|
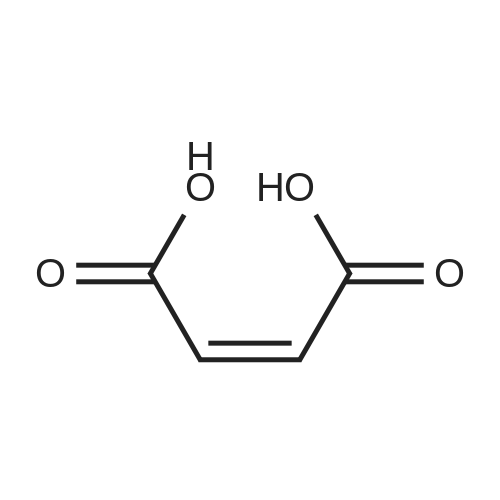
In 1,4-dioxane; water;Product distribution / selectivity; |
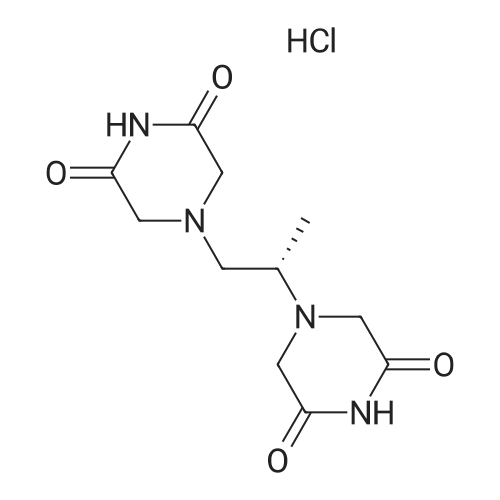
Cooling MethodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in the desired crystallization solvent or mixture of solvents (Table 2A). These solvents were chosen such that the <strong>[24584-09-6]dexrazoxane</strong> freebase is soluble in the solvents but the salts formed from the reaction of the freebase and acids when the respective acids are added to the crystallization solvents are not soluble. Equimolar amount of the desired acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. The precipitates, which were typically not crystalline or were partially crystalline are collected through filtration on a filter and dried by vacuum. Methanol was then added to the dried powder and heated to 65°C to dissolve the entire salt. The solution then cooled in a controlled manner to 5°C overnight in RS-IO Chemblock Reaction Station (Barnstead International, Dubuque, IA). The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < 40°C. <n="46"/>Anti-Solvent MethodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in the desired crystallization solvent or mixture of solvents (Table 1). Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution but the total solution volume is such that the salt formed in-situ remains dissolved in the solution or is soluble in the solution. While the solution was being gently stirred, an anti-solvent (Table 2A) was slowly added until the salt begins to precipitate from the solution. Additional anti-solvent is added until sufficient salt is formed. The crystals was then harvested on a filter and dried at <4O0C.Solvent Evaporation method ICRF- 187 freebase is dissolved in dioxane. Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. With gently stirring, minimum amount of water was added until the salt is completely dissolved. Nitrogen was introduced into the solution and the solvents were slowly evaporated until salt precipitation appeared. Additional anti-solvent is added until sufficient salt is formed. The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < 40°C.Direct precipitation methodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in dioxane. Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < or = 40°C.X-ray powder diffraction analysesThe XRPD analyses were performed using a Shimadzu XRD-6000 X-ray powder diffractometer using Cu Ka radiation. The instrument was equipped with a long fine focus X-ray tube. The tube voltage and amperage were set to 40 kV and 40 <n="47"/>mA, respectively. The divergence and scattering slits were set at 1° and the receiving slit was set at 0.15 mm. Diffracted radiation was detected by a NaI scintillation detector. A Psi-2Psi continuous scan at 37min (0.4 sec/0.02o step) from 2.5 to 40° 2Psi was used. A silicon standard was analyzed to check the instrument alignment. Data were collected and analyzed using XRD-6000 v. 4.1. The peak lists were generated with the Shimadzu software using default peak picking parameters on smoothed, background-subtracted, Ka1 -corrected traces. |
|
In 1,4-dioxane; methanol;Product distribution / selectivity; |
Cooling MethodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in the desired crystallization solvent or mixture of solvents (Table 2A). These solvents were chosen such that the <strong>[24584-09-6]dexrazoxane</strong> freebase is soluble in the solvents but the salts formed from the reaction of the freebase and acids when the respective acids are added to the crystallization solvents are not soluble. Equimolar amount of the desired acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. The precipitates, which were typically not crystalline or were partially crystalline are collected through filtration on a filter and dried by vacuum. Methanol was then added to the dried powder and heated to 65°C to dissolve the entire salt. The solution then cooled in a controlled manner to 5°C overnight in RS-IO Chemblock Reaction Station (Barnstead International, Dubuque, IA). The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < 40°C. <n="46"/>Anti-Solvent MethodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in the desired crystallization solvent or mixture of solvents (Table 1). Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution but the total solution volume is such that the salt formed in-situ remains dissolved in the solution or is soluble in the solution. While the solution was being gently stirred, an anti-solvent (Table 2A) was slowly added until the salt begins to precipitate from the solution. Additional anti-solvent is added until sufficient salt is formed. The crystals was then harvested on a filter and dried at <4O0C.Solvent Evaporation method ICRF- 187 freebase is dissolved in dioxane. Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. With gently stirring, minimum amount of water was added until the salt is completely dissolved. Nitrogen was introduced into the solution and the solvents were slowly evaporated until salt precipitation appeared. Additional anti-solvent is added until sufficient salt is formed. The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < 40°C.Direct precipitation methodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in dioxane. Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < or = 40°C.X-ray powder diffraction analysesThe XRPD analyses were performed using a Shimadzu XRD-6000 X-ray powder diffractometer using Cu Ka radiation. The instrument was equipped with a long fine focus X-ray tube. The tube voltage and amperage were set to 40 kV and 40 <n="47"/>mA, respectively. The divergence and scattering slits were set at 1° and the receiving slit was set at 0.15 mm. Diffracted radiation was detected by a NaI scintillation detector. A Psi-2Psi continuous scan at 37min (0.4 sec/0.02o step) from 2.5 to 40° 2Psi was used. A silicon standard was analyzed to check the instrument alignment. Data were collected and analyzed using XRD-6000 v. 4.1. The peak lists were generated with the Shimadzu software using default peak picking parameters on smoothed, background-subtracted, Ka1 -corrected traces. |
|
In 1,4-dioxane;Product distribution / selectivity; |
Cooling MethodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in the desired crystallization solvent or mixture of solvents (Table 2A). These solvents were chosen such that the <strong>[24584-09-6]dexrazoxane</strong> freebase is soluble in the solvents but the salts formed from the reaction of the freebase and acids when the respective acids are added to the crystallization solvents are not soluble. Equimolar amount of the desired acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. The precipitates, which were typically not crystalline or were partially crystalline are collected through filtration on a filter and dried by vacuum. Methanol was then added to the dried powder and heated to 65°C to dissolve the entire salt. The solution then cooled in a controlled manner to 5°C overnight in RS-IO Chemblock Reaction Station (Barnstead International, Dubuque, IA). The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < 40°C. <n="46"/>Anti-Solvent MethodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in the desired crystallization solvent or mixture of solvents (Table 1). Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution but the total solution volume is such that the salt formed in-situ remains dissolved in the solution or is soluble in the solution. While the solution was being gently stirred, an anti-solvent (Table 2A) was slowly added until the salt begins to precipitate from the solution. Additional anti-solvent is added until sufficient salt is formed. The crystals was then harvested on a filter and dried at <4O0C.Solvent Evaporation method ICRF- 187 freebase is dissolved in dioxane. Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. With gently stirring, minimum amount of water was added until the salt is completely dissolved. Nitrogen was introduced into the solution and the solvents were slowly evaporated until salt precipitation appeared. Additional anti-solvent is added until sufficient salt is formed. The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < 40°C.Direct precipitation methodICRF- 187 freebase was dissolved in dioxane. Equimolar amount of the acid - i.e. sulfuric, maleic, methanesulfonic or hydrochloric acid - was added to the solvent or mixtures of solvents to form a solution. The salt precipitated in the solution. The crystals are then harvested on a filter and dried at < or = 40°C.X-ray powder diffraction analysesThe XRPD analyses were performed using a Shimadzu XRD-6000 X-ray powder diffractometer using Cu Ka radiation. The instrument was equipped with a long fine focus X-ray tube. The tube voltage and amperage were set to 40 kV and 40 <n="47"/>mA, respectively. The divergence and scattering slits were set at 1° and the receiving slit was set at 0.15 mm. Diffracted radiation was detected by a NaI scintillation detector. A Psi-2Psi continuous scan at 37min (0.4 sec/0.02o step) from 2.5 to 40° 2Psi was used. A silicon standard was analyzed to check the instrument alignment. Data were collected and analyzed using XRD-6000 v. 4.1. The peak lists were generated with the Shimadzu software using default peak picking parameters on smoothed, background-subtracted, Ka1 -corrected traces. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science













 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping