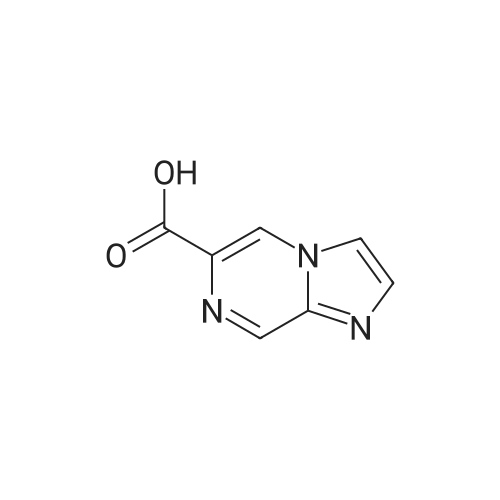
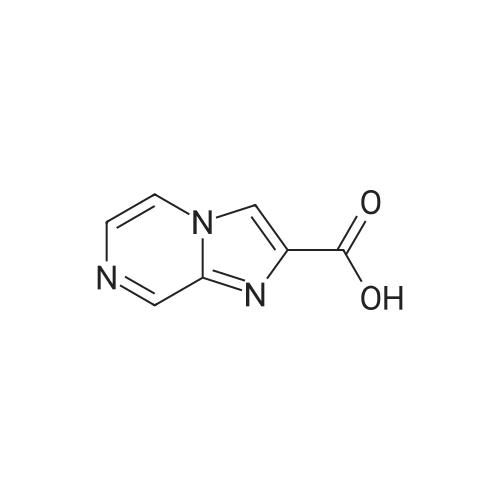
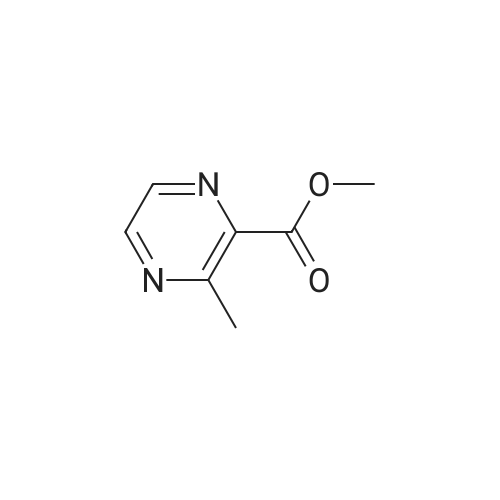
Synthesis and Characterization of 5-(2-Fluoro-4-[11C]methoxyphenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyridine-7-carboxamide as a PET Imaging Ligand for Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 2
Yuan, Gengyang
;
Dhaynaut, Maeva
;
Lan, Yu
, et al.
J. Med. Chem.,2022,65(3):2593-2609.
DOI:
10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c02004
PubMed ID:
35089713
More
Abstract: Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 (mGluR2) is a therapeutic target for several neuropsychiatric disorders. An mGluR2 function in etiology could be unveiled by positron emission tomography (PET). In this regard, 5-(2-fluoro-4-[11C]methoxyphenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyridine-7-carboxamide ([11C]13, [11C]mG2N001), a potent negative allosteric modulator (NAM), was developed to support this endeavor. [11C]13 was synthesized via the O-[11C]methylation of phenol 24 with a high molar activity of 212 ± 76 GBq/μmol (n = 5) and excellent radiochemical purity (>99%). PET imaging of [11C]13 in rats demonstrated its superior brain heterogeneity and reduced accumulation with pretreatment of mGluR2 NAMs, VU6001966 (9) and MNI-137 (26), the extent of which revealed a time-dependent drug effect of the blocking agents. In a nonhuman primate, [11C]13 selectively accumulated in mGluR2-rich regions and resulted in high-contrast brain images. Therefore, [11C]13 is a potential candidate for translational PET imaging of the mGluR2 function.
Purchased from AmBeed:
16289-54-6 ;
5521-55-1 ;
22047-25-2 ;
98-80-6 ;
40155-47-3 ;
5720-05-8 ;
879-65-2 ;
98-96-4 ;
31519-62-7 ;
23688-89-3 ;
23611-75-8 ;
33332-25-1 ;
20737-42-2 ;
61442-38-4 ;
17933-03-8 ;
50681-25-9 ;
13924-99-7 ;
40155-43-9 ;
166744-78-1 ;
36070-80-1 ;
4595-61-3 ;
118853-60-4 ;
41110-28-5 ;
40155-42-8 ;
937669-80-2 ;
31462-59-6 ;
16419-60-6 ;
5424-01-1 ;
59-67-6 ;
34604-60-9 ;
27398-39-6 ;
1196151-53-7 ;
19847-12-2 ;
13965-03-2 ;
876161-05-6 ;
27825-21-4 ;
2164-61-6 ;
4604-72-2 ;
98-97-5 ;
24005-61-6 ;
5521-61-9 ;
2516-34-9 ;
2719-27-9 ;
123-90-0 ;
6761-50-8 ;
625-43-4 ;
872-64-0 ;
1309866-36-1 ;
36932-49-7 ;
1528085-68-8 ;
1195533-51-7 ;
13534-79-7
...More
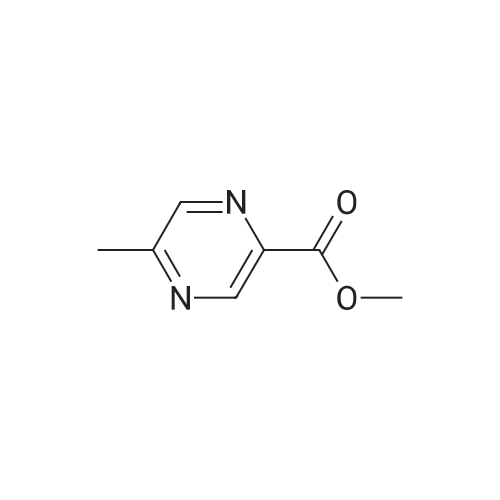
Structure activity relationship of pyrazinoic acid analogs as potential antimycobacterial agents
Hegde, Pooja V.
;
Aragaw, Wassihun W.
;
Cole, Malcolm S.
, et al.
Bioorgan. Med. Chem.,2022,74,117046.
DOI:
10.1016/j.bmc.2022.117046
PubMed ID:
36228522
More
Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a leading cause of infectious disease-related mortality and morbidity. Pyrazinamide (PZA) is a critical component of the first-line TB treatment regimen because of its sterilizing activity against non-replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), but its mechanism of action has remained enigmatic. PZA is a prodrug converted by pyrazinamidase encoded by pncA within Mtb to the active moiety, pyrazinoic acid (POA) and PZA resistance is caused by loss-of-function mutations to pyrazinamidase. We have recently shown that POA induces targeted protein degradation of the enzyme PanD, a crucial component of the CoA biosynthetic pathway essential in Mtb. Based on the newly identified mechanism of action of POA, along with the crystal structure of PanD bound to POA, we designed several POA analogs using structure for interpretation to improve potency and overcome PZA resistance. We prepared and tested ring and carboxylic acid bioisosteres as well as 3, 5, 6 substitutions on the ring to study the structure activity relationships of the POA scaffold. All the analogs were evaluated for their whole cell antimycobacterial activity, and a few representative mols. were evaluated for their binding affinity, towards PanD, through isothermal titration calorimetry. We report that analogs with ring and carboxylic acid bioisosteres did not significantly enhance the antimicrobial activity, whereas the alkylamino-group substitutions at the 3 and 5 position of POA were found to be up to 5 to 10-fold more potent than POA. Further development and mechanistic anal. of these analogs may lead to a next generation POA analog for treating TB.
