| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
1,3-Dioxan-2-one homopolymer can be copolymerized with other lactone monomers to produce materials with tunable physical and chemical properties. After cross-linking a flexible and elastic (co-)polymer network is obtained, with properties similar to those of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) rubber.The materials can be used in biomedical applications. PTMC-based polymers degrade in vivo by an enzymatic surface erosion mechanism without releasing acidic degradation products, which makes these polymers well suited as matrices for the preparation of biodegradable composites for bone tissue engineering and drug delivery. | [Production Methods]
The direct polymerization method is a continuous esterification reaction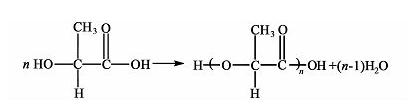
Open-loop polymerization includes three reaction steps: oligomerization, depolymerization and ring opening, which can achieve precise control of the polymerization reaction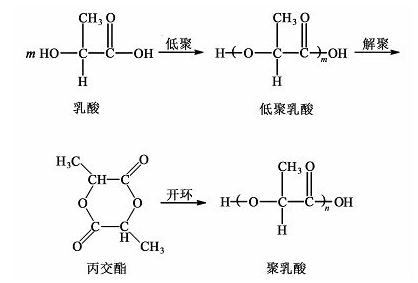 | [General Description]
1,3-Dioxan-2-one homopolymer is an amorphous polymer with low glass transition, prepared by ring-opening polymerization of cyclic trimethylene carbonate (TMC) monomers. | [Synthesis]
1,3-Propanediol (4.72 mL, 0.657 mol) and ethyl chloroformate (12.5 mL,0.131 mol) were dissolved in anhydrous THF (0.13 L). The mixture was stirred in an ice bath for 1 h and a solution of triethylamine (19.2 mL, 0.138 mol) in THF (9 mL) was slowly added. Then, the solution was transferred to ambient temperature and stirred for 2 h. The reaction mixture was filtered and the volume of the solution was reduced to 40-50 mL. The mixture was kept in a freezer for 12 h and the precipitate was recovered by filtration. The recovered solid was recrystallized in ethyl acetate and sublimed (2.9 g, 43%).
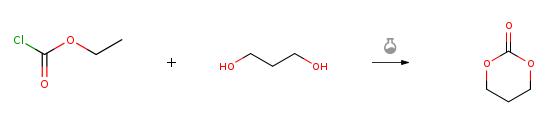 |
|
|