| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer | [CAS]
15956-28-2 | [Synonyms]
Rh2(OAc)4
Rh2(CH3CO2)4
RHODIUM(11) ACETATE
RHODIUM ACETATE DIMER
dirhodiumtetraacetate
rhodiumdiacetatedimer
tetraacetatodirhodium
Rhodium(Ⅱ) acetate dimer
RHODIUM(II) ACETATE DIMER
DIRHODIUM(II) TETRAACETATE
tetrakis(acetato)dirhodium
Rhodium(II)acetatedimer,99%
RHODIUMACETATEDIMER,ANHYDROUS
tetrakis(mu-acetato)di-rhodiu
tetrakis-(mu-acetato)dirhodium
TETRAKIS(ACETATO)DIRHODIUM(II)
Rhodium(II) acetate, dimer, 98+%
RHODIUM(II) ACETATE DIMER, POWDER
Rhodium(II)acetatedimeredihydrate
RHODIUM(II) ACETATE DIMER , (43%RH)
Rhodium(II) Acetate Dimer, Rh 46.6%
tetrakis[mu-(acetato-O:O')]dirhodium
TETRAKIS(ACETATO)DIRHODIUM(LL)HYDRATE
RhodiuM(II) acetate diMer,98% Rh2(OAc)4
Tetrakis(acetato) rhodium (II) –2-hydrat
tetrakis[micron-(acetato-o:o')]dirhodium
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer dihydrate, 98+%
Rhodium(II) acetate, dimer, Rh 46.2% min.
RhodiuM(Ⅱ) acetate diMer, anhydrous, 46% Rh
RHODIUM(II) ACETATE DIMER DIHYDRATE, ~43 % RH
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer, anhydrous, ca 46% Rh
RHODIUM(II) ACETATE DIMER, 99.99+% METALS BASIS
Rhodium(Ⅱ) acetate dimer ,99% [anhydrous, 46% Rh]
RhodiuM, tetrakis[M-(acetato-kO:kO')]di-, (Rh-Rh)
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer (46.5% Rh) for synthesis
Rhodium(II)acetate dimer rhodium(ii) acetate dimer
RhodiuM(II) acetate diMer, anhydrous, ca 46% Rh 1GR
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer 99.99% trace metals basis
RhodiuM(Ⅱ) acetate diMer, 42% Rh, Product of UMicore
RhodiuM(II) acetate diMer, anhydrous, ca 46% Rh 250MG
TETRAKIS[.MU.-(ACETATO-.KAPPA.O:.KAPPA.O'')]DI-RHODIUM
Dirhodium(II) Tetraacetate
Tetrakis(acetato)dirhodium(II)
Rhodium, tetrakis.mu.-(acetato-.kappa.O:.kappa.O)di-, (Rh-Rh)
Rhodium(II) acetate, dimer, Premion(R), 99.99% (metals basis), Rh 46.2% min
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer,Dirhodium tetraacetate, Tetrakis(acetato)dirhodium(II)
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer dihydrate,Dirhodium tetraacetate, Tetrakis(acetato)dirhodium(II) | [EINECS(EC#)]
226-843-6 | [Molecular Formula]
C8H12O8Rh2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00003538 | [MOL File]
15956-28-2.mol | [Molecular Weight]
441.99 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Emerald Green Powder | [Melting point ]
205 °C
| [storage temp. ]
Store below +30°C. | [solubility ]
Methanol + Water (Slightly) | [form ]
powder
| [color ]
Green to dark green | [Water Solubility ]
Soluble in aqueous solution like water. Slightly soluble in ethanol | [Hydrolytic Sensitivity]
0: forms stable aqueous solutions | [Exposure limits]
ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3
NIOSH: IDLH 2 mg/m3; TWA 0.001 mg/m3 | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic | [InChIKey]
ANSVJOOIUURYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
Emerald Green Powder | [Uses]
Rhodium (II) Acetate Dimer is used in the preparation of molybdenum triisopropylbenzoate isonicotinate which maintains ambivalent properties. | [Application]
Rhodium (II) Acetate Dimer is used in the preparation of molybdenum triisopropylbenzoate isonicotinate which maintains ambivalent properties. | [Preparation]
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer synthesis: A suspension of 10.0g. of Rh(OH)3.H20 in 400 ml. of glacial acetic acid dissolved upon refluxing for 18 hr. to give a deep emerald-green solution. Most of the acetic acid was evaporated on a steam bath; remaining traces mere removed by heating the residue at 120° for 1hr. The residue was then extracted with boiling acetone until the extract was colorless rather than bluish green. The extract was quickly passed through a fritted glass filter, concentrated on a steam bath to 1/3 its original volume, and placed in the freezing compartment of a refrigerator for 18hr. The resulting large dark green crystals were collected on a filter, washed with small portions of ice-cold acetone, and dried at 110°. When first collected, the product is the weak adduct [Rh(OOCCH3)2(CH3)2C0]2; however, acetone is lost fairly readily at room temperature and immediately in the drying oven; yield, 6.2g. (48%). | [Reactions]
Catalyst for insertion into C-H and X-H bonds.
