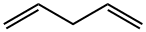
1,4-PENTADIENE synthesis
- Product Name:1,4-PENTADIENE
- CAS Number:591-93-5
- Molecular formula:C5H8
- Molecular Weight:68.12

109-66-0
438 suppliers
$10.00/25ml
513-35-9
183 suppliers
$12.00/25g
1574-41-0
41 suppliers
$239.00/1g
2004-70-8
57 suppliers
$72.00/1mL

591-93-5
45 suppliers
$38.50/1g

627-20-3
50 suppliers
$42.70/1g

646-04-8
64 suppliers
$45.00/500mg

109-67-1
172 suppliers
$35.00/25 g
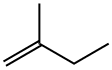
563-46-2
90 suppliers
$40.00/5 g

563-45-1
126 suppliers
$15.00/5 g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with hydrogen at 525; under 760.051 Torr; for 8 h;Reagent/catalyst;
Steps:
27 Example 27: Normal Pentane Dehydrogenation
All of the catalysts from Examples 2-25 (Catalysts A-X) were tested for dehydrogenation of n-pentane in a fixed bed reactor. Each of the catalysts (0.75 grams each) were tested for 8 hours on stream at 525° C. under atmospheric pressure, which reflects the relatively high stability of these catalysts. A feed of liquid n-pentane was supplied at a rate of 0.04 milliliters per minute (mL/min), such that the weight hourly space velocity was 2 per hour. The diluent gas used for each of the tests was a mixture of hydrogen (H2) and nitrogen (N2). The diluent gas was provided at a flow rate of 81.4 mL/min. For each of the catalysts, the ratio of hydrogen to steam in the diluent gas was varied as follows: 81.4 mL/min of H2 and 0 mL/min of N2 (pure hydrogen); 71.4 mL/min of H2 and 10 mL/min of N2; 61.4 mL/min of H2 and 20 mL/min of N2; 51.4 mL/min of H2 and 30 mL/min of N2; 41.4 mL/min of H2 and 40 mL/min of N2; 31.4 mL/min of H2 and 50 mL/min of N2; 21.4 mL/min of H2 and 60 mL/min of N2; 11.4 mL/min of H2 and 70 mL/min of N2; and 0 mL/min of H2 and 81.4 mL/min of N2 (pure nitrogen). It was found that a ratio of 11:70 of H2:N2 in the diluent gas provided maximum yields of the desired product (n-pentenes), and the results corresponding to this ratio are provided in Table 2. As shown in Table 2, although control Catalyst A (zirconia-free) exhibited the greatest dehydrogenation activity (conversion of n-pentane), it also exhibited relatively high hydroisomerization and isomerization activity (producing isopentane and branched pentenes) along with cracking and hydrocracking activity. In contrast, n-pentane conversion for zirconia-containing catalysts (Catalysts B through F) resulted in greater combined selectivity for normal pentenes and pentadienes and in a greater yield for normal pentenes (reaching a maximum of 45.6 mol. % and a minimum of less than 3 mol % selectivity for branched pentenes) in comparison to control Catalyst A. Furthermore, catalysts containing zirconia and ion-exchanged with potassium (Catalysts J through X) yielded greater selectivity for normal pentenes and pentadienes and lesser selectivity (less than 4 mol. %) for branched pentenes.
References:
Saudi Arabian Oil Company US2021/69683, 2021, A1 Location in patent:Paragraph 0056; 0122; 0123

109-66-0
438 suppliers
$10.00/25ml

1574-41-0
41 suppliers
$239.00/1g

2004-70-8
57 suppliers
$72.00/1mL

591-93-5
45 suppliers
$38.50/1g

627-20-3
50 suppliers
$42.70/1g

646-04-8
64 suppliers
$45.00/500mg

109-67-1
172 suppliers
$35.00/25 g

96-47-9
438 suppliers
$15.00/25mL
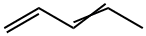
504-60-9
89 suppliers
$180.00/1ml
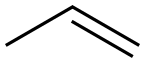
187737-37-7
1 suppliers
inquiry

591-93-5
45 suppliers
$38.50/1g

871-28-3
18 suppliers
inquiry

591-93-5
45 suppliers
$38.50/1g