Keywords:
Tuberculosis ;
Pyrazinoic acid ;
pyrazinamide
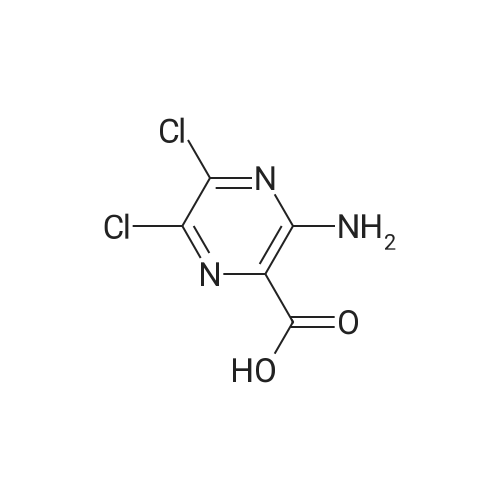
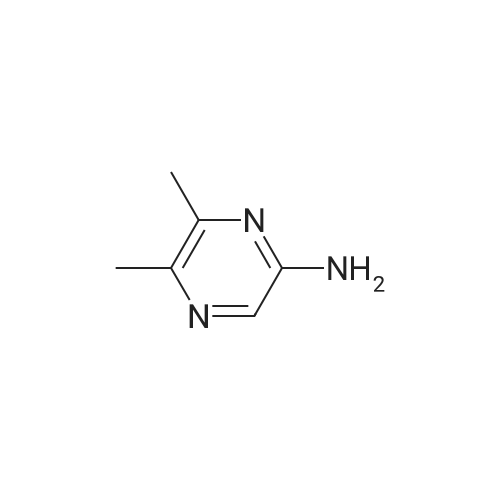
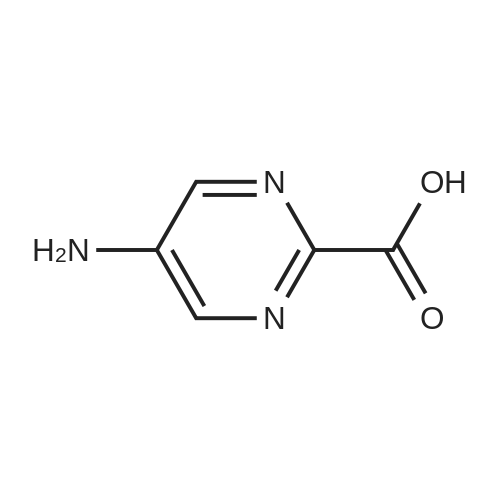
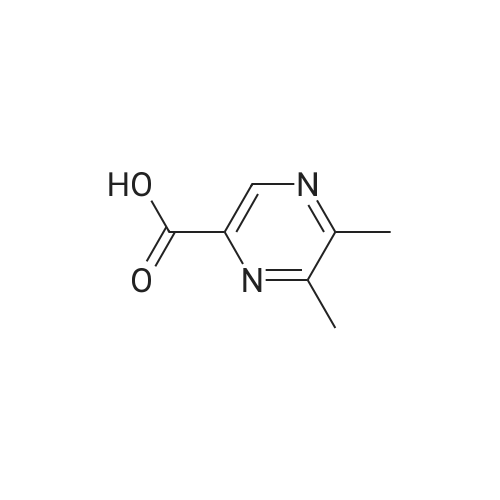
Purchased from AmBeed:
16289-54-6 ;
5521-55-1 ;
22047-25-2 ;
98-80-6 ;
40155-47-3 ;
5720-05-8 ;
879-65-2 ;
98-96-4 ;
31519-62-7 ;
23688-89-3 ;
23611-75-8 ;
33332-25-1 ;
20737-42-2 ;
61442-38-4 ;
17933-03-8 ;
50681-25-9 ;
13924-99-7 ;
40155-43-9 ;
36070-80-1 ;
4595-61-3 ;
118853-60-4 ;
41110-28-5 ;
40155-42-8 ;
937669-80-2 ;
98-98-6 ;
31462-59-6 ;
16419-60-6 ;
5424-01-1 ;
59-67-6 ;
34604-60-9 ;
27398-39-6 ;
1196151-53-7 ;
19847-12-2 ;
13965-03-2 ;
876161-05-6 ;
27825-21-4 ;
2164-61-6 ;
4604-72-2 ;
98-97-5 ;
24005-61-6 ;
103-67-3 ;
5521-61-9 ;
2516-34-9 ;
2719-27-9 ;
123-90-0 ;
6761-50-8 ;
625-43-4 ;
872-64-0 ;
36932-49-7 ;
1528085-68-8 ;
1195533-51-7 ;
13534-79-7
...More

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping