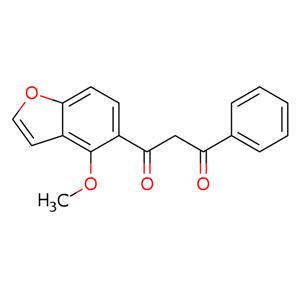
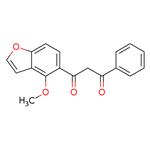
Pongamol is a chemical compound that contains a hydroxyl group and has been found to be toxic to cells in tissue culture. It has been shown to inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which is responsible for the destruction of acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter. Pongamol also inhibits protein synthesis by inhibiting the activity of glutamate pyruvate transaminase (GPT), which catalyzes the conversion of glutamate and pyruvate. This agent is also believed to have antioxidant properties due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules or atoms. Pongamol is stable in a variety of solvents, but can react with strong bases such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide.



 Canada
Canada