Catalyst for Ylide generation.
Doyle Kirmse Reaction of Allylic Sulfides with Diazoalkane.
Claisen rearrangement.
Epoxides from aldehydes.
Synthesis of aziridines from allylic N-tosyloxycarbamates.
Rh/NHC catalyzed direct intermolecular arylation of C-H bonds.
Chiral Bronsted acid-Rh catalyzed three component reactions of diazo compounds with alcohols and imines.
Rh-catalyzed cyclopropenations of ynamides.
Tandem asymmetric aza-Darzens/ring-opening reactions.
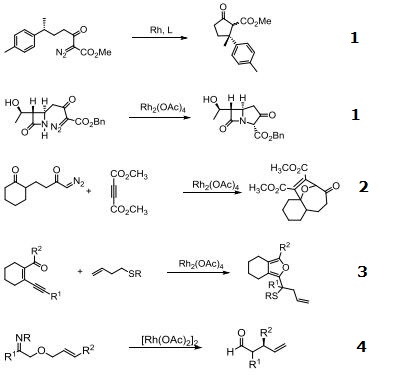
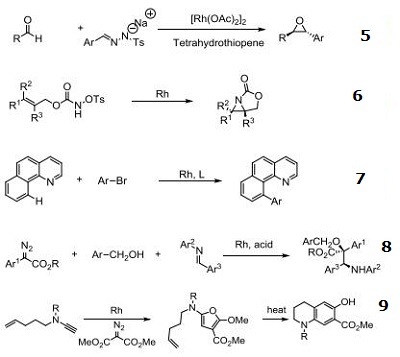
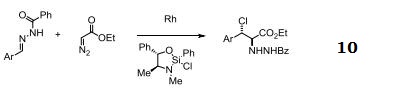 | [Purification Methods]
Dissolve 5g of the salt in boiling MeOH (ca 600mL) and filter. Concentrate it to 400mL and chill overnight at ca 0o to give dark green crystals of the MeOH adduct. Concentration of the mother liquors gives a further crop of [Rh(OAc)2]2.2MeOH. The adduct is then heated at 45o in a vacuum for 2hours (all MeOH is lost) to leave the emerald green crystals of the actetate. [Legzdins et al. J Chem Soc (A) 3322 1970.] Alternatively dissolve the acetate in glacial AcOH and reflux for a few hours to give an emerald green solution. Evaporate most of the AcOH on a steam bath, then heat the residue at 120o/1hour. Extract the residue with boiling Me2CO. Filter, concentrate to half its volume and keep at 0o/18hours. Collect the crystals, wash them with ice cold Me2CO and dry them at 110o. It is soluble in most organic solvents with which it forms adducts including Me3N and Me2S and gives solutions with different colours varying from green to orange and red. [UV: Johnson et al. Inorg Chem 2 960 1963, Beilstein 1 H 124.] |
|
|