| Identification | More | [Name]
4-Amino-3-phenylbutyric acid hydrochloride | [CAS]
1078-21-3 | [Synonyms]
4-AMINO-3-PHENYLBUTANOIC ACID HYDROCHLORIDE
4-AMINO-3-PHENYLBUTIRIC ACID
4-AMINO-3-PHENYL-BUTYRIC ACID
4-AMINO-3-PHENYLBUTYRIC ACID HCL
4-AMINO-3-PHENYL BUTYRIC ACID HYDROCHLORIDE
FENIBUT
PHENIBUT
TIMTEC-BB SBB001567
4-amino-3-phenylbutanoicacid
4-amino-3-phenyl-butyricaci
beta-(aminomethyl)-benzenepropanoicaci
beta-(aminomethyl)benzenepropanoicacid
beta-(aminomethyl)hydrocinnamicacid
beta-phenyl-gamma-aminobutyrate
beta-phenyl-gamma-aminobutyricacid
fenigam
fenigama
pgaba
phenigam
phenigama | [EINECS(EC#)]
214-079-6 | [Molecular Formula]
C10H14ClNO2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00456233 | [Molecular Weight]
215.68 | [MOL File]
1078-21-3.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
252.5°C (rough estimate) | [Boiling point ]
311.75°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1.1248 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.5710 (estimate) | [solubility ]
Free base: 35 mg/mL in DMSO (195.29 mM) at 25 °C (SellekChem, 2019).Hydrochloride salt (Cayman, 2016): 25 mg/ml in DMF; 20 mg/ml in DMSO; 14 mg/ml in ethanol; 10 mg/mL in PBS (pH 7.2). | [form ]
solid | [pka]
4.10±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
White | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C10H13NO2/c11-7-9(6-10(12)13)8-4-2-1-3-5-8/h1-5,9H,6-7,11H2,(H,12,13) | [InChIKey]
DAFOCGYVTAOKAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
C(O)(=O)CC(C1=CC=CC=C1)CN | [CAS DataBase Reference]
1078-21-3(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Benzenepropanoic acid, .beta.-(aminomethyl)- (1078-21-3) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [HazardClass ]
IRRITANT | [HS Code ]
2922498590 | [Toxicity]
TDLo orl-hmn: 5 mg/kg:CNS BEXBAN 57,52,64 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Phenibut, also known as fenibut, phenigamma, and beta-phenyl-gamma-aminobutyric acid, is a derivative of the neurotransmitter GABA. It was developed in Russia,and there it has been used clinically since the 1960s to treat anxiety and related conditions,including insomnia(Lapin�����,2001). Phenibut has anxiolytic properties and is commonlycompared to benzodiazepines and baclofen.Structurally,phenibut issimilar to GABA, with the addition of the phenyl ring. This allows thecompound to more easily cross the blood-brain barrier, but also changesits activity profile (Shulgina,1986). Scientific studies demonstrate that phenibut can be safely used to treat anxiety, depression,epilepsy, speech disorders, and insomnia. | [Uses]
4-amino-3-phenylbutanoic acid (cas# 1078-21-3) is a GABAA receptor agonist, used for treatment of disorders influenced by dysfunction of pancreatic β cells and also used in combination with other agents. | [Application]
Phenibut is an anxiolytic and nootropic drug, discovered in the Soviet Union used to treat several psychiatric disorders. It can be used in the treatment of anxiety, depression, asthenia, post-traumatic stress disorder, stuttering, and vestibular disorders. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Phenibut is an organonitrogen compound and an organooxygen compound. It is functionally related to a gamma-amino acid. | [Preparation]
Phenibut was synthesized by Perekalin and his associates at the Department of Organic Chemistry of the Herzen Pedagogic Institute in St. Petersburg, the Russian Federation. In initial publications phenibut was known as phenigamma (Lapin, 2001, V. V. Perekalin, 1954).
Fenibut synthesis: from benzoyl chloride and ethyl acetoacetate as raw materials, through condensation and hydrolysis of ethyl benzoyl acetate, and then condensation of benzaldehyde and nitromethane to generate trans-nitrostyrene, and then the two are combined. Micheal addition, the adduct is then catalytically hydrogenated with Raney nickel, and finally hydrolyzed in concentrated hydrochloric acid to produce phenibate.
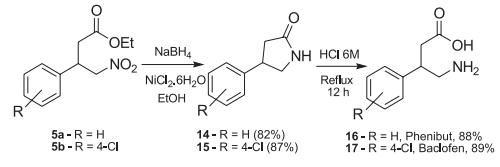
Synthesis of Phenibut (16) and Baclofen (17). | [Side effects]
When taken by mouth: Phenibut is likely unsafe. Phenibut can cause many side effects, including reduced consciousness, dizziness, nausea, poor balance, and fatigue. Taking large doses can cause trouble breathing, unconsciousness, and death.
Phenibut can cause dependence. People who use phenibut for 3 days or more and then stop taking it might experience withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can include decreased appetite, nausea, muscle aches, fast heart rate, anxiety, agitation, trouble sleeping, and seizures.
| [Safety Profile]
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Human systemic effects by ingestion: somnolence, hallucinations, distorted perception. Used as a mood elevator and tranquilizer. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. | [Drug interactions]
Pregabalin (Lyrica) interacts with Phenibut: Phenibut acts on the brain in a similar way to pregabalin. Taking these two chemicals together might increase the risk for side effects.
Sedative medications (CNS depressants) interacts with Phenibut: Phenibut might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Some medications, called sedatives, can also cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking phenibut with sedative medications might cause breathing problems and/or too much sleepiness.
| [Regulatory Status]
USA - Phenibut is still an uncontrolled substance in the United States, and it is legal to sell and possess phenibut. It has not been approved for clinical use in the United States.
Europe - Unscheduled. It is not regulated by the European Medicines Agency. However, some nootropic substances such as piracetam are available only on prescription in some European Union countries and are freely available in others.
Russia - Phenibut is a licensed prescription medication used for a variety of conditions including anxiety, insomnia, post-traumatic stress disorders, depression, stuttering, tics, attention deficit disorders, and vestibular disorders. Russian cosmonauts were reported to have been supplied with the substance to help relieve tension, anxiety and fear (Buckley 2006). |
|
|