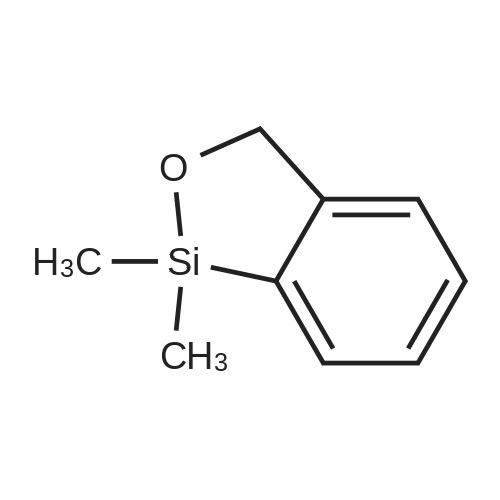
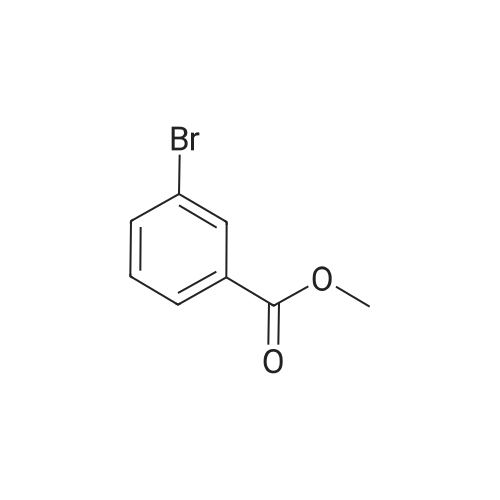
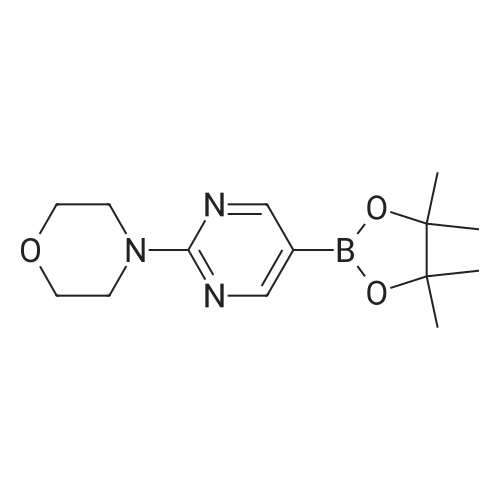
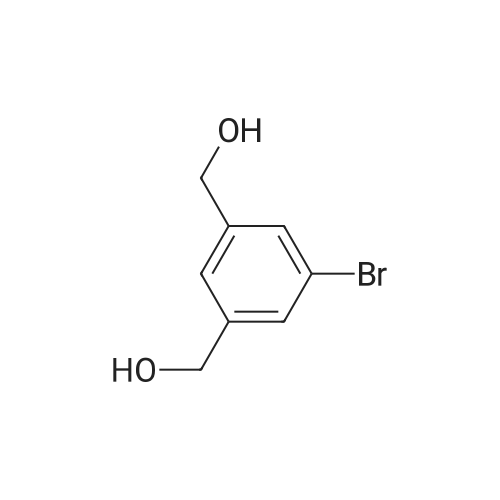
| 57% |
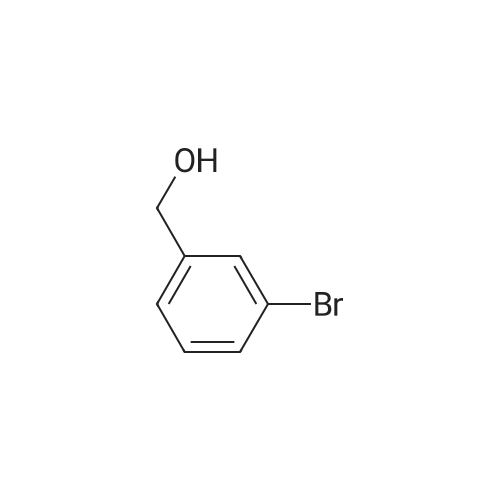
With sodium hydroxide;tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); In ethanol; water; toluene; at 90℃; for 4h; |
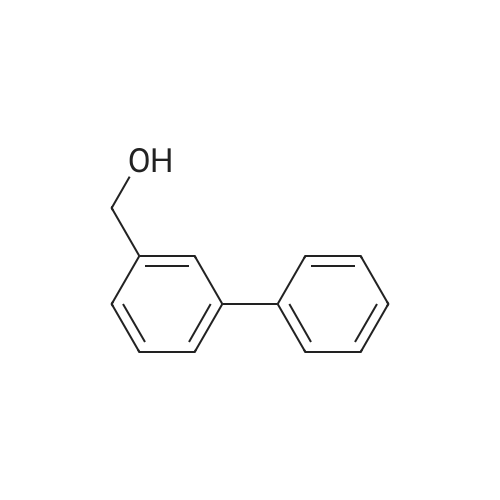
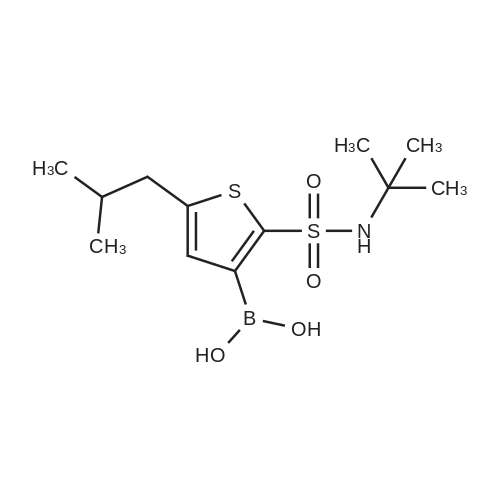
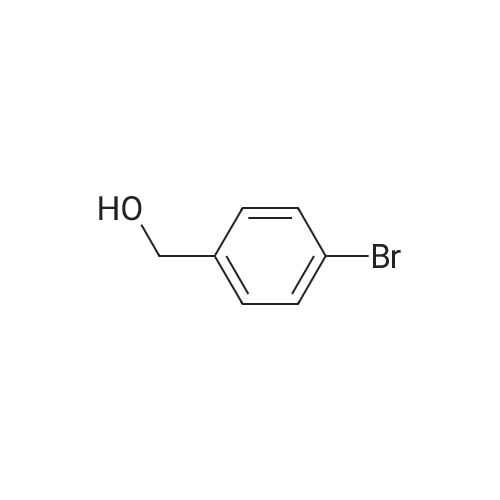
(d) 3-r3-Hvdroxymethylphenyl)-5-/j'o-butyl-N-fert-butyltm'ophene-2-sulfonamide; A mixture of r°-bromobenzyl alcohol (1.05 g, 5.80 mmol), 5-iso-butyl-2-(/V-tert- butylaminosulfonyl)thiophene-3-boronic acid (2.41 g, 7.55 mmol; see step (c)), Pd(PPh3)4 (270 mg, 0.235 mmol), NaOH (19.1 mL, 1.5 M aq5 28.6 mmol), EtOH (5.0 mL) and toluene (30 mL) was stirred under N2 at 9O0C for about 4 h. After cooling, water (10 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and this was then extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic phase was dried and concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified on column EPO <DP n="35"/>chromatography (EtOAc/hexane, 30:70) to give sub-title compound as a colourless syrup in 57% yield (1.26 g, 3.31 mmol).1H NMR delta (CDCl3): 0.96 (d, J = 6.6 Hz5 6H), 0.98 (s, 9H)5 1.82-2.00 (m, IH), 2.66 (d, J= 7.1 Hz5 2H)5 3.28 (br s5 IH), 4.67 (s, 2H)5 4.81 (hr s5 IH), 6.76 (s, IH), 7.30-7.50 (m, 3H)5 7.64 (s, IH).13C NMR delta (CDCl3): 22.1, 29.4, 30.4, 39.1, 54.4, 64.6, 127.1, 127.8, 128.5, 129.0, 134.9, 136.2, 141.2, 143.2, 148.2. MS (ESI) m/z: 382(MH-I)+.IRv (neat, cm-1): 3498, 3286, 2958, 2870, 1465, 1313. ' Anal. Calcd. for C19H27NO3S2: C, 59.81; H, 7.13; N5 3.67. Found: C, 60.05; H, 7.31; N5 3.90. |
| 57% |
With sodium hydroxide;tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium(0); In ethanol; water; toluene; at 90℃; for 4h; |
(d) 3-(3-HydroxymethyIphenyl)-5-/i'o-butyl-Lambdar-fer?'-butylthiophene-2-sulfonamide; A mixture of m-bromobenzyl alcohol (1.05 g, 5.80 mmol), 5-iso-butyl-2-(iV-tert- butylaminosulfonyl)thiophene-3-boronic acid (2.41 g, 7.55 mmol; see step (c))5 Pd(PPh3)4 (270 mg5 0.235 mmol), NaOH (19.1 mL, 1.5 M aq5 28.6 mmol), EtOH (5.0 mL) and toluene (30 mL) was stirred under N2 at 900C for about 4 h. After cooling, water (10 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and this was then extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic phase was dried and concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified on column EPO <DP n="38"/>chromatography (EtOAc/hexane, 30:70) to give sub-title compound as a colourless syrup in 57% yield (1.26 g, 3.31 mmol).1H NMR delta (CDCl3): 0.96 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 6H), 0.98 (s, 9H), 1.82-2.00 (m, IH), 2.66 (d, J= 7.1 Hz, 2H)5 3.28 (br s, IH), 4.67 (s, 2H), 4.81 (br s, IH), 6.76 (s, IH), 7.30-7.50 (m, 3H)5 7.64 (s, IH).13C NMR delta (CDCl3): 22.1, 29.4, 30.4, 39.1, 54.4, 64.6, 127.1, 127.8, 128.5, 129.0, 134.9, 136.2, 141.2, 143.2, 148.2. MS (ESI) m/z: 382(M+1)+.IRv (neat, cm"1): 3498, 3286, 2958, 2870, 1465, 1313. Anal. Calcd. for C19H27NO3S2: C, 59.81; H, 7.13; N, 3.67. Found: C, 60.05; H, 7.31; N, 3.90. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping