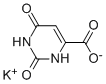
| Identification | More | [Name]
Potassium orotate | [CAS]
24598-73-0 | [Synonyms]
6-CARBOXY-2,4-DIHYDROXYPYRIMIDINE MONOPOTASSIUM SALT
6-CARBOXY-2,4-DIHYDROXYPYRIMIDINE POTASSIUM SALT
OROTIC ACID MONOPOTASSIUM SALT
OROTIC ACID POTASSIUM SALT
POTASSIUM OROTATE
URACIL-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID MONOPOTASSIUM SALT
URACIL-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID POTASSIUM SALT
1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidinecarboxylicacimonopotassiumsal
1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidinecarboxylicacimonopotassiumsalt
ba2658
dioron
orotic acid monopotassium
potassium 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-2,6-dioxopyrimidine-4-carboxylate
potassoum oratate
6-Carboxy-2,4-dihydroxypyrimidine, Uracil-6-carboxylic acid
1,2,3,6-Tetrahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid potassium salt
Olotic acid potassium salt | [EINECS(EC#)]
246-341-0 | [Molecular Formula]
C5H3KN2O4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00039118 | [Molecular Weight]
194.19 | [MOL File]
24598-73-0.mol |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
Orotic acid (OA) is an intermediate in de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis that may be used to study the specificity and kinetics of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRT) which catalyzes the reversible phosphoribosyl transfer from 5′-phospho-α-d-ribose 1′-diphosphate (PRPP) to orotic acid (OA), forming pyrophosphate and orotidine 5′-monophosphate (OMP). Orotic acid is used as a starting material for the potential commercial bioproduction of uridine 5′-monophosphate (UMP) by microbes such as Corynebacterium ammoniagenes (ATCC 6872) or Saccharomyces cerevisiae. OA may be used to study the AMPK/SREBP-1 dependent cell signaling pathway and transcription regulation mechanisms that induce hepatic lipogenesis. |
|
|