| 96% |
With tri-tert-butyl phosphine; sodium t-butanolate;bis(dibenzylideneacetone)-palladium(0); In hexane; xylene; at 130℃; for 4.5h;Inert atmosphere; |
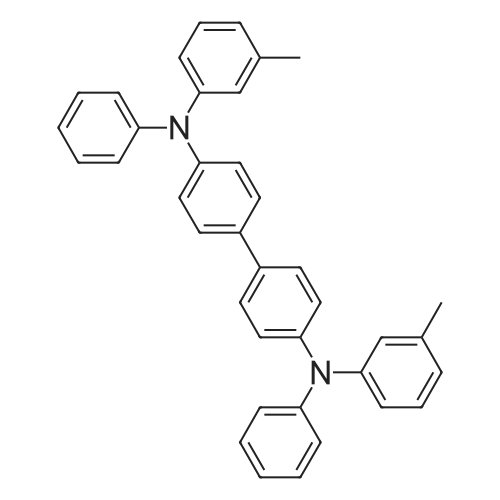
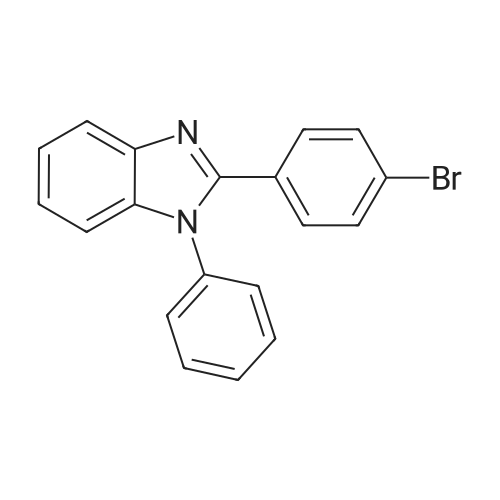
In a 50 mL three-neck flask were put 1.4 g (5.2 mmol) of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-benzoxazole, 0.8 g (2.5 mmol) of N,N'-diphenylbenzidine, 1.0 g (10 mmol) of sodium tert-butoxide, and 28 mg (50 μmol) of bis(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium(0), and the air in the flask was replaced with nitrogen. Then, 20 mL of dehydrated xylene was added to this mixture. After the mixture was deaerated while being stirred under reduced pressure, 0.3 mL (0.2 mmol) of tri(tert-butyl)phosphine (10 wt % hexane solution) was added thereto. This mixture was stirred under a nitrogen atmosphere at 130 C. for 4.5 hours to be reacted.After the reaction, 200 mL of ethyl acetate was added to this reaction mixture, and this suspension was filtered through Florisil and Celite. The obtained filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography (developing solvent, toluene:ethyl acetate=9:1). The obtained fraction was concentrated, and acetone and methanol were added thereto. The mixture was irradiated with supersonic and then recrystallized, so that the object of the synthesis was obtained as 1.7 g of a yellow powder in a yield of 96%.A reaction scheme of the above synthesis method is illustrated in the following scheme (B-1). The Rf values of the object of the synthesis, 2-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-benzoxazole, and N,N'-diphenylbenzidine were respectively 0.35, 0.67, and 0.30 which were found by silica gel thin layer chromatography (TLC) (developing solvent, ethyl acetate:hexane=1:5).Results of nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry (1H-NMR), by which the compound obtained by the above synthesis method was analyzed, are shown below. In addition, the 1H-NMR charts are shown in FIGS. 10A and 10B. FIG. 10B illustrates an enlarged view within a range of 6 ppm to 9 ppm in FIG. 10A. The results reveal that N,N'-diphenyl-N,N'-di-{4-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-phenyl}benzidine (abbreviation: BOxABP), which is the triarylamine compound of one embodiment of the present invention represented by the structural formula (135) shown above, was obtained.1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ (ppm)=7.11-7.24 (m, 14H), 7.28-7.35 (m, 8H), 7.51-7.55 (m, 6H), 7.70-7.73 (m, 2H), 8.90 (d, J=8.7 Hz, 4H).Next, ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra (hereinafter, simply referred to as “absorption spectra”) and emission spectra of BOxABP were measured. The absorption spectra were measured using an ultraviolet-visible light spectrophotometer (V550 type manufactured by Japan Spectroscopy Corporation). The emission spectra were measured using a fluorescence spectrophotometer (FS920 manufactured by Hamamatsu Photonics Corporation). The absorption spectra and the emission spectra of a toluene solution of BOxABP and a thin film of BOxABP were measured. Put in a quartz cell, the toluene solution (0.120 mmol/L) was subjected to the measurements at room temperature. As for the measurements of the absorption spectrum of the thin film, the thin film which was evaporated over a quartz substrate was used and a value obtained by subtraction of an absorption spectrum of quartz from absorption spectra of the thin film and quartz is shown.FIGS. 11A and 11B show measurement results of the absorption spectra and emission spectra. FIG. 11A shows the measurement results of the toluene solution of BOxABP. FIG. 11B shows the measurement results of the thin film of BOxABP. In each of FIGS. 11A and 11B, the horizontal axis represents wavelength (nm) and the vertical axis represents absorption intensity (arbitrary unit) or emission intensity (arbitrary unit). In each of FIGS. 11A and 11B, the two solid lines are shown, and the thin line represents absorption spectrum while the thick line represents emission spectrum.In the case of the toluene solution of BOxABP, an absorption peak is observed at around 381 nm as shown in FIG. 11A. In the case of the thin film of BOxABP, an absorption peak is observed at around 384 nm as shown in FIG. 11B.Further, in the case of the toluene solution of BOxABP, the maximum emission wavelength is 435 nm (excitation wavelength: 380 nm) as shown in FIG. 11A. In the case of the thin film of BOxABP, the maximum emission wavelength is 472 nm (excitation wavelength: 400 nm) as shown in FIG. 11B.As described above, BOxABP was found to emit blue light and accordingly can be used for a blue light-emitting material.Further, the HOMO level and the LUMO level of BOxABP were obtained by cyclic voltammetry (CV) measurements. An electrochemical analyzer (ALS model 600A or 600C, manufactured by BAS Inc.) was used for the CV measurements.Further, as for a solution used for the CV measurements, dehydrated dimethylformamide (DMF, manufactured by Sigma-Aldrich Inc., 99.8%, Catalog No. 22705-6) was used as a solvent, and tetra-n-butylammonium perchlorate (n-Bu4NClO4, manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Catalog No. T0836), which was a supporting electrolyte, was dissolved in the solvent such that the concentration of tetra-n-butylammonium perchlorate was 100 mmol/L. Furthe... |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping