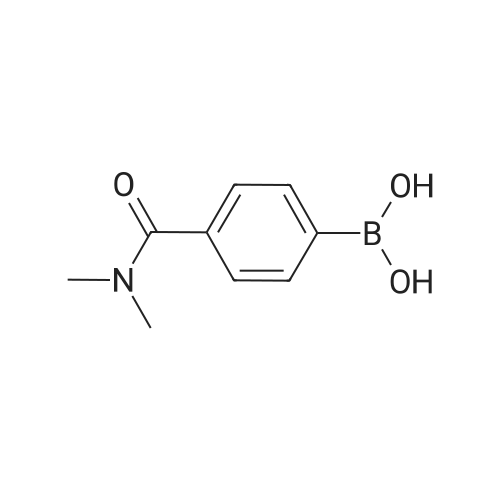
Identification of a Noxo1 inhibitor by addition of a polyethylene glycol chain
Mokhtarpour, Nazanin
;
Sterling, Alyssa
;
Garcia, Joshua J.
, et al.
Bioorgan. Med. Chem.,2023,85,117274.
DOI:
10.1016/j.bmc.2023.117274
PubMed ID:
37031566
More
Abstract: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a heterogeneous group of highly reactive ions and mols. derived from mol. oxygen (O2) which can cause DNA damage and lead to skin cancer. NADPH oxidase 1 (Nox1) is a major producer of ROS in the skin upon exposure to UV light. Functionally, Nox1 forms a holoenzyme complex that generates two superoxide mols. and reduces NADPH. The signaling activation occurs when the organizer subunit Noxo1 translocates to the plasma membrane bringing a cytochrome P 450, through interaction with Cyba. We propose to design inhibitors that prevent Cyba-Noxo1 binding as a topical application to reduce UV-generated ROS in human skin cells. Design started from an apocynin backbone structure to generate a small mol. to serve as an anchor point. The initial compound was then modified by addition of a polyethylene glycol linked biotin. Both inhibitors were found to be non-toxic in human keratinocyte cells. Further in vitro experiments using isothermal calorimetric binding quantification showed the modified biotinylated compound bound Noxo1 peptide with a KD of 2 nM. Both using isothermal calorimetric binding and MALDI (TOF) MS showed that binding of a Cyba peptide to Noxo1 was blocked. In vivo experiments were performed using donated skin explants with topical application of the two inhibitors. Experiments show that UV light exposure of with the lead compound was able to reduce the amount of cyclobutene pyrimidine dimers in DNA, a mol. known to lead to carcinogenesis. Further synthesis showed that the polyethylene glycol but not the biotin was essential for inhibition.
Keywords:
Reactive oxygen species ;
Apocynin ;
UV ;
Noxo1 ;
Cyba ;
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer ;
CPD ;
UV protection
Purchased from AmBeed:
615-43-0 ;
58-85-5 ;
351422-73-6 ;
158407-04-6 ;
103-67-3 ;
103-67-3

Development of reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibitors and prodrugs for multiple applications
Senevirathne, Priyangika Prasadini
;
University of Cincinnati,2022.
More
Abstract: Reactive oxygen species are a group of highly reactive oxygen-containing entities that are important at a cellular level for multiple biological processes. Low concentrations of ROS can be beneficial as powerful signaling molecules in those biological processes, although excessive concentrations can promote high levels of DNA damage and a variety of diseases such as skin cancer. A newly identified intracellular ROS production source in skin cells is NADPH oxidases. Out of the NOX enzyme family, the NOX1 holoenzyme is most abundantly expressed in the human keratinocyte cells. UV radiation can trigger the activation of NOX1 isoforms which stimulate the assembling of member CYBA and the cytoplasmic protein NOXO1. Inhibition of these enzymes represents a catalytic approach toward reducing ROS for the prevention of ROS inducible diseases. Key disease states include melanoma induced by UV exposure. The first half of the dissertation focuses on investigating new small molecule inhibitors of a key NOX1 holoenzyme to address these challenges. We designed a series of molecules by optimizing the structure of diapocynin and evaluated by in-silico docking methods to determine the binding affinity with NOXO1 cytoplasmic protein (1WLP crystal structure). And have synthesized the series of target molecules for the structure-activity relationship studies. In the first section of the project, we discovered that inhibitor NOX_inh_5 was not cytotoxic, but instead improved the viability of human primary cells from UV exposure, decreased the cellular stress in human skin through the p53 pathway, and reduced the UV-induced DNA damage as monitored by quantification of cyclobutane dimer formation after UV exposure. Then, we characterized the inhibition potential of NOX_inh_5 by using an Isothermal calorimetric (ITC) binding assay and heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) technique and revealed that the candidate iii molecule can prevent the complex formation of NOXO1 and CYBA membrane protein. In the second section of the project, we did a structure-activity relationship study for the NOX_inh_5 small molecule to optimize the biological characteristics. The last section of the dissertation discussed the development of ROS sensible prodrug to combat the opioid overdose crisis. Here we used oxidative stress conditions caused by opioid overdose to activate the prodrug. Even though opioid antagonist naloxone has a high affinity to bind with opioid receptors to block opioid-induced activation, it is metabolically unstable and has a short half-life of around 33 min. We developed a peroxide-induced prodrug to overcome this issue that can release a steady stream of naloxone. This allows the concentration of naloxone to remain high for longer periods.
Purchased from AmBeed:
1007-16-5 ;
111-24-0 ;
14221-01-3 ;
99769-19-4 ;
351422-73-6 ;
158407-04-6 ;
1462-37-9 ;
583-61-9 ;
13965-03-2 ;
455-85-6 ;
148893-10-1

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping