Alternatived Products of [ 63139-21-9 ]

Product Citations
Synthesis and biological evaluation of structurally diverse 6-aryl-3-aroyl-indole analogues as inhibitors of tubulin polymerization
Wen Ren
;
Yuling Deng
;
Jacob D. Ward
, et al.
Eur. J. Med. Chem.,2024,263,115794.
DOI:
10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115794
More
Abstract: The synthesis and evaluation of small-molecule inhibitors of tubulin polymerization remains a promising approach for the development of new therapeutic agents for cancer treatment. The natural products colchicine and combretastatin A-4 (CA4) inspired significant drug discovery campaigns targeting the colchicine site located on the beta-subunit of the tubulin heterodimer, but so far these efforts have not yielded an approved drug for cancer treatment in human patients. Interest in the colchicine site was enhanced by the discovery that a subset of colchicine site agents demonstrated dual functionality as both potent antiproliferative agents and effective vascular disrupting agents (VDAs). Our previous studies led to the discovery and development of a 2-aryl-3-aroyl-indole analogue (OXi8006) that inhibited tubulin polymerization and demonstrated low nM IC50 values against a variety of human cancer cell lines. A water-soluble phosphate prodrug salt (OXi8007), synthesized from OXi8006, displayed promising vascular disrupting activity in mouse models of cancer. To further extend structure-activity relationship correlations, a series of 6-aryl-3-aroyl-indole analogues was synthesized and evaluated for their inhibition of tubulin polymerization and cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines. Several structurally diverse molecules in this small library were strong inhibitors of tubulin polymerization and of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. One of the most promising analogues (KGP591) caused significant G2/M arrest of MDA-MB-231 cells, disrupted microtubule structure and cell morphology in MDA-MB-231 cells, and demonstrated significant inhibition of MDA-MB-231 cell migration in a wound healing (scratch) assay. A phosphate prodrug salt, KGP618, synthesized from its parent phenolic precursor, KGP591, demonstrated significant reduction in bioluminescence signal when evaluated in vivo against an orthotopic model of kidney cancer (RENCA-luc) in BALB/c mice, indicative of VDA efficacy. The most active compounds from this series offer promise as anticancer therapeutic agents.
Keywords:
Inhibitors of tubulin polymerization ;
Vascular disrupting agents ;
Indole synthesis ;
Molecular docking ;
Antiproliferative agents ;
Inhibitors of cell migration
Purchased from AmBeed:
128796-39-4 ;
10365-98-7 ;
98-80-6 ;
98437-24-2 ;
5720-05-8 ;
64-86-8 ;
13331-27-6 ;
206551-43-1 ;
63139-21-9 ;
622864-48-6 ;
5720-07-0 ;
87199-18-6 ;
30418-59-8 ;
4521-61-3 ;
4521-61-3 ;
87199-18-6 ;
64-86-8 ;
64-86-8 ;
128796-39-4 ;
5720-05-8 ;
64-86-8
...More

Product Details of [ 63139-21-9 ]
| CAS No. : | 63139-21-9 |
MDL No. : | MFCD00859377 |
| Formula : |
C8H11BO2
|
Boiling Point : |
- |
| Linear Structure Formula : | C2H5C6H4B(OH)2 |
InChI Key : | RZCPLOMUUCFPQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| M.W : |
149.98
|
Pubchem ID : | 2734352 |
| Synonyms : |
|
Application In Synthesis of [ 63139-21-9 ]
* All experimental methods are cited from the reference, please refer to the original source for details. We do not guarantee the accuracy of the content in the reference.
- Downstream synthetic route of [ 63139-21-9 ]
- 1
-
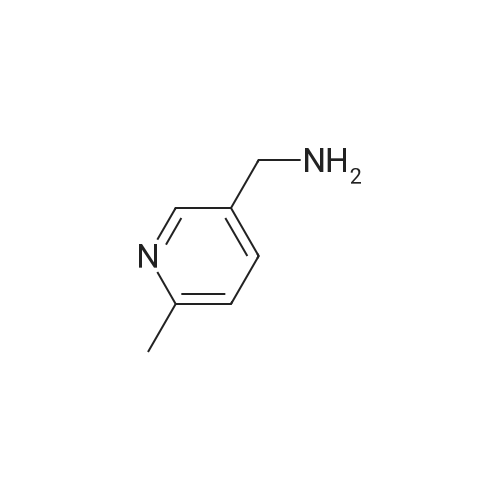 [ 56622-54-9 ]
[ 56622-54-9 ]

-
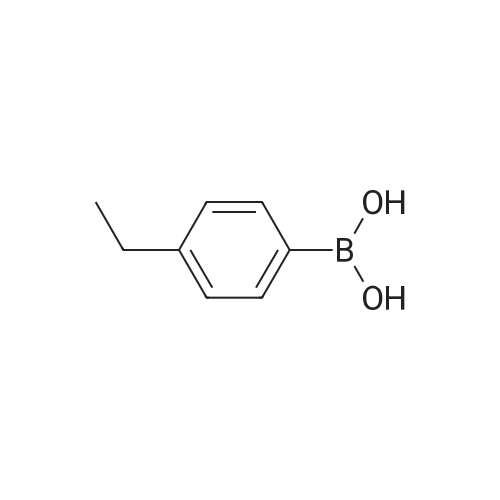 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
 [ 916587-13-8 ]
[ 916587-13-8 ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
| 4% |
copper diacetate; In 1,2-dichloro-ethane; at 20℃; for 24h; |
GP-1b: Synthesis of secondary amines by reaction of a boronic acid with a primary amineThe primary amine 2 is dissolved in dichloroethane. 1.0 eq. copper-(II)-acetate and optionally 1.0 eq. 2.6 lutidine are added followed by boronic acid 1. After stirring for one day at RT, the EPO <DP n="109"/>solvent is removed at the evaporator. After addition of approx. 20-80 ml 2N NaOH solution and approx. 20-80 ml dichloromethane, the white precipitate is removed by centrifugation. The aqueous phase is extracted three times with dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are dried over magnesium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The desired secondary amine 3 was obtained, which was used either directly for further reactions or purified by flashchromatography or HPLC.; Step 2:900 mg (7.37 mmol) of the crude compound 2 is reacted according to GP-1B with A- ethylphenylboronic acid (3) without lutidine yielding 788 mg of crude product. After purification by flash chromatography 60.4 mg (0.27 mmol; 4%) of 4 could be obtained. |
- 2
-
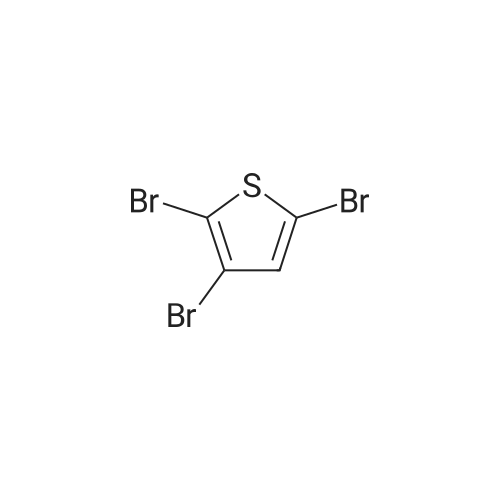 [ 3141-24-0 ]
[ 3141-24-0 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
 [ 1208902-91-3 ]
[ 1208902-91-3 ]
- 3
-
 [ 3141-24-0 ]
[ 3141-24-0 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
 [ 1208902-81-1 ]
[ 1208902-81-1 ]
- 4
-
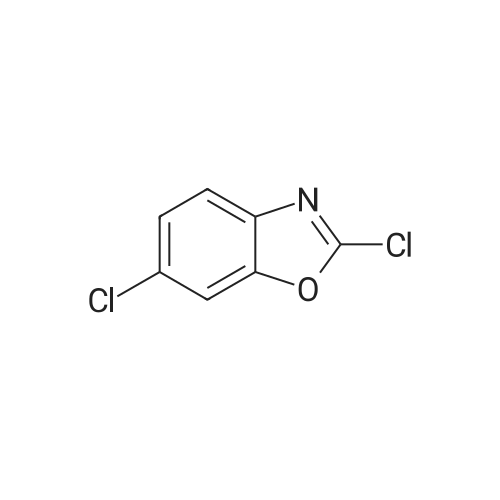 [ 3621-82-7 ]
[ 3621-82-7 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
 [ 1421278-27-4 ]
[ 1421278-27-4 ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
| 81% |
With tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); potassium carbonate; In 1,4-dioxane; water; at 80℃; for 6h;Inert atmosphere; |
General procedure: A 1,4-dioxane solution (3?mL) of 1, arylboronic acid (1.2?equiv), aqueous K2CO3 (2.0?M, 1.0?mL) and Pd(PPh3)4 (3?mol?percent) was heated at 80?°C for 6?h under argon atmosphere. After cooling to 20?°C, H2O was added and the reaction mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3×25?mL). The organic layers were dried (Na2SO4), filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by column chromatography (silica gel, heptane/EtOAc).#10; |
- 5
-
 [ 3621-82-7 ]
[ 3621-82-7 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
 [ 1421278-32-1 ]
[ 1421278-32-1 ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
| 88% |
With tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); potassium carbonate; In 1,4-dioxane; water; at 120℃; for 8h;Inert atmosphere; |
General procedure: A 1,4-dioxane solution (3?mL) of 1, arylboronic acid (2.2?equiv), aqueous K2CO3 (2.0?M, 1.0?mL) and Pd(PPh3)4 (6?mol?percent) was heated at 120?°C for 8?h under argon atmosphere. After cooling to 20?°C, H2O was added and the reaction mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3×25?mL). The organic layers were dried (Na2SO4), filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by column chromatography (silica gel, heptane/EtAOc).#10; |
- 6
-
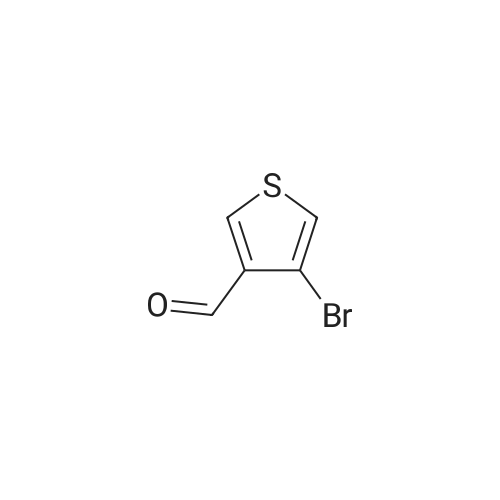 [ 18791-78-1 ]
[ 18791-78-1 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
4-(4-ethylphenyl)thiophene-3-carbaldehyde
[ No CAS ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
| 64% |
With tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); sodium carbonate; In ethanol; water; toluene; at 128℃; for 5h;Sealed tube; Inert atmosphere; |
Step 1: 4-(4-ethylphenyl)thiophene-3-carbaldehyde A mixture of <strong>[18791-78-1]3-bromo-4-formylthiophene</strong> (0.62 g, 3.18 mmol) and 4-ethylphenylboronic acid (0.95 g, 6.36 mmol) in toluene (12 mL), EtOH (12 mL) and aqueous Na2CO3 solution (2 M, 3.18 mL, 6.36 mmol) in a seal tube was deoxygenated under reduced pressure and flushed with argon for 3 times, followed by addition of Pd(PPh3)4 (184 mg, 0.16 mmol) and deoxygenated again. The resulting solution was stirred at 128 C. in an oil bath for 5 hour. The reaction progress was monitored by TLC/LCMS (ethyl acetate/petroleum ether=1:6). The reaction was partitioned between ethyl acetate and water. Collected the organic phases and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was applied onto a silica gel column with ethyl acetate/petroleum ether (1:10). This resulted in 440 mg (64%) of 4-(4-ethylphenyl)thiophene-3-carbaldehyde as light yellow oil. |
| 64% |
With tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); sodium carbonate; In ethanol; water; toluene; at 128℃; for 5h;Inert atmosphere; Sealed tube; |
A mixture of <strong>[18791-78-1]3-bromo-4-formylthiophene</strong> (0.62 g, 3.18 mmol) and 4-ethylphenylboronic acid (0.95 g, 6.36 mmol) in toluene (12 mL), EtOH (12 mL) and aqueous Na2CO3 solution (2 M, 3.18 mL, 6.36 mmol) in a seal tube was deoxygenated under reduced pressure and flushed with argon for 3 times, followed by addition of Pd(PPh3)4 (184 mg, 0.16 mmol) and deoxygenated again. The resulting solution was stirred at 128 C. in an oil bath for 5 hour. The reaction progress was monitored by TLC/LCMS (ethyl acetate/petroleum ether=1:6). The reaction was partitioned between ethyl acetate and water. Collected the organic phases and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was applied onto a silica gel column with ethyl acetate/petroleum ether (1:10). This resulted in 440 mg (64%) of 4-(4-ethylphenyl)thiophene-3-carbaldehyde as light yellow oil. |
| 64% |
With tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); sodium carbonate; In ethanol; water; toluene; at 128℃; for 5h;Sealed tube; Inert atmosphere; |
A mixture of <strong>[18791-78-1]3-bromo-4-formylthiophene</strong> (0.62 g, 3.18 mmol) and 4- ethylphenylboronic acid (0.95 g, 6.36 mmol) in toluene (12 mL), EtOH (12 mL) and aqueous a2C03 solution (2 M, 3.18 mL, 6.36 mmol) in a seal tube was deoxygenated under reduced pressure and flushed with argon for 3 times, followed by addition of Pd(PPh3)4 (184 mg, 0.16 mmol) and deoxygenated again. The resulting solution was stirred at 128C in an oil bath for 5 hour. The reaction progress was monitored by TLC/LCMS (ethyl acetate/petroleum ether = 1 :6). The reaction was partitioned between ethyl acetate and water. Collected the organic phases and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was applied onto a silica gel column with ethyl acetate/petroleum ether (1 : 10). This resulted in 440 mg (64%) of 4-(4-ethylphenyl)thiophene-3 - carbaldehyde as light yellow oil. |
- 7
-
 [ 18791-78-1 ]
[ 18791-78-1 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
(4-(4-ethylphenyl)thiophen-3-yl)methanol
[ No CAS ]
- 8
-
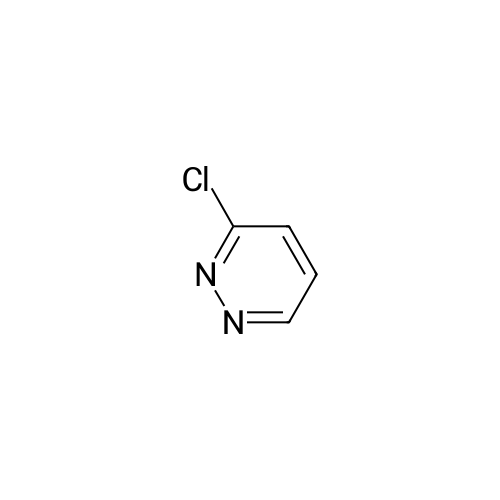 [ 1120-95-2 ]
[ 1120-95-2 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
3-(4-ethylphenyl)pyridazine
[ No CAS ]
- 9
-
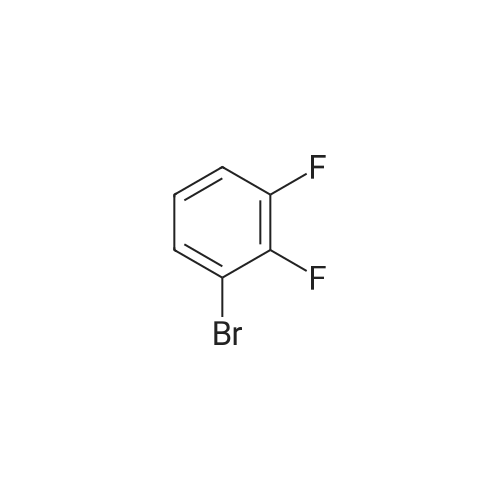 [ 38573-88-5 ]
[ 38573-88-5 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
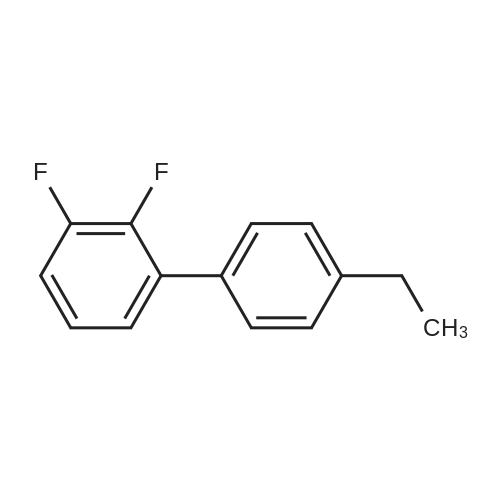 [ 1178550-13-4 ]
[ 1178550-13-4 ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
|
With tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); potassium carbonate; In water; N,N-dimethyl-formamide; at 80℃; for 8h; |
To a 500 mL three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, a condenser and a magnetic stirrer were added 33.0 (0.21 mol) of 4-ethylbenzeneboronic acid, 38.6 g (0.20 mol) of <strong>[38573-88-5]2,3-difluorobromobenzene</strong>, 58.0 g (0.42 mol) of potassium carbonate, 240 mL of N, N- dimethylformamide and 80 mL of H2O. The temperature was raised to 80°C. After the solid was totally dissolved, 2.3g (2mmol) of tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium was added and the reaction was carried out at 80 ° C for 8 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with petroleum ether and the organic phase was separated. The aqueous layer was extracted three times with petroleum ether The organic phase was combined and washed with water until neutral, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. A fraction of 110-115C / 40Pa was collected to obtain a colorless oil. |
- 10
-
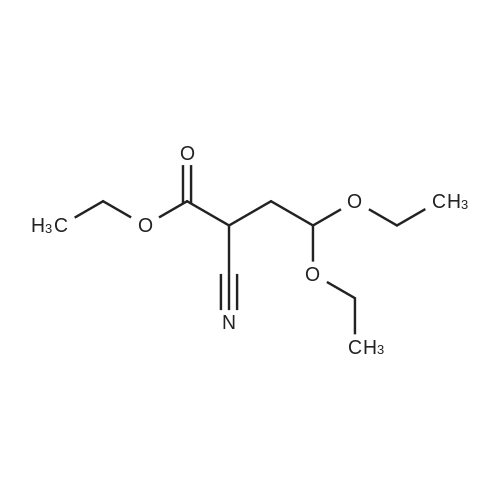 [ 52133-67-2 ]
[ 52133-67-2 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
ethyl 2-(4-ethylphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate
[ No CAS ]
- 11
-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
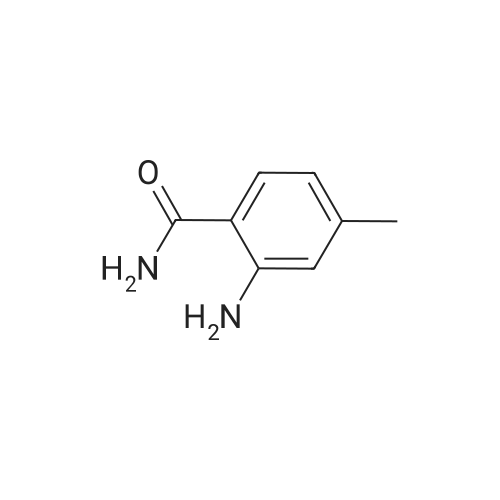 [ 39549-79-6 ]
[ 39549-79-6 ]

-
2-(4-ethylphenyl)-7-methyl-2,3-dihydrobenzo[d][1,3,2]diazaborinin-4(1H)-one
[ No CAS ]
- 12
-
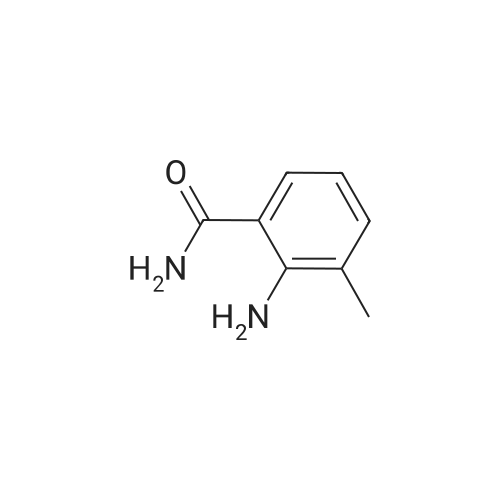 [ 1885-32-1 ]
[ 1885-32-1 ]

-
 [ 63139-21-9 ]
[ 63139-21-9 ]

-
2-(4-ethylphenyl)-8-methyl-2,3-dihydrobenzo[d][1,3,2]diazaborinin-4(1H)-one
[ No CAS ]

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science















 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping

















