| Identification | More | [Name]
N-(2-Diphenylmethoxyethyl)-N,N-dimethylamine hydrochloride | [CAS]
147-24-0 | [Synonyms]
2-(benzhydryloxy)-n,n-dimethylethylamine hydrochloride
2-DIPHENYLMETHOXY-N,N-DIMETHYLETHYLAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
ALLERGINA
BENADRYL HCL
BENZHYDRAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
DIMEDROLUM
DIPHENHYDRAMINE HCL
DIPHENHYDRAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
LABOTEST-BB LT00159910
LABOTEST-BB LT00248571
N-(2-DIPHENYLMETHOXYETHYL)-N,N-DIMETHYLAMIDE
N-[2-DIPHENYLMETHOXYETHYL]-N,N-DIMETHYLAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
N-(2-DIPHENYLMETHOXYETHYL)-N,N-DIMETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE
N,N-DIMETHYL-N-(2-DIPHENYLMETHOXYETHYL)-AMMONIUM CHLORIDE
2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethyl-ethanaminhydrochloride
2-(diphenylmethoxy)-n,n-dimethyl-ethylaminhydrochloride
Actifed
alpha-Hydroxydiphenylmethane-beta-dimethylaminoethyl ether hydrochloride
alpha-hydroxydiphenylmethane-beta-dimethylaminoethyletherhydrochloride
Ambenyl | [EINECS(EC#)]
205-687-2 | [Molecular Formula]
C17H22ClNO | [MDL Number]
MFCD00012479 | [Molecular Weight]
291.82 | [MOL File]
147-24-0.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white crystalline powder | [Melting point ]
168-172 °C
| [Boiling point ]
163-167 °C(Press: 3 Torr) | [density ]
1.0489 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.5800 (estimate) | [Fp ]
9℃ | [storage temp. ]
Desiccate at RT | [solubility ]
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol. | [form ]
Crystalline Powder or Adhering Crystals | [color ]
White | [PH]
pH(100g/L, 25℃) 4.0~5.5 | [Stability:]
Stable, but slowly darkens upon exposure to light. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. | [Water Solubility ]
1000 g/L | [Sensitive ]
Light Sensitive | [Usage]
H1-Histamine receptor antagonist. Antihistaminic; sedative, hypnotic | [Merck ]
3309 | [Contact allergens]
This antihistaminic drug with sedative properties is
mainly sold over the counter. It can be used both topically
(treatment of pruritis) and orally for its antiallergic,
antiemetic, sedative, and anticough properties.
Allergic or photoallergic contact dermatitis and fixeddrug
eruption seem to be rare. | [InChIKey]
PCHPORCSPXIHLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [LogP]
3.662 (est) | [CAS DataBase Reference]
147-24-0(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
diphenhydramine hydrochloride(147-24-0) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
147-24-0(EPA Substance) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
white crystalline powder | [Uses]
A histamine H1-receptor antagonist. | [Uses]
antihistamine, sedative, treatment of allergic | [Uses]
Diphenhydramine is a H1-histamine receptor antagonist. Diphenhydramine is categorized as an antihistaminic; sedative, hypnotic. | [Uses]
H1-Histamine receptor antagonist. Antihistaminic; sedative, hypnotic | [Definition]
ChEBI: The hydrochloride salt of diphenhydramine. | [General Description]
White or almost-white crystalline powder. Odorless with a bitter numbing taste. pH (5% aqueous solution) 4-6. | [Reactivity Profile]
DIPHENHYDRAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE(147-24-0) gives acidic solutions in water. Neutralizes bases. May react with strong oxidizing and strong reducing agents. May catalyze organic reactions. Slowly darkens on exposure to light. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Water soluble. Aqueous solutions are acidic. | [Biological Activity]
H 1 receptor antagonist. Antihistamine. | [Fire Hazard]
Flash point data for this chemical are not available; however, DIPHENHYDRAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE is probably combustible. | [Originator]
Benadryl,Parke Davis,US,1946 | [Application]
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is used as an antihistamine and for its antieholinergie (drying) and sedative effects; for allergic conjunctivitis due to foods; for mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema; for amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma; for dermatographism; in therapy for anaphylaetie reactions adjunctive to epinephrine and other standard measures after the acute manifestations have been controlled; for active and prophylactie treatment of motion sickness; for parkinsonism; an antiemetic; has local anesthetic properties; in preparations for the relief of cough; in the prevention and treatment of radiation sickness, nausea and vomiting; for treatment of allergie cheilitis and stomatitis. | [Preparation]
Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride synthesis is a four-step sequence starting with a Grignard reaction.
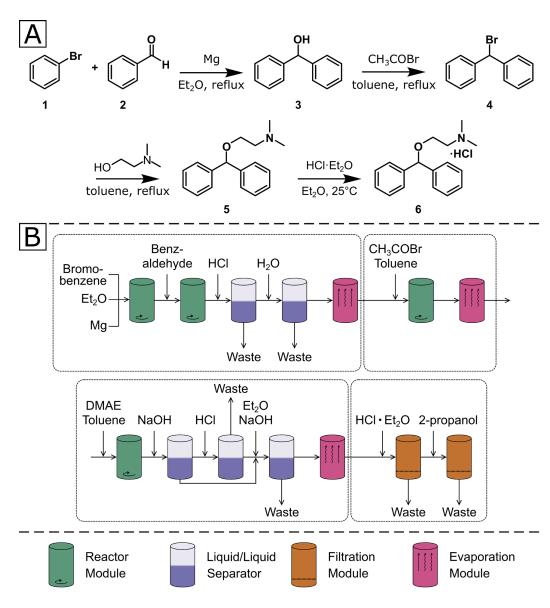
Synthesis of Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride 6.
A) modified synthetic route to diphenhydramine hydrochloride.
B) Sequence of unit operations required for the synthesis. The dotted boxes denote the four stages of the synthesis. DMAE: dimethylaminoethanol.
Organic synthesis in a modular robotic system driven by a chemical programming language | [Manufacturing Process]
As described in US Patent 2,421,714: (a) benzhydryl
omide is first prepared
as follows: 840 parts by weight of diphenylmethane is heated to 130°C with
stirring. In the presence of a 200 watt electric light 6 inches from the flask,
880 parts of
omine is added slowly. Liberation of H
occurs and addition
requires 1 hour and 45 minutes. The temperature is maintained at 130°C for
an additional 30 minutes. A fine stream of air is blown in to remove H
and
2 while the reaction mixture cools. Benzene (180 parts) is added and the
solution used immediately in (b) below.
If pure benzhydryl
omide is desired the above reaction mixture is dissolved
in ether, washed with water, sodium carbonate solution and finally with water.
The ether is removed, benzene added and distilled off and the benzhydryl
omide distilled in vacuo. Yield 85%.
(b) 490 parts β-dimethylaminoethanol and 530 parts of anhydrous sodium
carbonate are heated to 110°C with stirring. The addition of the benzene�benzhydryl
omide mixture is then begun. The temperature is raised to 120°-
125°C. As reaction takes place carbon dioxide is evolved, the addition requires1? hours. The mixture is kept at 125°C for 5 hours additional time. After
cooling, 3,000 parts of water is added and the mixture stirred until the
inorganic salts are dissolved. The mixture is transferred to a large separatory
funnel and 1,500 parts of ether added. The ether solution is washed several
times with water and then the ether layer extracted with 1 to 4 hydrochloric
acid. The acid solution is treated with 30 parts of Darco and 30 parts Filter-Cel
and filtered.
The free base is liberated from the acid solution with 20% sodium hydroxide
solution and taken up in ether. The ether layer is washed with water, saturated
with NaCl and then shaken with solid potassium hydroxide. The ether is
removed by distillation, 200 parts of benzene added and distilled off. The
residue is distilled in vacuo and the fraction 150°-165°C/2 mm is collected
and amounts to 433 parts. The hydrochloride salt is prepared by dissolving
the free base in anhydrous ether and slowly adding an alcoholic solution of
hydrogen chloride. The solid is recrystallized from absolute alcohol-ether
mixture or isopropanol-ether mixture and has a MP of 161-162°C. | [Brand name]
Benadryl (Parke-Davis). | [Therapeutic Function]
Antihistaminic | [Health Hazard]
Potentially. If taken in large quantities, diphenhydramine can cause severe agitation and confusion, fever, skin flushing, problems with vision, dry mouth, dry eyes, and inability to sweat. Overdoses can lead to high heart rates, abnormal heart rhythms, seizures, and death.
If given to elderly patients, diphenhydramine can cause confusion and agitation. Because of this, diphenhydramine is not recommended in elderly patients for insomnia or treatment for the common cold; though it should still be given in cases of allergic reaction. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
H1 histamine receptor antagonistDiphenhydramine hydrochloride (DPH) is an antihistaminic agent that relieves symptoms of hypersensitive reactions. It exhibits antimuscarinic and marked sedative effects. DPH is also used to prevent nausea, vomiting and vertigo of various causes. In addition, it acts as a potential therapeutic for insomnia. | [Veterinary Drugs and Treatments]
In veterinary medicine, diphenhydramine is used principally for its
antihistaminic
effects, but also for other pharmacologic actions. Its
sedative effects can be of benefit
in treating the agitation (pruritus,
etc.) associated with allergic responses. It has also been used for
treatment and prevention of motion sickness and as an antiemetic
in small animals. It has been suggested for use as adjunctive treatment
of aseptic laminitis in cattle and it may be useful as an adjunctive
treatment for feline pancreatitis. For other suggested uses, refer
to the Dosage section below. | [storage]
Desiccate at RT | [Toxics Screening Level]
The CORRECTED Screening Level for DIPHENHYDRAMINE HCL (CAS # 147-24-0) has
been set at 50 μg/m3 (annual average) based on the particulate standard. |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R22:Harmful if swallowed. | [Safety Statements ]
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing . | [RIDADR ]
2811 | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
KR7000000
| [HS Code ]
29221990 | [Safety Profile]
Poison by ingestion,
subcutaneous, intravenous, and
intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic
effects by ingestion or skin contact:
arrhythmias, ataxia, blood pressure
elevation, convulsions, distorted
perceptions, eye effects, and hallucinations.
Experimental teratogenic and reproductive
effects. Questionable carcinogen with
experimental tumorigenic data. When heated
to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes
of NO, and HCl. See also ESTERS and
ETHERS. | [Toxicity]
LD50 orally in rats: 500 mg/kg (Gruhzit, Fisken) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Description]
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is an antihistamine drug having the chemical name 2-(Diphenylmethoxy)- N,N-dimethylethylamine hydrochloride. It occurs as a white, crystalline powder, is freely soluble in water and alcohol and has a molecular weight of 291.82.
The molecular formula is C17H21NO·HCl and the structural formula is as follows:
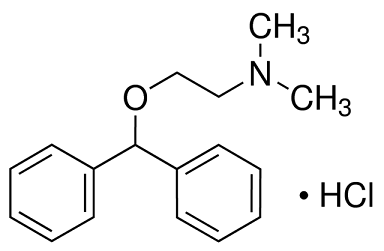
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the parenteral form is a sterile, pyrogen-free solution available in a concentration of 50 mg of diphenhydramine hydrochloride per mL. The solutions for parenteral use have been adjusted to a pH between 5.0 and 6.0 with either sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid and contains 0.1 mg/mL benzethonium chloride as a germicidal agent.
| [Clinical Pharmacology]
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is an antihistamine with anticholinergic (drying) and sedative side effects. Antihistamines appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells. Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the injectable form has a rapid onset of action. Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is widely distributed throughout the body, including the CNS. A portion of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine, while the rest is metabolized via the liver. Detailed information on the pharmacokinetics of Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride Injection is not available.
| [Indications and Usage]
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the injectable form is effective in adults and pediatric patients, other than premature infants and neonates, for the following conditions when diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the oral form is impractical.
- antihistaminic: For amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma, in anaphylaxis as an adjunct to epinephrine and other standard measures after the acute symptoms have been controlled, and for other uncomplicated allergic conditions of the immediate type when oral therapy is impossible or contraindicated.
- Motion Sickness: For active treatment of motion sickness.
- Antiparkinsonism: For use in parkinsonism, when oral therapy is impossible or contraindicated, as follows: parkinsonism in the elderly who are unable to tolerate more potent agents; mild cases of parkinsonism in other age groups, and in other cases of parkinsonism in combination with centrally acting anticholinergic agents.
| [Drug overdose]
Antihistamine overdosage reactions may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation. Stimulation is particularly likely in pediatric patients. Atropine-like signs and symptoms; dry mouth; fixed, dilated pupils; flushing; and gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur. Stimulants should not be used. Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension.
| [Contraindications]
- Use in Neonates or Premature Infants: This drug should not be used in neonates or premature infants.
- Use in Nursing Mothers: Because of the higher risk of antihistamines for infants generally, and for neonates and prematures in particular, antihistamine therapy is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
- Use as a Local Anesthetic: Because of the risk of local necrosis, this drug should not be used as a local anesthetic.
- Antihistamines are also contraindicated in the following conditions: Hyper sensitivity to diphenhydramine hydrochloride and other antihistamines of similar chemical structure.
|
|
|