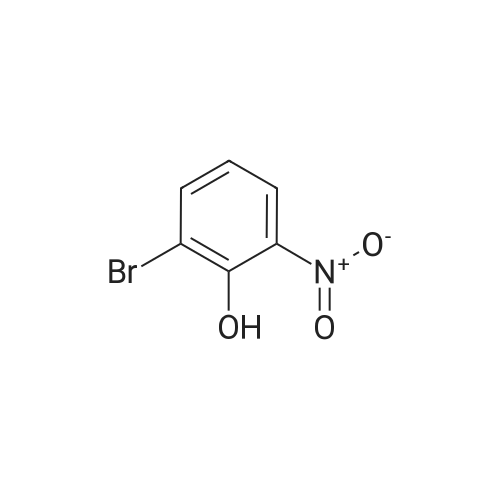
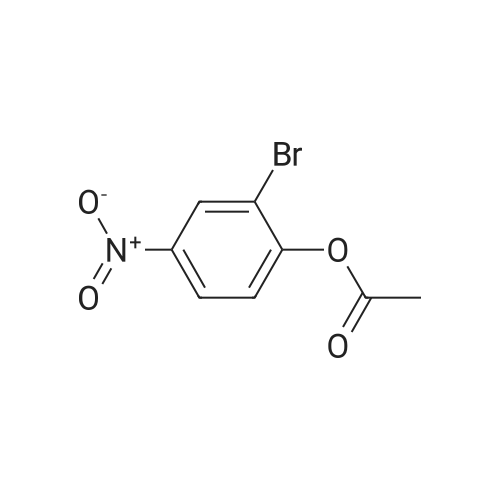
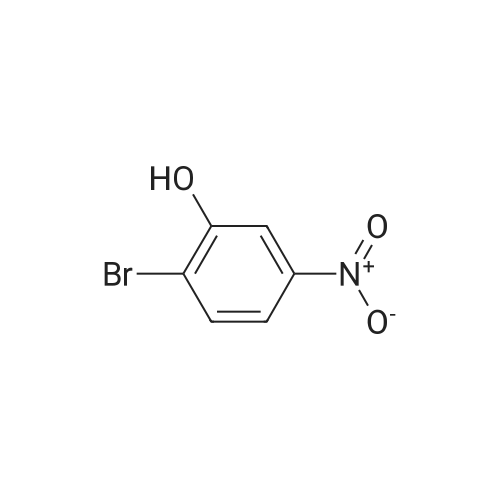
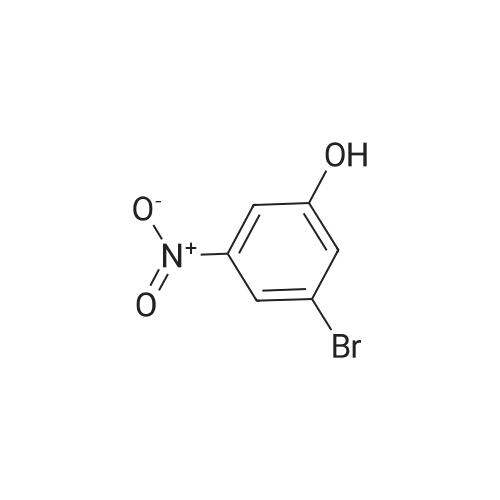
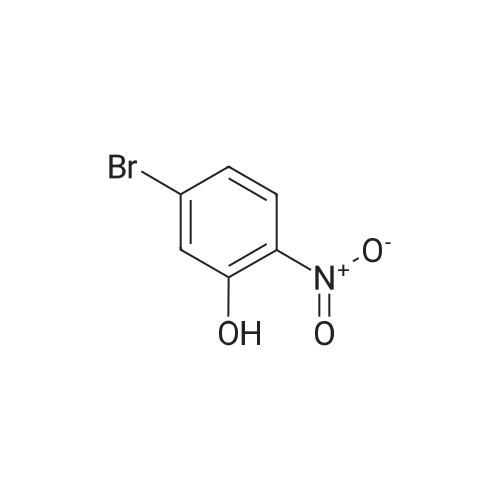
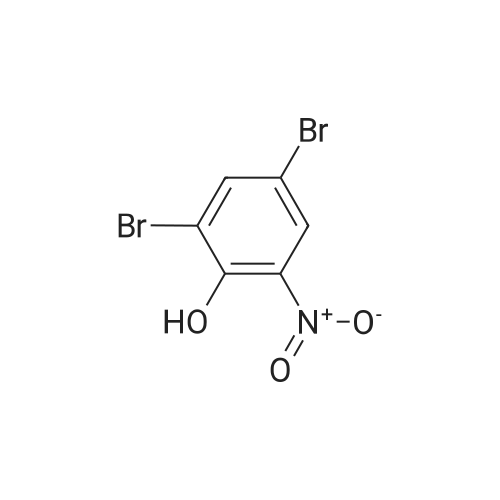
| 65% |
With potassium hydrogensulfate; isoquinolinium dichromate; potassium bromide; In water; at 20℃;Sonication; |
General procedure: The general method for ultrasonically assisted brominationreaction is almost similar to conventional reaction as mentionedabove. A centimolar (0.01 mol) organic substrate (phenols,anilines, or acetanilides), 0.001 mol potassium halide(KBr), about 50 mg of dilute KHSO4, and hypervalent Cr(VI) reagent (IQCC or IQDC) were suspended in about30 mL solvent (DCE or ACN) in a previously cleaned roundbottom(R.B) flask placed in a sonicator. The reaction mixtureis sonicated at room temperature about 30-40 min. Progressof the reaction was monitored by TLC technique. Workupprocedure after completion of the reaction mixture is similarto the one described previously. |
| 51% |
With acetic acid; potassium bromide; In water; acetic acid; at 35℃; |
General procedure: 0.11 g (1.0 mmol) of 4-methylphenol, 5 mL of acetic acid, 0.5 mL of water, and 0.12 g (1.0 mmol)potassium bromide were placed in round-bottomed flask. Then, 0.19 g (0.2 mmol)ZnAl-BrO3--LDHs was added in the flask under stirring at 35 C. After the addition, stirring wascontinued to the end of reaction (monitored by thin layer chromatography). The residualZnAl-BrO3--LDHs were removed by centrifugation. The product was extracted with 3 × 10 mLdichloromethane. The combined extract was washed with sodium sulfite solution, brine, and dried(Na2SO4). Evaporation of the solvent left the crude product. The crude product was purified bycolumn chromatography over silica gel (ethyl acetate-petroleum ether) to obtain pure product. |
| 45% |
With tetrabutylammomium bromide; isoquinolinium chlorochromate; In water; at 25 - 30℃; for 9h; |
General procedure: Phenol (1 mmol, 10 mL) dissolved in 1M PEG-600, isoquinolinium dichromate (IQDC) or isoquinolinium chlorochromate (IQCC) reagent, and tetrabutylammonium halide (TBAX) (1.1 mmol each) were taken in a reaction flask and refluxed with constant stirring at about 25 to 30 C, till the completion of reaction, as as certainedby thin layer chromatography. Then the contents of reaction were diluted with ethyl acetate (10 mL) and separated from aqueous layer. Organic layer was then washed two to three time swith 5 mL water and separated. Finally, the resultant mass is dried over sodium sulphate. The anhydrous ethyl acetate layerwas separated under reduced pressure to give crude product, which was further purified by column chromatography (silicagel, 100-200 mesh) using EtOAc-hexane (3:7). For the separation and recyclization of PEG, aqueous mother liquor (reaction mixture of PEG-600 and water) was treated with ether because PEG is insoluble in ether. The aqueous layer obtained after the removal of ether, was then distilled directly at 100 C to remove water and recover PEG-600. The recovered PEG-600 could be reused for consecutive runs. |
|
With N-Bromosuccinimide; |
A. Synthesis of 2-Bromo-4-nitrophenol 2-Bromo-4-nitrophenol was prepared by reaction of 4-nitrophenol and N-bromosuccinimide. The experimental method of preparation was described by T. Oberhouser in J. Org. Chem. 1997 (62), page 4504. |
|
With dihydrogen peroxide; acetic acid; potassium bromide; In water; at 20℃; for 6h; |
General procedure: Catalytic reaction was carried out in a 50 mL two necked round bottom flask, which charged with 0.05 g of catalyst, substrate (2 mmol) in acetic acid (5 mL) and KBr (2.2 mmol). 30% H2O2 (2.2 mmol) was then added drop wise to the reaction mixture. The content in the flask was stirred continuously at room temperature. After specified time of the reaction, the catalyst was filtered and the solid was washed with ether. The combined filtrates were washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and then shaken with ether in a separating funnel. The organic extract was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The products were analysed by Varian 3400 gas chromatograph equipped with a 30 m CP-SIL8CB capillary column and a Flame Ionization Detector. Identity of the products was also confirmed by using an Agilent GC-MS. |
|
With perchloric acid; dihydrogen peroxide; oxygen; potassium bromide; In water; at 20℃; for 6h; |
General procedure: In a typical reaction, aqueous 30% H2O2 (20 mmol) was added to the mixture of substrates (10 mmol) and KBr (20 mmol) taken in 10 mL of water. Catalyst (50 mg) and HClO4 (5 mmol) were added to it and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature. An additional 15 mmol HClO4 was added to the reaction mixture in three equal portions at 30 min intervals under continuous stirring. After specified time of the reaction, the catalyst was filtered and the solid was washed with ether. The combined filtrates were washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and then shaken with ether in a separating funnel. The organic extract was dried over anhydrous sodium sulphate. The products were analysed by Varian 3400 gas chromatograph equipped with a 30 m CP-SIL8CB capillary column and a Flame Ionization Detector. |
|
With N-Bromosuccinimide; In sulfuric acid; at 0℃; |
4-Nitrophenol (5.00g, 35.9mmol) was dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid (40ml) at room temperature. The solution was cooled to 0C, and N-bromosuccinimide (6.40g, 36.0mmol) was added portionally. Once the complete conversion was detected, the mixture was poured onto ice. The resulted precipitates were collected by filtration, washed with water, and dried. The above-obtained crude 2-bromo-4-nitrophenol was dissolved in acetone (100ml), and stirred with potassium carbonate (12.5g, 90.4mmol) and benzyl bromide (6.20g, 36.2mmol) under reflux for 5h. The mixture was filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate 20:1-9:1) to give the title compound as a light yellow solid (8.38g, 76% for two steps). |
|
With N-Bromosuccinimide; |
A. Synthesis of 2-bromo-4-nitrophenol 2-bromo-4-nitrophenol is prepared by reaction of 4-nitrophenol with N-brom-succinimide, according to the paper by T. Oberhouser in J. Org. Chem. 62, pp. 4504 and following (1997). |
|
With bromine; acetic acid; at 5 - 20℃; for 0.333333h; |
General procedure: (ii) To a mixture of 4-nitro-1-naphthanol (10 mmol) inacetic acid (25 mL), Br2 (10 mmol, 1.60 g) in acetic acid (5mL) was added dropwise at 5-10oC. The mixture was allowedto stir at room temperature for 20min. The solventwas removed under reduced pressure to yield 3-bromo-4-nitro-1-naphthanol as a yellow solid in 99% yield. It can beused directly for the next step without further purification. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping