthritis. In inflammatory site, it can selectivity inhibit the prostaglandin synthesis to exert its anti-inflammatory effect. It is especially applicable to the elderly patients. This product appears as white crystalline powder with the melting point of 145~148 ℃.
Etodolac was first developed by a subsidiary of AHP in the United States. It had been successfully listed in the UK in 1985, followed by being listed in France, the United States, Germany, Japan and other countries. | [NSAID]
Etodolac (Etodolac), also known as indole acetic acid, indole acetic acid pyran and rodin etc, and the tradename is Lodine, a new generation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs which has a high selective of COX-2. This product is a kind of weak acid drug and has the form of molecular at lower pH values which is conducive to drug absorption. This product is widely used in the clinical treatment of pain after surgery, has a good effect of analgesic and anti-inflammatory that can relieve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, delay the bone pathology caused by arthritis and synthesis the prostaglandin at the sites of inflammation selectively. The product apply to the elderly patients. The etodolac is white crystalline powder, has the melting point of 145~148 ℃.
Etodolac was first developed by the subsidiary of AHP and successfully listed in the UK in 1985. The product have been listed in many countries like France, the United States, Germany and Japan etc. | [Chemical properties]
It is crystallized by the hexane-chloroform, with the melting point of 145~148 ℃. | [Mechanism]
This product is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Its effects is similar to aspirin. It can inactivated the cyclooxygenase at the sites of inflammation thereby inhibit the biosynthesis of prostaglandins selectively.The product has little side effect for the gastrointestinal since its inhibition of PGE2 is mild and transient. It can be quickly absorbed by oral with a single dose of 200mg.It has the Tmax of 1 h, Cmax of 18.6 μg/ml, T1/2 of 7.4 h and PPB of 95%. The product do not accumulate in the body and 60% of the dose can be excreted after 24hr by the cellular metabolism, among the them, 74% is excreted in urine by the kidneys and 19% in feces. The product can reduce the incidence and damage of bone and joint and improce the condition of patients. The current study shows that the product has no teratogenic effect in animal experiments and has little impact on fertility and reproductive function. | [Pharmacokinetics]
According to the current study abroad, the drug is well absorbed orally and has the the systemic bioavailability of 80% or more. The dosage should be within 600mg every 12 hours, the area under the curve of plasma concentration-time is in direct proportion to the dosage. More than 99% of etodolac can combine with the plasma protein, the free fraction is less than 1%. The single dose is at the range of 200-600mg and the the average peak plasma concentration (Cmax) within 80 ± 30 the minute is in the scope of 14 ± 4-37 ± 9μg/ml range. The average plasma clearance rate is 47 (± 16) ml/hr/kg and the elimination half-life is 7.3 (± 4.0) hours. Etodolac can be metabolized by the liver and 16% of the dose excreted by the faeces. The dose of the product is not determined by the weight, but the recommended dosage can use the body weight as reference. | [Uses]
(1) The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of Indole acetic acid class has the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. It can inhibit prostaglandin synthesis at the site of inflammation selectively. The product can be absorbed rapidly and has no signs of drug savings. It can be used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and postoperative pain relief etc. It is a medicament that suitable for elderly patients.
(2) Using as anti-inflammatory drugs. | [Used in Particular Diseases]
Acute Gouty Arthritis:
Dosage and Frequency: 300 mg twice daily
| [Production method]
The acylation reaction of o-ethyl aniline, chloral hydrate and hydroxylamine can form the oxime, after the cyclization by using the sulfuric as the catalyst and the reduction by lithium aluminium hydride , oxime can turn into the indole derivatives. The reaction with the oxalyl chloride and ethanol can bring 1,2-carbonyl side chain in 3 bit and then be restored to hydroxyethyl by lithium aluminium hydride, after the condensation , cyclization with ethyl propionylacetate and hydrolyzation. The final product-etodolac can be obtained. | [Synthetic routes]
The etodolac ester should be prepared at first, and the final product can be obtained after the hydrolyzation, acidification, crystallization of the organic phase and rectification by the toluene (or benzene)-refined petroleum ether. Using the industrial 7-Ethyl tryptophol and ethyl propionylacetateas as the raw material to synthesis the etodolac ethyl, and get the crude etodolac by hydrolyzation and acidification. The refined etodolac can be obtained by recrystallization with isopropanol-water.
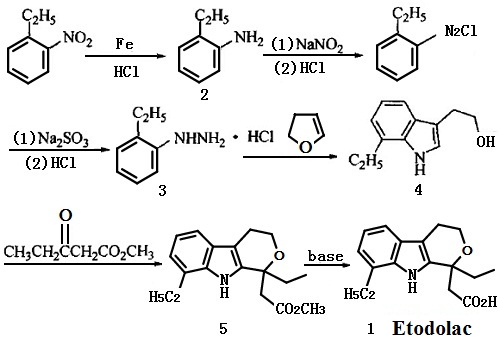
Figure 1 shows the synthetic route of etodolac | [Usage and dosage]
The usage are various with the different applications, as follows:
1. For pain: The recommended dose is 0.2-0.4g every 8 hours for acute pain , the maximum daily dose should not exceed 1.2g. The maximum daily dose for the patients who weight under 60kg should not exceed 20mg per kilogram of body weight. The etodolac still has analgesic effect on some patients.
2. For chronic diseases such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: The recommended dose of daily is 0.4-1.2g in divided doses orally, the maximum daily dose should not exceed 1.2g. The maximum daily dose for the patients who weight over 60kg should not exceed 20mg per kilogram of body weight. The daily dose for etodolac is 0.4g or less in divided doses.It has a certain effect for some patients. | [Adverse drug reaction]
The product may cause some side effect like the allergic symptoms include the rash, eczema, itching and redness etc; nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, heartburn, indigestion, bloating, abdominal pain, stomach cramps, constipation and vomiting for the gastrointestinal system; headache , dizziness, drowsiness, insomnia, nervousness, anxiety, depression, general malaise, fatigue, weakness, frequent urination, palpitations, edema and tinnitus for the central nervous system. The side effect like the increasing of the ALT, AST and BUN , the decline of the hemoglobin, white blood cells, red blood cells and thrombocytopenia are rarely.
The mechanism of action of Etodolac, the route of synthesis, adverse reactions, etc., were edited by Baoquan, Chemicalbook. (2016-11-18) | [Attention]
The drug security of pregnant and lactating women has not been established and should be used with caution. The first three months of pregnancy should not use this drug. The patients who allergic to aspirin and other NSAIDs or have the active peptic ulcer can not use this product disabled. The patients with the history of gastrointestinal disease include peptic ulcer should be closely monitored and be discontinued immediately when the peptic ulcer come. Even it has no direct effect on platelets, but the inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis can interfere the platelet function in some ways. The patients who has liver and kidney dysfunction sjpi;d adjust the dose according to need. |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Etodolac (etodolic acid) is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory/analgesic agent
useful in the treatment of various inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid
and osteoarthritis. | [Originator]
Ayerst (USA) | [Definition]
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is acetic acid in which one of the methyl hydrogens is substituted by a 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl moiety. A preferential inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenase 2 and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory,
it is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, and for the alleviation of postoperative pain. Administered as the racemate, only the (S)-enantiomer is active. | [Indications]
Etodolac (Lodine) is indicated for the treatment of
osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute pain. It inhibits
COX-2 with slightly more selectivity than COX-1
and therefore produces less GI toxicity than many other
NSAIDs. Common adverse effects include skin rashes
and CNS effects. | [Brand name]
Lodine(Wyeth). | [General Description]
Etodolac (Lodine, Ultradol), a chiral, COX-2 selectiveNSAID drug that is marketed as a racemate, possesses an indolering as the aryl portion of this group of NSAID drugs.It shares many similar properties of this group and is indicatedfor short- and long-term management of pain and OA.
Similar to ketorolac, etodolac exhibits several uniqueenantioselective pharmacokinetic properties. For example,the “inactive” (R)-enantiomer has approximately a 10-foldhigher plasma concentration than the active (S)-enantiomer.Furthermore, the active (S)-enantiomer is less protein boundthan its (R)-enantiomer and therefore has a very large volumeof distribution. It is well absorbed with an elimination halflifeof 6 to 8 hours. Etodolac is extensively metabolized intothree major inactive metabolites, 6-hydroxy etodolac (via aromatichydroxylation), 7-hydroxy-etodolac (via aromatic hydroxylation),and 8-(1'-hydroxylethyl) etodolac (via benzylichydroxylation), which are eliminated as the correspondingether glucuronides. Its unstable, acyl glucuronide, however,is subject to enterohepatic circulation and reactivation tothe parent drug, similar to other NSAIDS in this class. | [Biological Activity]
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that selectively inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) (IC 50 values are 53 and >100 μ M for COX-2 and COX-1 respectively). Displays anti-inflammatory effects in both adjuvant arthritic and normal rats. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compound that is a non-selective inhibitor of COX-1 and COX-2. | [Mechanism of action]
The primary mechanism of action appears to be
inhibition of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins at the cyclooxygenase step, with no inhibition of the lipoxygenase
system. Etodolac, however, possesses a more favorable ratio of inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis in human
rheumatoid synoviocytes and chondrocytes than by cultured human gastric mucosal cells compared to ibuprofen,
indomethacin, naproxen, diclofenac, and piroxicam. | [Clinical Use]
Etodolac is promoted as the first of a new chemical class of anti-inflammatory drugs, the pyranocarboxylic acids.
Although not strictly an arylacetic acid derivative (because there is a two-carbon atom separation between the
carboxylic acid function and the hetero-aromatic ring), it still possesses structural characteristics similar
to those of the heteroarylacetic acids and is classified here. It was introduced in the United States in 1991 for acute
and long-term use in the management of osteoarthritis and as an analgetic. It also possesses antipyretic activity.
Etodolac is marketed as a racemic mixture, although only the S-(+)-enantiomer possesses anti-inflammatory activity
in animal models. Etodolac also displays a high degree of enantioselectivity in its inhibitory effects on the
arachidonic acid cyclooxygenase system. | [Veterinary Drugs and Treatments]
Etodolac is labeled for the management of pain and inflammation
associated with osteoarthritis in dogs. It may find uses, however, for
a variety of conditions where pain and/or inflammation
should be
treated. | [Drug interactions]
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect, increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemiaAnalgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects);
avoid with ketorolac, increased risk of side effects and
haemorrhage.Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones.Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and
phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of
bleeding with heparin, dabigatran and edoxaban -
avoid long term use with edoxaban.Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlafaxine.Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas
enhanced.Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin
concentration.Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavirCiclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicityCytotoxic agents: reduced excretion of methotrexate;
increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib.Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
antagonism of diuretic effect; hyperkalaemia with
potassium-sparing diuretics.Lithium: excretion decreased.Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleedingTacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity. | [Metabolism]
Etodolac is metabolized to three hydroxylated metabolites and to glucuronide conjugates, none of which
possesses important pharmacological activity. Metabolism appears to be the same in the elderly as in the general
population, so no dosage adjustment appears necessary.
Etodolac is indicated for the management of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and for the management of
pain. | [storage]
Store at -20°C | [References]
[1] kumagai k1, kubo m, imai s, toyoda f, maeda t, okumura n, matsuura h, matsusue y.the cox-2 selective blocker etodolac inhibits tnfα-induced apoptosis in isolated rabbit articular chondrocytes. int j mol sci. 2013 sep 30;14(10):19705-15.
[2] hakozaki m1, hojo h, kikuchi s, abe m. etodolac, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, induces apoptosis by activating caspases in human malignant rhabdoid tumor cells (frtk-1). oncol rep. 2007 jan;17(1):169-73. |
|
|