| Identification | More | [Name]
PHENANTHRIDINE | [CAS]
229-87-8 | [Synonyms]
3,4-BENZOQUINOLINE
BENZO[C]QUINOLINE
PHENANTHRIDIN
PHENANTHRIDINE
3,4-Benzoisoquinoline
5-azaphenanthrene
6-Phenanthridine
9-Azaphenanthrene
PHENANTHRIDINE, SUBLIMED, 99+%
PHENANTHRIDINE, FOR FLUORESCENCE
Phenanthridine, 98+% | [EINECS(EC#)]
205-934-4 | [Molecular Formula]
C13H9N | [MDL Number]
MFCD00004989 | [Molecular Weight]
179.22 | [MOL File]
229-87-8.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white to beige powder | [Melting point ]
104-107 °C (lit.) | [Boiling point ]
349 °C/769 mmHg (lit.) | [density ]
1.1255 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.7270 (estimate) | [Fp ]
100 °C
| [solubility ]
phosphate buffer: soluble | [form ]
Powder | [pka]
5.58(at 20℃) | [color ]
White to beige | [Water Solubility ]
0.3g/L(20 ºC) | [BRN ]
120204 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
229-87-8(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Phenanthridine (229-87-8) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R37/38:Irritating to respiratory system and skin .
R41:Risk of serious damage to eyes. | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S39:Wear eye/face protection . | [RIDADR ]
UN 2811 6.1/PG 3
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
SF7928000
| [HS Code ]
29333990 | [Toxicity]
mic-bac-sat 50 mg/plate 50NNAZ7,73,83 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
Crystalline needles. Mutagenic. | [Reactivity Profile]
PHENANTHRIDINE(229-87-8) neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Sparingly soluble in water. | [Fire Hazard]
Flash point data are not available for this chemical, but is probably combustible. | [Chemical Properties]
white to beige powder | [History]
Phenanthridine was first discovered by Ame Pictet and H. J. Ankersmit in 1891 by pyrolysis of the condensed product of benzaldehyde and aniline. Earlier, phenanathridine and related compounds were prepared using mainly Pictect-Hurbert and modified Morgan-Walls type of condensation reactions. | [Uses]
- Used in the study of ecotoxicity.
- Used in rotational spectroscopic investigations and radio astronomical searches.
- Used as a dye in biological and chemical sensors.
| [Uses]
Used in the study of ecotoxicity. 1 Used in rotational spectroscopic investigations and radio astronomical searches. 2 Used as a dye in biological and chemical sensors. 3 | [Definition]
ChEBI: An azaarene that is the 9-aza derivative of phenanthrene. The parent of the class of phenanthridines. | [Preparation]
Palladium catalyzed synthesis of phenanthridine has been accomplished by Pritchard and coworkers from imidoyl selenides. This was the first report of palladium insertion into the C-Se bond. The palladium insertion into the imidoyl selenides 3.20 followed by intramolecular cyclization and subsequent aromatization via the elimination of HSePh lead to the formation of substituted phenanthridines 3.21.
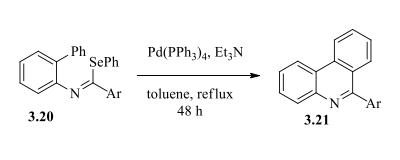
Pd-catalysed synthesis of phenanathridine | [Synthesis Reference(s)]
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 74, p. 6295, 1952 DOI: 10.1021/ja01144a521
Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 26, p. 865, 1989 DOI: 10.1002/jhet.5570260366
Tetrahedron Letters, 29, p. 5463, 1988 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)80787-X | [Safety Profile]
Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx. |
|
| Company Name: |
Energy Chemical
|
| Tel: |
021-021-58432009 400-005-6266 |
| Website: |
http://www.energy-chemical.com |
|