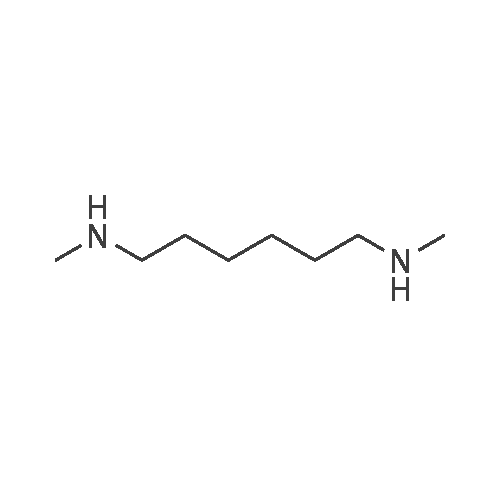
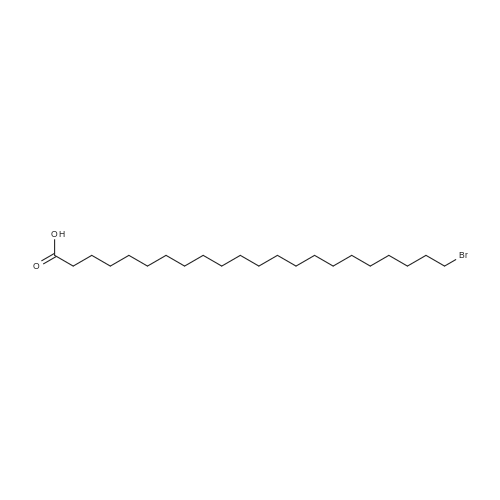
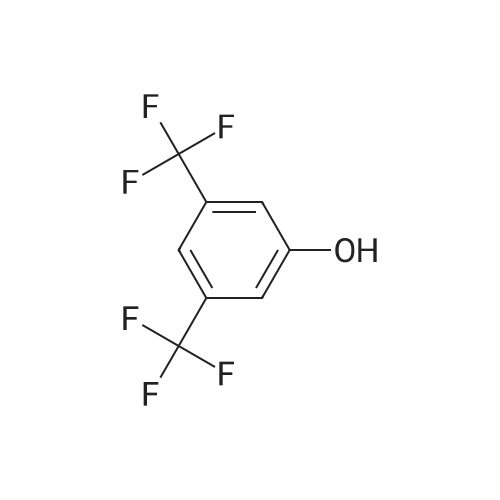
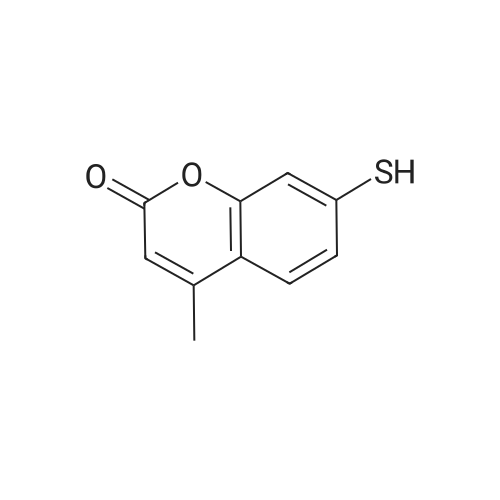
| 99.5% |
|
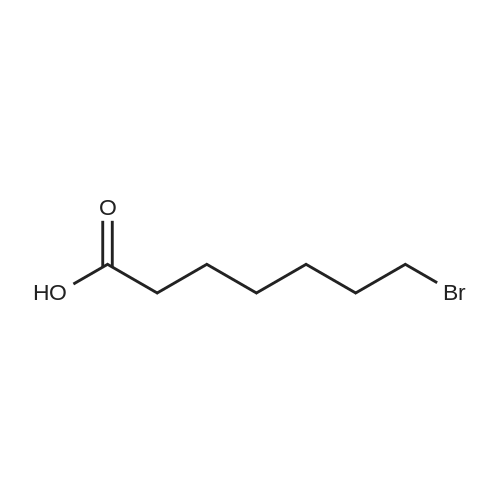
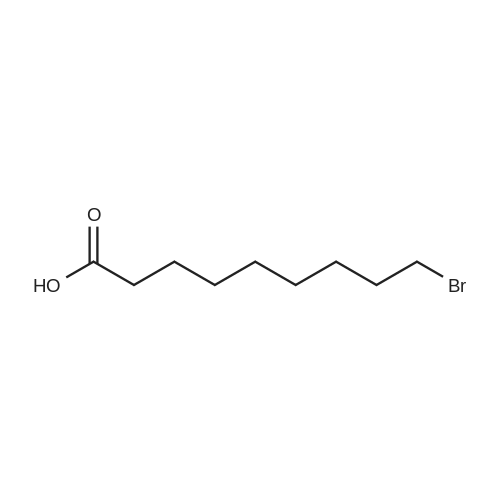
To a suspension of potassium carbonate (0.680 g, 5 mmol)in 20 mL deaerated acetone was added 7-mercapto-4-methylcoumarin (0.481 g, 2.5 mmol), followed by stirring atroom temperature for 1 h, whereupon a cloudy orange solutionformed. To this solution was added 11-bromoundecanoic acid(0.796 g, 3.0 mmol) in 10 mL acetone, and on continued stirring atroom temperature for 2 h the color of the reaction mixture changedto light yellow. The solvent was then evaporated and the residuewas washed by acetone (3×50 mL), treated with 100 mL H2O, andacidified by addition of 1 M HCl to pH 4. The resulting solutionwas extracted with 100 mL CHCl3, the organic layer was washedwith 100 mL H2O, then the solvent was evaporated and the solidresidue was chromatographed on silica gel using CHCl3-EtOAc(9:1) as eluent. The fractions of the product were combined andfreeze-dried from benzene to give 4 as a light yellow powder(0.998 g, 99.5%). IR (CHCl3): 1738, 1732, 1721, 1603 cm-1; 1H NMR(CDCl3, 200 MHz) 1.16-1.82 (br m, 16H), 2.36 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H),2.41 (s, 3H), 2.99 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 6.22 (s, 1H), 7.16 (d, J = 8.1 Hz,2H), 7.47 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 200 MHz) 18.72,24.80, 28.82, 29.01, 29.24, 29.34, 29.46, 29.52, 29.61, 32.32, 34.23,113.85, 113.99, 117.09, 123.10, 124.63, 143.97, 152.43, 154.06,160.94, 179.35; Anal. Calcd for C21H28O4S: C 66.99, H 7.50; Found:C 67.29, H 7.77; MS M+ (C21H28O4S) Calcd: 376.1700; Found:376.1708; Rf (CHCl3-EtOAc 9:1) = 0.18. |
| 87% |
|
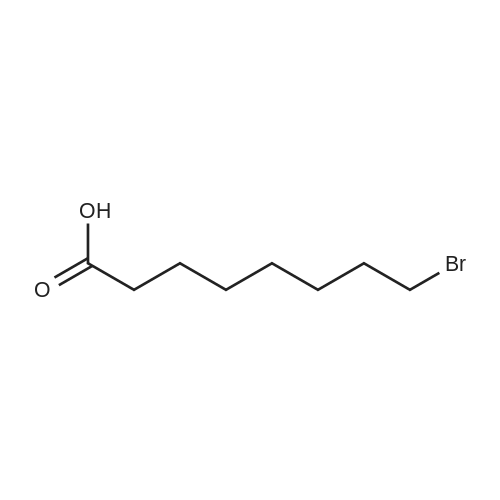
To a suspension of K2CO3 (1.0 g, 7.2 mmol) in 20 mL acetone thathas been bubbled by nitrogen for 20 min, 7-mercapto-4-methylcoumarin (0.72 g, 3.8 mmol) was added. Reaction mixture wasstirred at room temperature for 30 min and a cloudy orangesolution formed. To this solution was added 11-bromoundecanoi-cacid (1.2 g, 4.5 mmol) in 15 mL acetone, yielding a pale yellowprecipitate. The reaction was stirred for 2 h at room temperatureand solvent was evaporated with a rotary evaporator to form a paleyellow product. 100 mL deionized water was added to this paleyellow residue, followed by addition of 1 M HCl until the pH was 4.The resulting solution was extracted with 100 mL CHCl3. Theorganic layer was washed with 100 mL deionized water andextracted again. The organic layer was dried over anhydroussodium sulfate and the solvent was removed with a rotaryevaporator to give a light yellow residue. This residue waschromatographed twice on silica gel using CHCl3-EtOAc (9:1) aseluent. The fractions of the product were collected and solventswere evaporated to give a very light yellow powder 10 (1.30 g,87%); Rf (CHCl3-EtOAc 9:1) = 0.20. Our experimental data matchedthat of a previous report (Wang et al., 2013). |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping