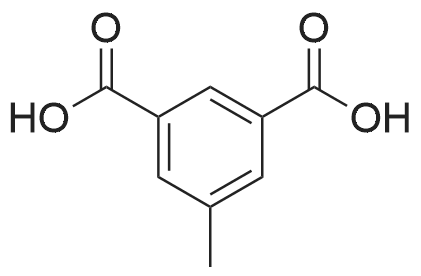
| 96% |
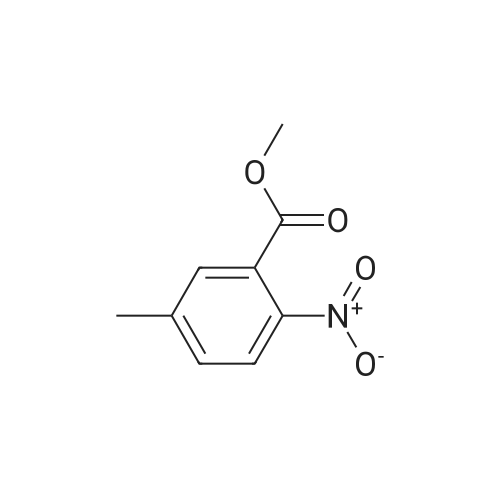
With Zn-MCM-22 catalyst; at 100 - 280℃; under 15001.5 Torr; for 6h;Inert atmosphere; Large scale; |
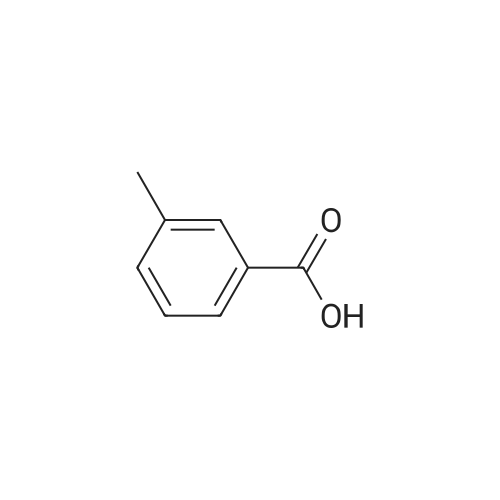
In a 2-cubic stirred reactor, 486 kg of m-methylbenzoic acid, 1314 kg of diethylamine was added,Steam jacket heated to 100 , open stirring, and keep the stirring speed of 120 r / min, to be methyl benzoic acid in diethylamine completely dissolved, the analysis of raw materials without free m-methyl benzoic acid raw materials.The reactor is filled with Zn-MCM-22 catalyst with an effective volume of about 2 m3, about 1.6 tons of catalyst, and the reactor is chargedAfter full nitrogen, open the circulating compressor, nitrogen circulation of 9m3 / min. The reactor pressure was maintained at 2.0 MPa through the reactor upper pressure regulator, and the reactor catalyst bed temperature was slowly raised to 250 C by means of a heat exchanger. Start the feed pump to 250kg / h liquid flow rate of raw materials into the raw material preheater, the material heated to 280 , through the heat exchanger to the reactor gas phase discharge temperature down to 150 into the gas-liquid separator, In the separator, most of the water as the liquid phase in the bottom of the separator, the gas phase for the circulating nitrogen and a small amount of organic amine raw materials, after heating and pressure, re-from the bottom of the reactor into the reactor, countercurrent contact with the reaction product to provide the reaction The required heat, and timely out of the organic ammonium salt from the water out of the reactor to promote the progress of the reaction.The product at the bottom of the reactor enters the product purification column and the impurities are removed by distillation to obtain N, N-diethyl-m-tolueneAmide products. Through 6 hours of continuous industrial reaction, refined after the product 550 kg, according to m-methyl benzoic acid, the product yield 96%. |
|
|
Example 2; Preparation of N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide; A 10 liter stirred autoclave (Buechi) was initially charged with 3.28 kg of diethylamine (45 mol) and, with sufficient cooling, 4.08 kg of m-toluic acid (30 mol) were introduced gradually. In a strongly exothermic reaction, the m-toluic acid diethylammonium salt formed, and was kept at 50 C.The molten salt thus obtained was pumped through the reaction tube continuously at 3 l/h at a working pressure of 35 bar and exposed to a microwave power of 2.5 kW, 94% of which was absorbed by the reaction mixture. The residence time of the reaction mixture in the irradiation zone was approx. 57 seconds. At the end of the reaction tube, the reaction mixture had a temperature of 295 C.A conversion of 91% of the m-toluic acid used was attained. The crude product was pale yellow in color and contained <2 ppm of iron. After distillative removal of water of reaction and excess diethylamine and vacuum distillation of the crude product, 4.8 kg of N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide were obtained with a purity of 99%. |
|
|
Example 4Preparation of N,N-diethyl-m-toluamideA 500 ml three-neck flask with gas inlet tube, stirrer, internal thermometer and pressure equalizer was initially charged with 136.2 g of m-toluic acid (1 mol) which were neutralized cautiously with 109.71 g of diethylamine (1.5 mol). In a strongly exothermic reaction, the m-toluic acid N,N-diethylammonium salt formed. Aliquots were taken from this stock solution and adjusted to the water contents specified in table 4 by adding water.2 ml of the ammonium salt or of the aqueous solutions thereof were in each case heated to a temperature of 250 C. in the microwave reactor, which established a pressure of about 20 bar. On attainment of thermal equilibrium (after approx. 1 minute), the samples were kept at this temperature and this pressure under further microwave irradiation for 20 minutes. By means of 1H NMR signal integration, the relative proportions of reactants and product in the reaction mixture were determined. The conversion rates achieved are reproduced in the last column of table 4. TABLE 4 m-Toluic acid Water Molar Conversion to N,N-dimethyl- [% by ratio of N,N-dimethyl- Reaction ammonium salt wt.] acid:amine decanamide (12) 100% by wt. 0 1:1.5 5 mol % (13) 75% by wt. 25 1:1.5 15 mol % (14) 65% by wt. 35 1:1.5 19 mol % (15) 51% by wt. 49 1:1.5 22 mol % |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping