195529-54-5
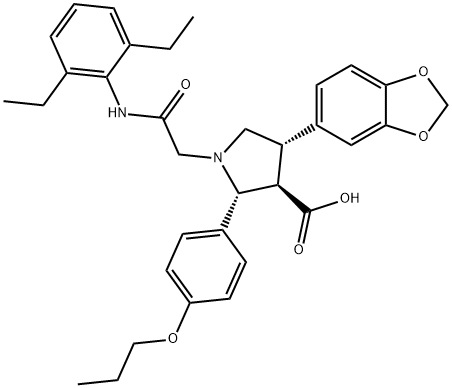 195529-54-5 結構式
195529-54-5 結構式
基本信息
A192621,CID 5310991
A192621 >=98 (HPLC)
(2R,3R,4S)-4-(1,3-BENZODIOXOL-5-YL)-1-[2-[(2,6-DIETHYLPHENYL)AMINO]-2-OXOETHYL]-2-(4-PROPOXYPHENYL)PYRROLIDINE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID
3-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid, 4-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-[2-[(2,6-diethylphenyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl]-2-(4-propoxyphenyl)-, (2R,3R,4S)-
物理化學性質
常見問題列表
|
ET B 4.5 nM (IC 50 ) |
ET B 8.8 nM (Ki) |
ET A 4280 nM (IC 50 ) |
ET A 5600 nM (Ki) |
A-192621 (1-100 μM; 48 hours; PASMCs) treatment markedly reduces the cell viability of PASMCs in a dose-dependent manner.
A-192621 (1-100 μM; 48 hours; PASMCs) treatment significantly increases the caspase-3/7 activity and cleaved caspase-3 expression in PASMCs. A-192621 induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner and increases the cells' susceptibility to apoptosis by Doxorubicin treatment.
Cell Viability Assay
| Cell Line: | Pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) with Doxorubicin |
| Concentration: | 1 μM, 10 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM |
| Incubation Time: | 72 hours |
| Result: | The viability of PASMCs was significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner. |
Western Blot Analysis
| Cell Line: | Pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) with Doxorubicin |
| Concentration: | 1 μM, 10 μM, 100 μM |
| Incubation Time: | 72 hours |
| Result: | The caspase-3/7 activity in PASMCs was significantly increased in a dose-dependent manner. |
A-192621 (30-100 mg/kg; oral administration; daily; for 3 days; male Sprague-Dawley rats) treatment inhibits both dilatory and pressor responses induced by S6c mediated by ET B with an ED 50 value of 30 mg/kg, and failed to inhibit the ET-1-induced pressor response mediated by ET A . A-192621 alone causes elevation of arterial blood pressure and an elevation in the plasma ET-1 level in the conscious normotensive rat.
| Animal Model: | Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250-350 g) |
| Dosage: | 30 mg/kg 100 mg/kg |
| Administration: | Oral administration; daily; for 3 days |
| Result: | Inhibited both dilatory and pressor responses induced by S6c mediated by ET B with an ED 50 value of 30 mg/kg. |