More
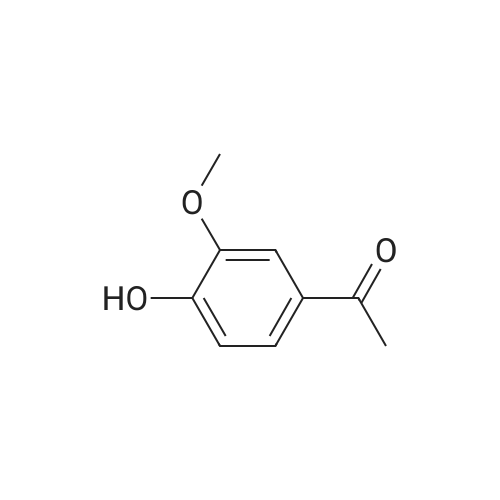
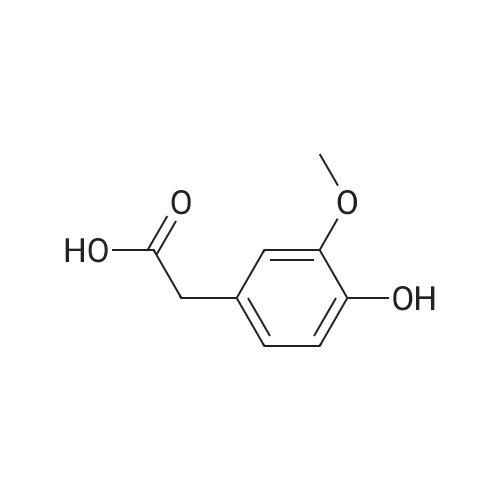
Abstract: Breast cancer (BC) is the second greatest contributor to the death of women, second only to heart disease, and is the most common type of cancer. BC treatments involve the administration of adjuvant chemotherapies which often have side effects that prevent patients from completing the full course of drugs or the refusal to take these potentially lifesaving treatments. Many chemotherapy drugs are developed from plants, and some plant extracts can exhibit significant anticancer activities while also having less toxic side effects. However, these potential "plant therapeutics" suffer from poor oral bioavailability. The Apiaceae plant family consists of several species that are used as culinarily spices including anise, celery, cumin, and coriander, all of which have demonstrated antioxidant, chemopreventive, and anticancer activities. One method to improve the systemic distribution of anticancer phytochemicals is their encapsulation in naturally produced membrane bound nanoparticles known as exosomes. Exosomes are produced by most eukaryotic organisms, as well as some prokaryotes, and are involved in cell-to-cell communication through the delivery of proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules from one cell to another. Exosomes are found in many extracellular fluids including blood, urine, and milk. Bovine milk exosomes represent a scalable source of exosomes that are already present in the human diet and have been explored as a drug delivery system that can increase effectiveness and improve bioavailability. To enhance the loading potential and anticancer bioactivity of Apiaceae phytochemicals, an acid hydrolysis (AH) of the glycoside compounds present in ethanolic spice extracts was performed on eight ethanolic spice extracts. The antiproliferative effects of AH extracts and exosomal formulations were assayed with three model types of BC cells. Cumin was characterized in greater detail as these extracts had the highest concentration of terpenoids and alkaloids while also having significant concentrations of phenolics and responded well to AH with increased antiproliferative activity and exosomal loading. Extracts and exosomal formulations exhibited broad antiproliferative effects with lower IC50s in the extracts delivered with exosomes. The phytochemical contents of AH-cumin extracts and exosomal formulations were assayed with HPLC-DAD, LC-MS/MS, and GC-MS, while the potential anticancer mechanisms of these treatments were investigated in triple negative BC (TNBC). AHcumin extracts were determined to have numerous phenolic compounds, many of which have known anticancer mechanisms, in addition to several alkaloids and lipid compounds, some of which have activities that could contribute to the anticancer effects observed. Mechanistically, AH-cumin extracts and exosomal formulations were shown to interact with multidrug resistance proteins and inhibit lipid metabolism in TNBC cells. These results indicate that acid hydrolyzed cumin extracts delivered through exosome nanoparticles represent a possible avenue towards the development of novel treatments for TNBC, the hardest type of BC to treat.

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping