|
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenol; N-benzyl-N,N,N-triethylammonium chloride; at 80℃; for 48h;Product distribution / selectivity; |
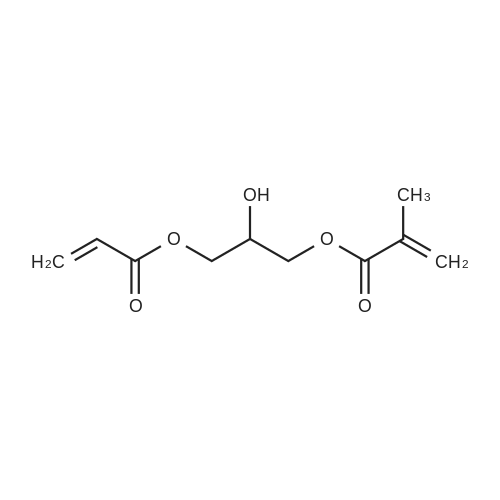
13.27 g of glycidyl methacrylate, 0.02 g of 2,6-ditert.-butyl-4-methylphenol, 6.78 g of acrylic acid and 0.10 g of one of the catalysts set forth in Table 1 were reacted each time at 80 C. in a glass vessel with a small opening and with magnetic stirring. The acid value was determined after 24 and 48 hours. If it was greater than 4 mg KOH/g after 48 hours, the batch was discarded without further analysis. The catalysts in comparison examples C2 to C6 exhibit, for a given weight, much lower activity, and those in C7 and C8 a lower activity, than the catalyst in example 9 according to the invention. The reaction product was at least equal to the comparison products according to the acid value, hydroxyl value and purity (GPC analysis). |
|
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenol; dibutyltin dilaurate; at 80℃; for 48h;Product distribution / selectivity; |
13.27 g of glycidyl methacrylate, 0.02 g of 2,6-ditert.-butyl-4-methylphenol, 6.78 g of acrylic acid and 0.10 g of one of the catalysts set forth in Table 1 were reacted each time at 80 C. in a glass vessel with a small opening and with magnetic stirring. The acid value was determined after 24 and 48 hours. If it was greater than 4 mg KOH/g after 48 hours, the batch was discarded without further analysis. The catalysts in comparison examples C2 to C6 exhibit, for a given weight, much lower activity, and those in C7 and C8 a lower activity, than the catalyst in example 9 according to the invention. The reaction product was at least equal to the comparison products according to the acid value, hydroxyl value and purity (GPC analysis). |
|
2,2'-thiobis-ethanol; 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenol; at 80℃; for 48h;Product distribution / selectivity; |
13.27 g of glycidyl methacrylate, 0.02 g of 2,6-ditert.-butyl-4-methylphenol, 6.78 g of acrylic acid and 0.10 g of one of the catalysts set forth in Table 1 were reacted each time at 80 C. in a glass vessel with a small opening and with magnetic stirring. The acid value was determined after 24 and 48 hours. If it was greater than 4 mg KOH/g after 48 hours, the batch was discarded without further analysis. The catalysts in comparison examples C2 to C6 exhibit, for a given weight, much lower activity, and those in C7 and C8 a lower activity, than the catalyst in example 9 according to the invention. The reaction product was at least equal to the comparison products according to the acid value, hydroxyl value and purity (GPC analysis). |
|
stannous octoate; 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenol; at 80℃; for 24h;Product distribution / selectivity; |
13.27 g of glycidyl methacrylate, 0.02 g of 2,6-ditert.-butyl-4-methylphenol, 6.78 g of acrylic acid and 0.10 g of one of the catalysts set forth in Table 1 were reacted each time at 80 C. in a glass vessel with a small opening and with magnetic stirring. The acid value was determined after 24 and 48 hours. If it was greater than 4 mg KOH/g after 48 hours, the batch was discarded without further analysis. The catalysts in comparison examples C2 to C6 exhibit, for a given weight, much lower activity, and those in C7 and C8 a lower activity, than the catalyst in example 9 according to the invention. The reaction product was at least equal to the comparison products according to the acid value, hydroxyl value and purity (GPC analysis). |
|
tris(dimethylamino)borane; 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenol; at 80℃; for 48h;Product distribution / selectivity; |
13.27 g of glycidyl methacrylate, 0.02 g of 2,6-ditert.-butyl-4-methylphenol, 6.78 g of acrylic acid and 0.10 g of one of the catalysts set forth in Table 1 were reacted each time at 80 C. in a glass vessel with a small opening and with magnetic stirring. The acid value was determined after 24 and 48 hours. If it was greater than 4 mg KOH/g after 48 hours, the batch was discarded without further analysis. The catalysts in comparison examples C2 to C6 exhibit, for a given weight, much lower activity, and those in C7 and C8 a lower activity, than the catalyst in example 9 according to the invention. The reaction product was at least equal to the comparison products according to the acid value, hydroxyl value and purity (GPC analysis). |
|
With 10H-phenothiazine; triphenylphosphine; at 80 - 110℃; |
Example 2Synthesis of 3-acryloyloxy-2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate (GAMA); The apparatus from Example 1 is used. All of the chemicals used are available commercially, from Sigma Aldrich, for example.Reservoir 1 is charged with a GMA solution whose composition is as follows:Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA): 98.2% by weightTriphenylphosphine (TPP): 1.5% by weightPhenothiazine: 0.004% by weightDi-tert-butylmethylphenol (inhibitor KB) 0.22% by weightReservoir 2 is charged with acrylic acid.The reaction apparatus is heated to 80 C. empty. Reactant is metered in from reservoir 1 with a mass flow rate of 3.07 kg/h; from reservoir 2, reactant is metered in with a mass flow rate of 1.56 kg/h.The reactors are each thermally conditioned with a mass flow rate of 500 kg of thermostat oil (silicone oil) per hour (WK1, WK2).After the start of the metered feeds, the plant is slowly flooded. When the reactors of the first heating circuit (WK1) have been filled, the temperature in this circuit is slowly raised, in a number of steps, to a jacket temperature of 110 C. The same procedure at the same rate is carried out with the reactors of the second thermal conditioning circuit (WK2) when they are filled, the jacket temperature set here being 110 C. After a further 3 residence times, the product (GAMA) is obtained.Result: residual monomer content: 0.5% by weight acrylic acid, 0.48% by weight GMA |
|
With tetramethlyammonium chloride; at 90℃; for 4h; |
(1) Weigh 64 g of glycidyl methacrylate, Adding tetramethylammonium chloride 3.0g, Hydroxyanisole 0.1g, In a three-necked flask, Stirring to 90 C, Using a constant pressure dropping funnel, 37.8 g of acrylic acid was added dropwise to the reaction system. After the addition is completed, The acid value was tested after 4 hours of reaction. When the acid value is less than 10 mg KOH / g, the reaction is stopped. |
|
With tetramethlyammonium chloride; at 90℃; for 4h; |
A method for preparing a methacrylate monomer for a dental restorative material, comprising the following steps: (1) Weigh 64 g of glycidyl methacrylate, and add 3.0 g of tetramethylammonium chloride and 0.1 g of hydroxyanisole in a three-necked flask.The temperature was raised to 90 C, and 37.8 g of acrylic acid was added dropwise to the reaction system by a constant pressure dropping funnel. After the completion of the dropwise addition, the acid value was measured after the reaction was continued for 4 hours, and when the acid value was less than 10 mg KOH/g, the reaction was stopped |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science













 HazMat Fee +
HazMat Fee +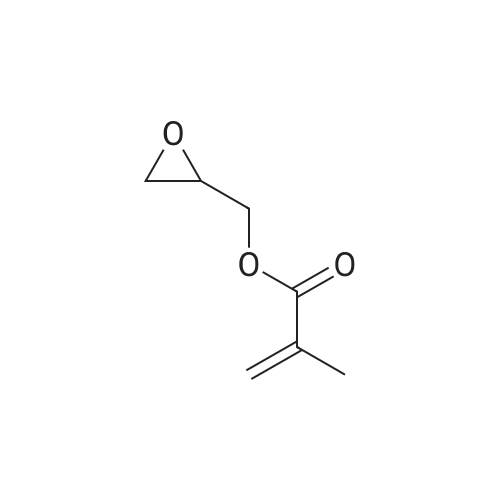

 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping